The picture below depicts a type of transport across cell membranes where water flows from low to high concentration of solutes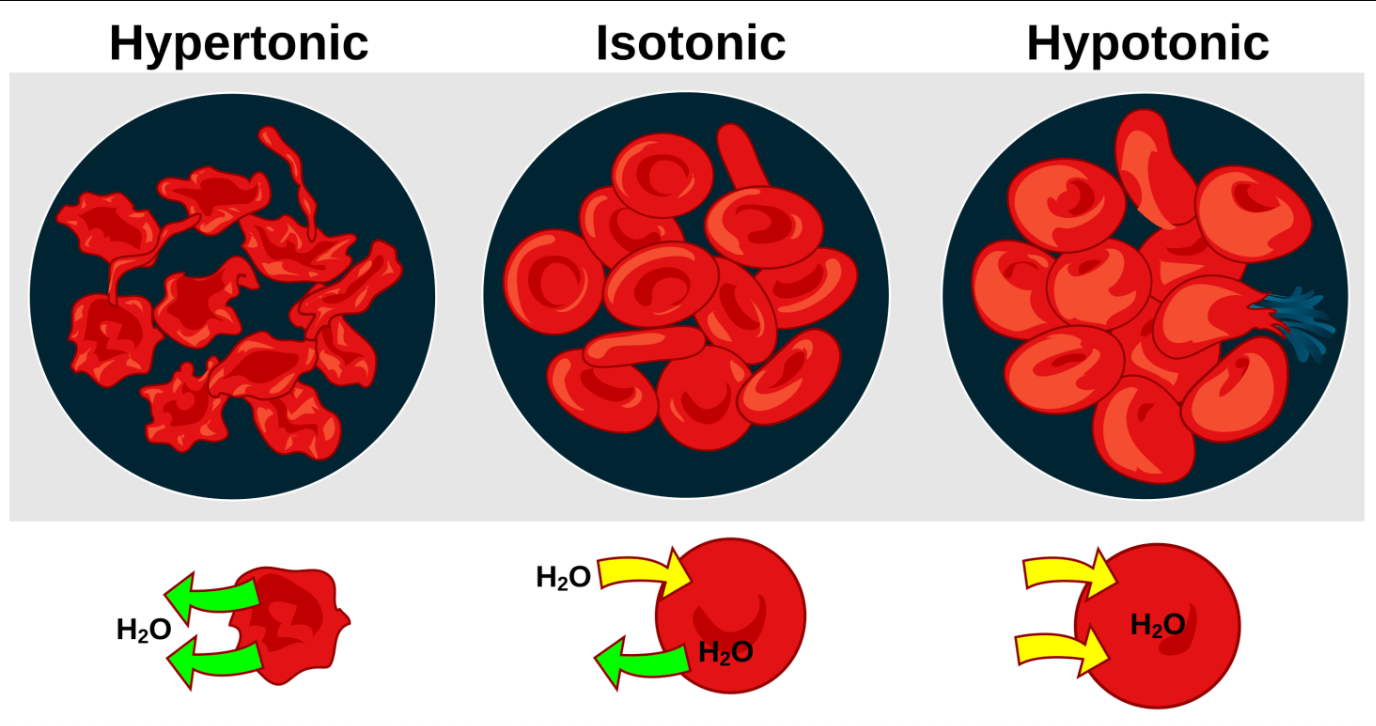
What is Osmosis
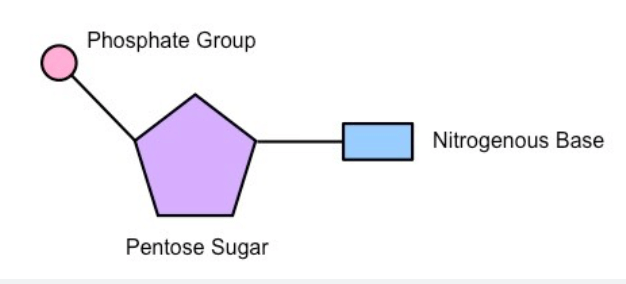
Stored in the nucleus, the template used to make proteins, exists as a double helix
