Define species richness and species evenness.
Species richness = number of species in an area; species evenness = relative abundance of individuals across species.
Distinguish between genotype and phenotype.
Genotype = genetic makeup (alleles); phenotype = observable traits.
Define natural selection.
Process where individuals with advantageous traits survive and reproduce, passing traits on.
Using the Simpson’s Diversity Index formula, calculate the diversity of a community where there are: 20 frogs, 10 snakes, 5 lizards, and 15 birds.
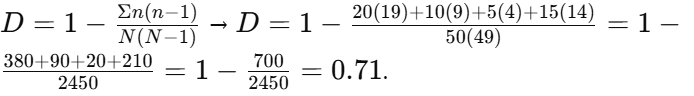
In peas, purple flowers (P) are dominant over white (p). A heterozygous plant is crossed with a homozygous recessive. Determine the expected genotypic and phenotypic ratios.
Cross = Pp × pp → genotypes: 50% Pp, 50% pp → phenotype: 1 purple : 1 white.
Explain how antibiotic resistance in bacteria is an example of evolution by natural selection
Mutations create resistant bacteria → antibiotics kill non-resistant → resistant survive/reproduce → frequency of resistant allele increases.
Compare the advantages and limitations of using quadrats versus transects when sampling vegetation
Quadrats: good for stationary species, easy to replicate, but limited area; transects: capture gradient data, broader coverage, but time-consuming.
Explain how crossing over contributes to genetic variation
Homologous chromosomes exchange genetic material in prophase I → new allele combinations → increases variation.
Compare the evidence provided by homologous structures and analogous structures
Homologous = same structure, different function → evidence of common ancestry; analogous = different structure, same function → evidence of convergent evolution.
A national park experiences an increase in an invasive plant species. Predict how this would affect species richness and evenness of native plant communities.
Native richness decreases, evenness declines as invasive dominates.
Justify why mitochondrial DNA is often used in tracing maternal lineages.
mtDNA is maternally inherited, not recombined, has high mutation rate, useful for lineage tracking.
ossil evidence shows that some species become extinct rapidly after climate shifts. Predict what characteristics might allow some species to survive while others perish.
Species with genetic variation, short generation times, broad ecological niches survive better.
Explain how keystone species maintain ecosystem stability, using an Australian example.
Example: dingoes in Australia → regulate kangaroo populations → prevent overgrazing → support plant diversity.