This macromolecule is the primary source of short-term energy and has a 1:2:1 ratio of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen.
Carbohydrates
This organelle is responsible for producing ATP through cellular respiration
Mitochondria
What is the basic unit of life according to the cell theory?
Cells
What type of cell transport requires energy (In the form of ATP) to move substances against a concentration gradient?
Active Transport
Which part of the flower attracts pollinators?
Petals
What are the building blocks (monomers) of proteins?
Amino Acids
What is the primary function of ribosomes?
To make Proteins
How do enzymes affect the activation energy of a chemical reaction?
They lower the activation energy.
What is the primary component of the cell membrane that creates a barrier between the inside and outside of the cell?
Phospholipid Bilayer
What type of plant tissue transports water upward from the roots?
Xylem
This macromolecule forms the structural basis of cell membranes and provides long-term energy storage.
Lipids
Name 3 organelles that are found only in plant cells.
cell wall, chloroplasts, and large central vacuole
State two parts of the cell theory.
All living things are composed of cells; cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things; all cells come from pre-existing cells." (Any two)
What type of transport does not require energy and moves substances from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration?
Passive Transport
After photosynthesis, glucose is stored in what kind of plant tissue type?
Ground Tissue
Describe the primary function of nucleic acids and name the monomer that makes them up.
To store and transmit genetic information. The monomer is a nucleotide.
Explain the relationship between chloroplasts and mitochondria in terms of energy flow
Chloroplasts convert light energy into chemical energy (glucose) through photosynthesis, and mitochondria convert that chemical energy into ATP through cellular respiration.
The optimum pH of the Red enzyme is shown below. What is the optimum pH of Pepsin?
Approximately 2.5
This image shows an example of what kind of cell transport? How do you know?

Passive transport. Solutes are moving from high to low concentration across the cell membrane.
 List the name of these structures, their function, and what kind of tissue they're normally found on.
List the name of these structures, their function, and what kind of tissue they're normally found on.
Stomata (with guard cells)
Gas Exchange
Dermal Tissue (On the surface of the leaves)
Correctly Identify all of the following Macromolecules:
#5, #6, and #7
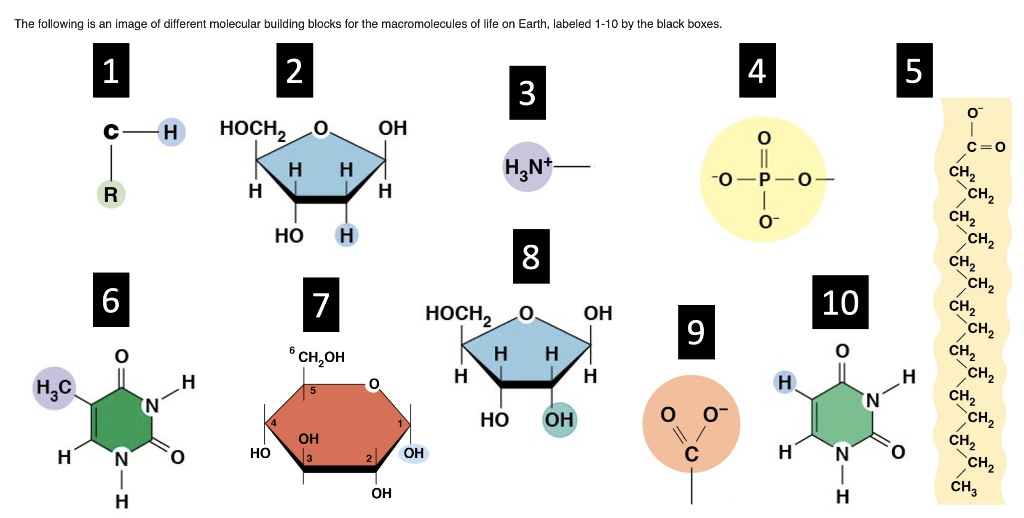
#5: Lipid
#6: Protein
#7: Carbohydrate
Describe the role of the cell membrane in regulating the movement of substances into and out of the cell (Hint: Term for allowing the movement of "some" things, but not others).
It is semi-permeable, allowing some substances to pass through while blocking others.
What component of the Cell Theory disproves the idea of Spontaneous Generation?
All Cells come from pre-existing cells.

The image above shows the process of osmosis. Is this an example of active or passive transport? Describe what is happening in the image in regards to the water and solute concentration.
Osmos is a passive transport mode. In osmosis, water moves through the semi-permeable membrane from a low solute concentration to high solute concentration to establish equilibrium (AKA high water concentration to low water concentration).
Describe the process of pollination and fertilization from beginning to end.
- Pollen is created in the Anther (F)
- Pollen is taken (pollinator, wind, rain, etc.) from the anther to the stigma (D)
- Pollen then travels down the style (C) and reaches the ovaries (B)
- The pollen then fertilizes the ovum (egg cell, A) and becomes a seed.