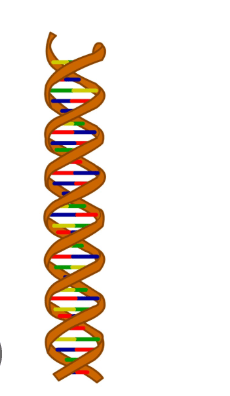
What is DNA
Living factors that contribute to environment
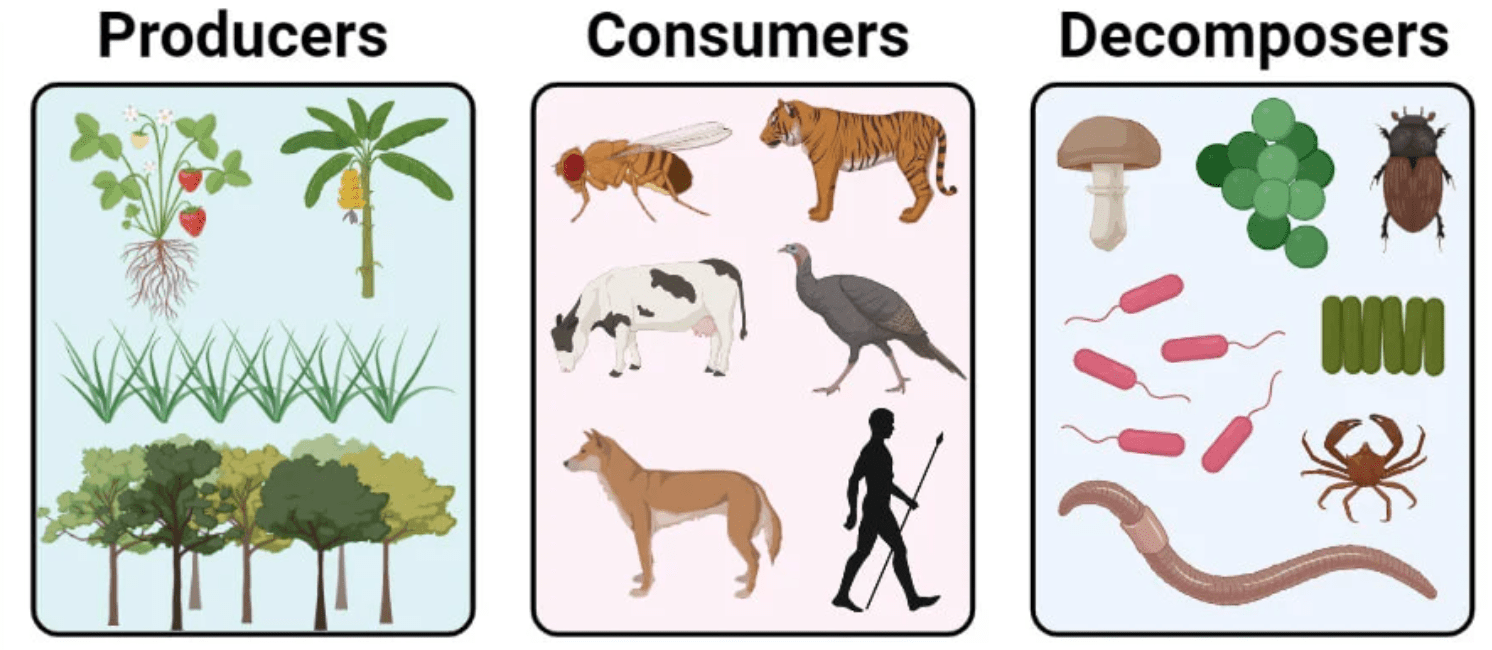
What is biotic factors
Species change over long periods of time due to competitive advantages of genetics.
