This organelle controls what enters or leaves the cell
cell membrane
These structures may be found floating freely in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum; site of protein synthesis.
Ribosomes
Does not require ATP
What is passive transport
Define Diffusion
Movement of PARTICLES from high concentration to low concentration
List four basic structures that are common to all types of cells.
All cells are surrounded by a barrier (cell membrane).
All cells have an interior substance (cytoplasm).
All cells have DNA
All cells have ribosomes
Give ONE reason why some of the particles were able to diffuse across the dialysis tubing membrane.

Particles moved from high to low concentration.
Particles were small enough to diffuse.
the portion of the cell within the membrane that includes a "jelly" like fluid and all organelles except for the nucleus.
cytoplasm
This organelle converts glucose and other organic molecules into a form of usable cell energy called ATP.
Mitochondria
The sodium-potassium pump is an example of this; keeps sodium from building up in the cell by moving sodium against the concentration gradient.
Active transport
Diffusion of water is called?
Osmosis
does not have a true nucleus or any membrane-bound organelles.
What is a prokaryotic cell?
High solute and low water concentration. Causes cells to lose water and shrink.
Hypertonic environment
This organelle sorts and packages proteins and ships them to their final destinations.
Golgi apparatus
These name for condensed DNA and serve as the storehouse for genetic information.
Chromosomes
Filtration, simple diffusion, dialysis, osmosis are examples of what?
What is passive transport
When the cell needs to use energy to move things across the membrane
Active transport
has a true nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
what is a eukaryotic cell?
Food coloring diffusing in water is which type of transport?
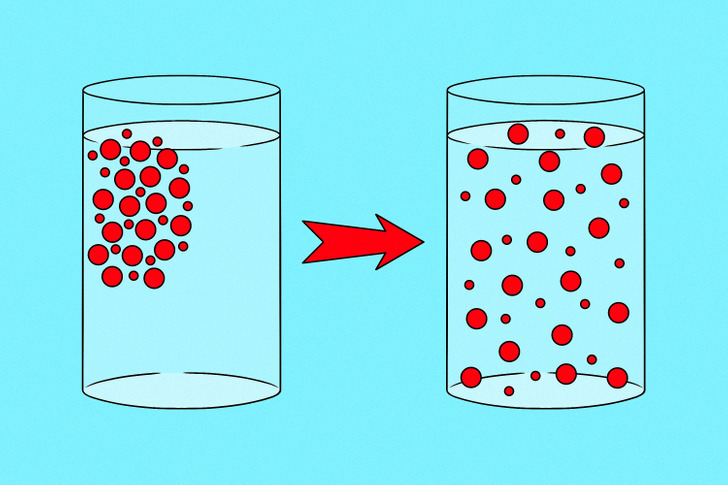
Passive Transport
controls all the activities of the cell, including cell reproduction and protein synthesis
Nucleus
Modifies and transports proteins after they are built.
Rough ER
If you have a high amounts of water in solution A, and low amounts water in solution B. What would you expect to happen?
What is solution A moving with the concentration gradient towards solution B.
Movement across the membrane that does not need energy, but does need help from transport proteins
Facilitated diffusion
What organisms are prokaryotes?
What organisms are eukaryotes?
Bacteria are prokaryotes. Animals, Plants, Fungi, and Protists are eukaryotes.
Cellular respiration involves animals and plants taking in glucose (chemical energy) and oxygen. The products are?
carbon dioxide, water, and ATP energy
What is the difference between the rough ER and the smooth ER?
Rough ER has ribosomes attached to it. Smooth ER has no ribosomes.
In what place are the ribosomal subunits manufactured?
Nucleolus
Vesicles transport wastes out of the cell through this process; type of active transport
Exocytosis
Which way will the pink molecules diffuse?

To the right
This material is found in the cell walls of fungus and the exoskeletons of arthropods.
Chitin
The ingestion of liquid into a cell by the budding of small vesicles from the cell membrane
These small spherical sacs that are classified by their contents may contain enzymes or other types of proteins for transport.
Vesicles
This organelle makes the lipids that will be used in membranes.
Smooth ER
Molecules that are too large to move in the cell are transported through this process.
endocytosis
If you have high amounts of glucose in solution A and low amounts of glucose in solution B, what would happen to the water.
What is the water moving towards solution A.
Cell respiration involves animals and plants taking in glucose (chemical energy) and oxygen. The products are?
carbon dioxide, water, and ATP energy
High solute and low water concentration. Causes cells to lose water and shrink.
Hypertonic environment
Name this organelle:
Chloroplast
Name this organelle:
Rough and Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
molecules moving from low concentration to high concentration across the cell membrane.
Active Transport
When will a substance be likely to enter a cell through diffusion?
When the concentration of the substance is greater outside the cell than in.
This domain includes prokaryotes that have peptidoglycan in their cell walls.
Bacteria
Food is broken down into very small molecules through the process of _____ and converted to energy (ATP) through the process of _____.
Digestion
Respiration