This type of microscope is used to observe the surface details of specimens in three dimensions.
scanning electron microscope (SEM)
Organisms that can produce their own food using sunlight are called what?
autotrophs or producers
What property of water allows ice to float?
expansion upon freezing
What is the term for the maximum number of individuals that an ecosystem can support?
Carrying Capacity
Organisms that are introduced to a new environment and outcompete native species are called what?
Invasive Species
A student wants to view multiple living cells at 400x magnification (Medium Strength). Which type of microscope should they use?
compound light microscope
What percentage of energy is typically transferred from one trophic level to the next in a food pyramid?
10%
What property of water allows it to dissolve many substances?
universal solvent
List two abiotic factors that can affect population size.
temperature, water/food availability, sunlight, pH, salinity, space/territory availability, etc.
How does the burning of fossil fuels contribute to global warming?
It releases carbon dioxide (CO2) into the atmosphere, which traps heat.
This type of microscope uses electrons to pass through a very thin section of a specimen, allowing the viewer to see internal cell structures with very high resolution.
transmission electron microscope (TEM)
Organisms that obtain energy by consuming other organisms are called what?
heterotrophs or consumers
What property of water helps organisms maintain a stable internal temperature?
moderation of temperature or high specific heat
What happens to a population's size if the number of births and immigration is greater than the number of deaths and emigration?
The population size increases
What is the difference between primary and secondary succession?
Primary succession occurs in areas with no soil (e.g., after a volcanic eruption), while secondary succession occurs in areas with existing soil (e.g., after a forest fire).
This graph shows how many animals were present in a zoo over time.
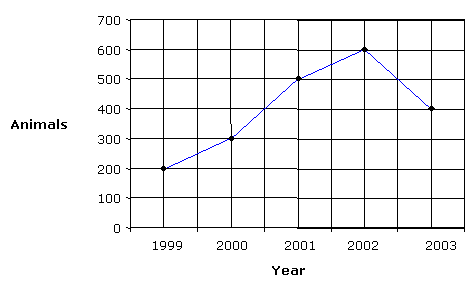
In what year did the zoo have the most animals? And how many animals were in the zoo that year?
The year 2002 with 600 animals.
Below is a food web.
Which organism contains the most available energy?
Grass (producer)
Explain how the cohesive properties of water allow certain insects to walk on its surface.
Water molecules are attracted to each other (cohesion), creating surface tension. This surface tension is strong enough to support the weight of light insects.
How can the introduction of a new predator affect the population dynamics of a prey species?
The predator can cause a decrease in the prey population through increased predation. The prey population may then fluctuate as it adapts
Explain how a decrease in biodiversity can make an ecosystem more vulnerable to invasive species.
Low biodiversity means fewer native species and less competition, allowing invasive species to establish themselves more easily.
Below is a graph depicting Enzymatic Activity in various temperatures.
In what temperature does this enzyme work optimally?
Approximately 36-37 degrees Celsius.
Explain why there are typically fewer top-level consumers than producers in an ecosystem, relating your answer to energy transfer.
Sample Answer: Because only 10% of energy is transferred between trophic levels, there is less energy available for top-level consumers, limiting their population size.
Describe the journey of water from the ocean to a plant and back again, using these terms: evaporation, condensation, precipitation, and transpiration.
- Water from the ocean turns into vapor and rises into the air. This is called evaporation.
- The vapor cools and forms clouds, which is condensation.
- Water falls from the clouds as rain, which is precipitation.
- Plants take in some of this water, and then release water vapor into the air, which is transpiration.
- Eventually that water vapor will condense, and precipitate back into the ocean.
Below is a graph showing bird populations over multiple generations.
 What is the approximate number of individuals when the population reaches carrying capacity?
What is the approximate number of individuals when the population reaches carrying capacity?
Approximately 75 individuals.
The use of resources in a way that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs is called what?
Sustainability