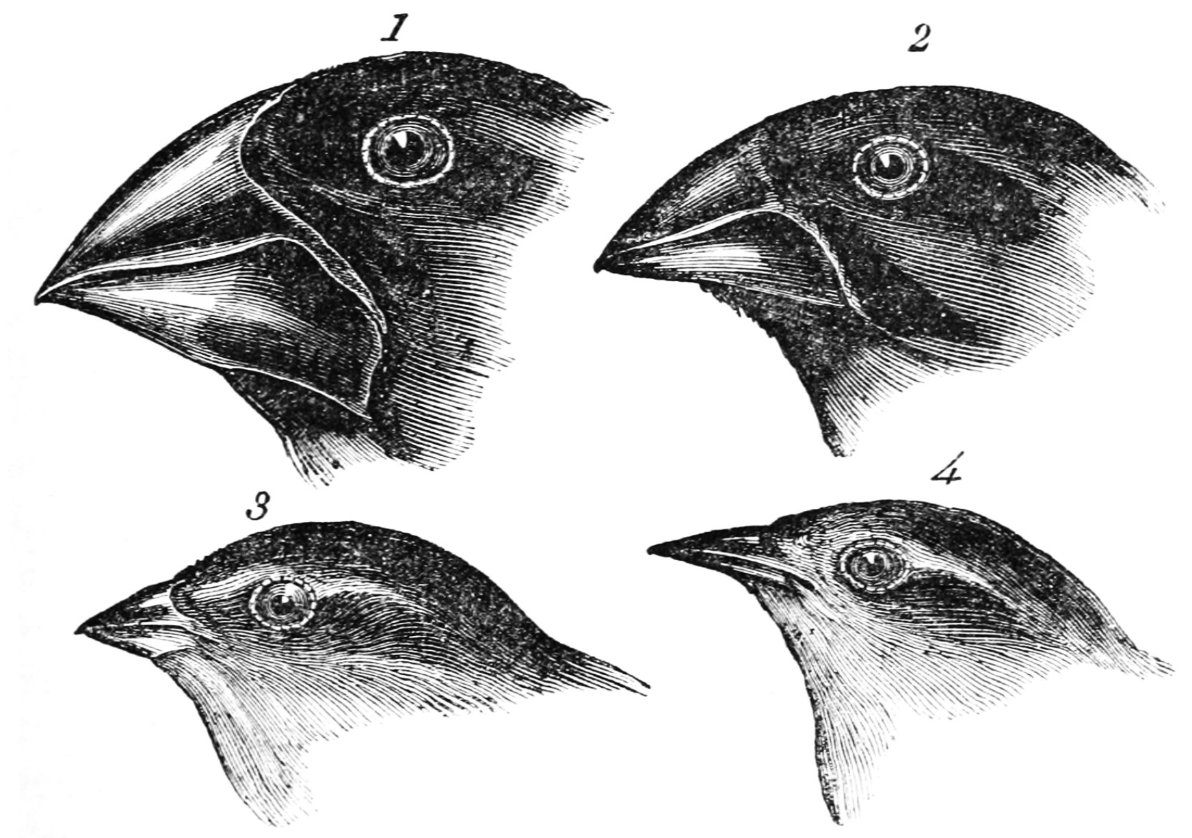
What is evolution
Species moved to a non-native area and threatens native species with the same niche.
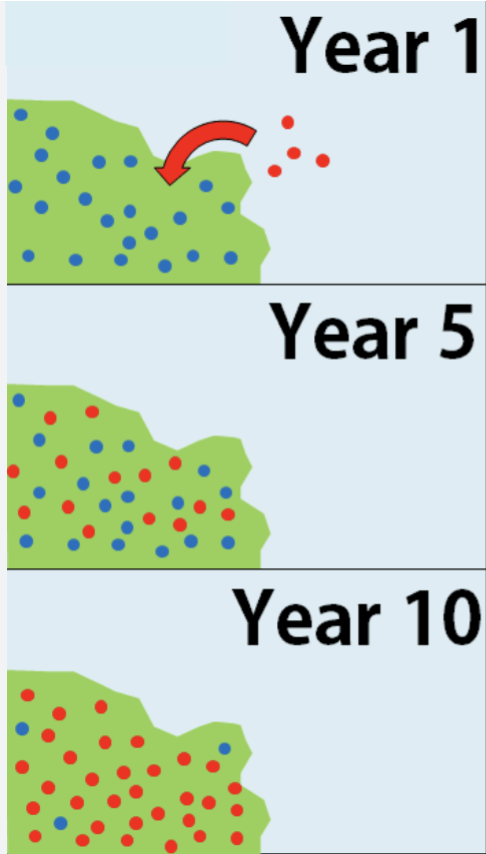
What is an Invasive species
Three types of transports require energy to move various molecules across the membrane. 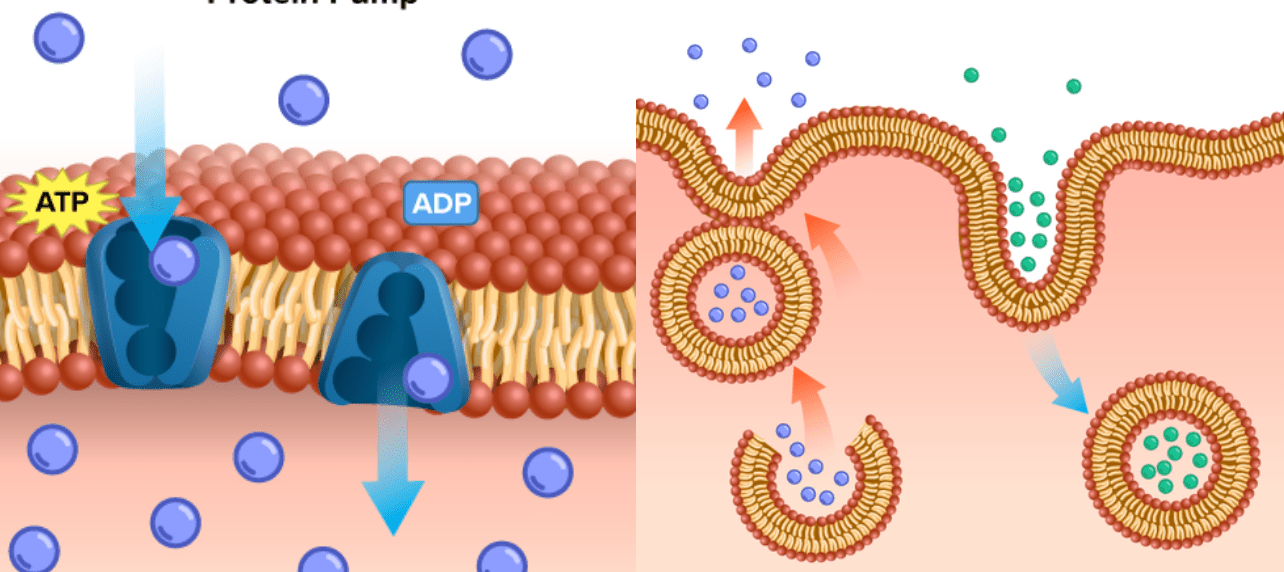
What is protein pump, exocytosis, and endocytosis
The image below depicts a proess that allows us to look at the genetic information from different individuals to determine if the committed crimes, produced offspring, or if their genetic information is closely related to another.
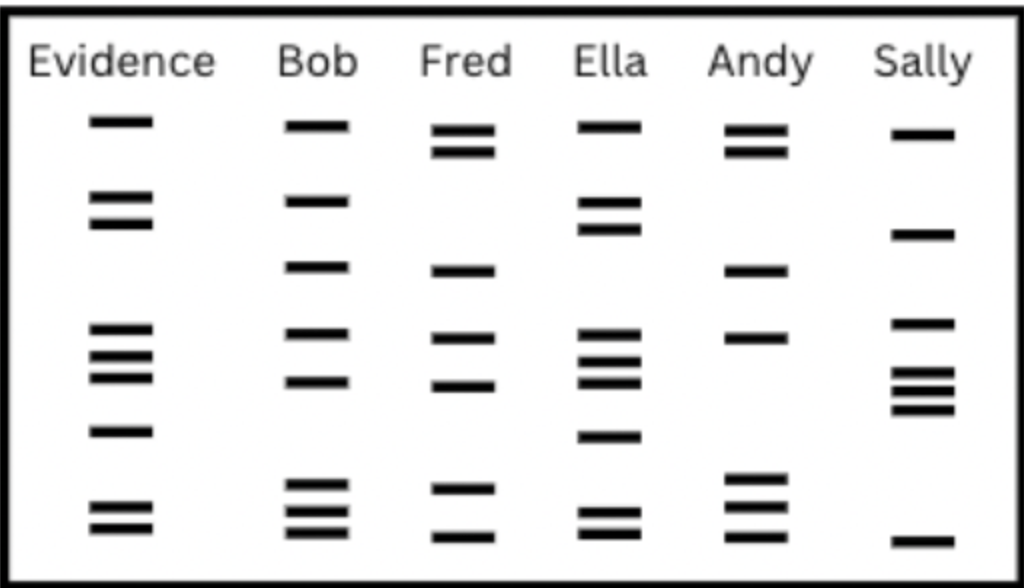
What is DNA Finger Printing (Gel electrophoresis)
Non living factors that contribute to an environment
What are abiotic factors
An organism's ability to pass its genetic material to its offspring
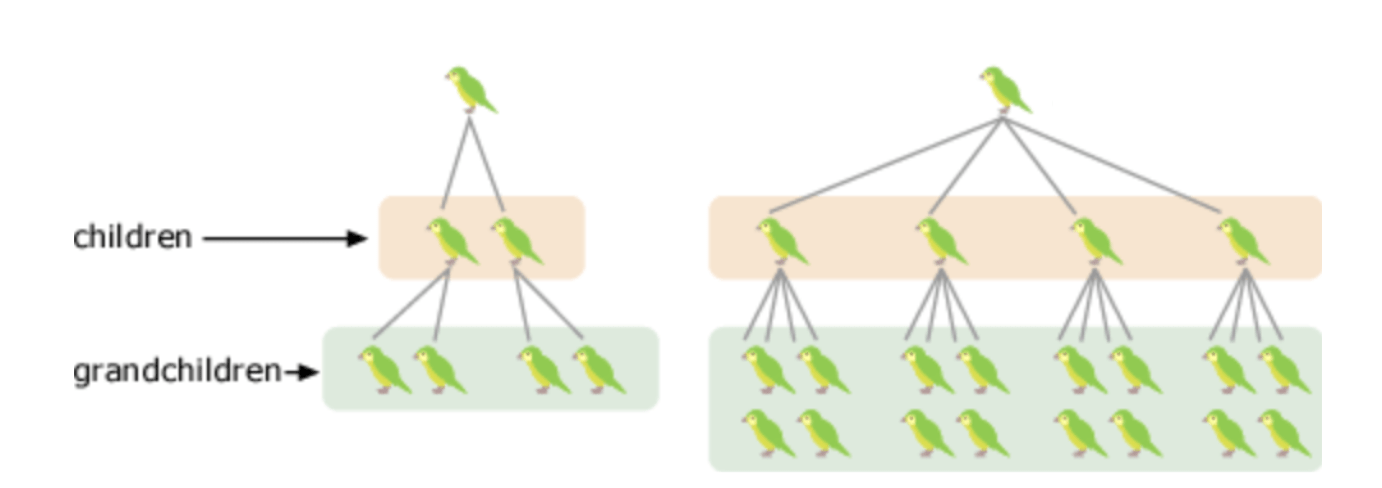
What is biological fitness
The diagram below illustrates the population size, the amount of pollution at each trophic level, and the consumers and produces in an ecosystem. What is it called?
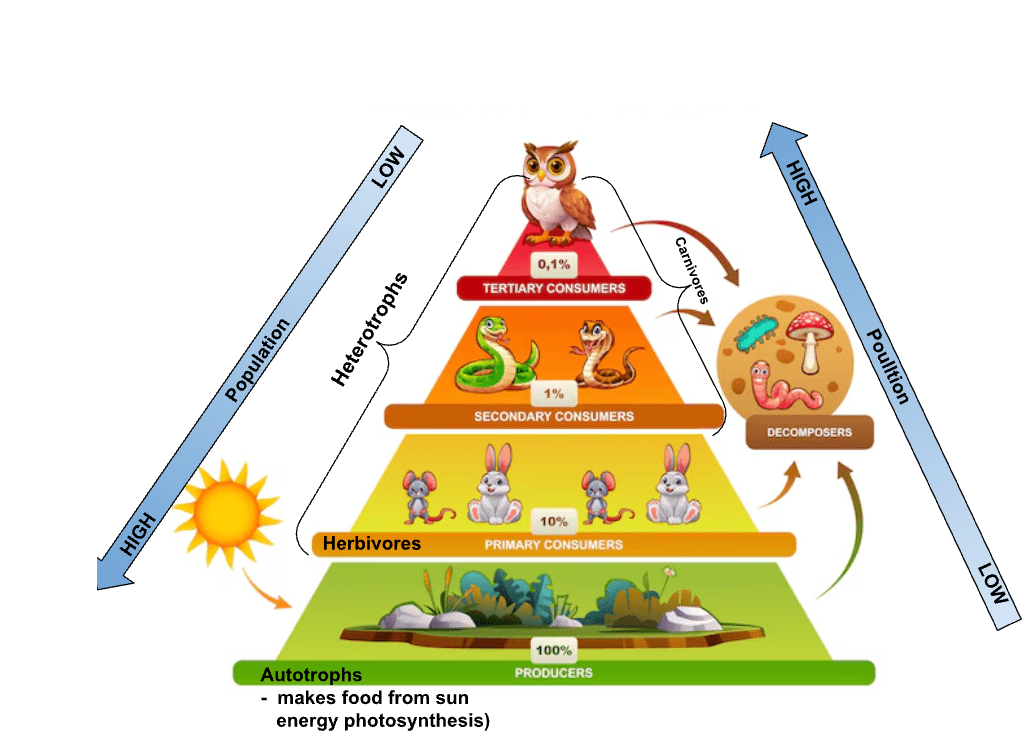
What is an energy pyramid
The two factors that affect how enzymes work in work in cells. If the enzyme is out of range in one or both of these it can cause the enzyme to denautre. 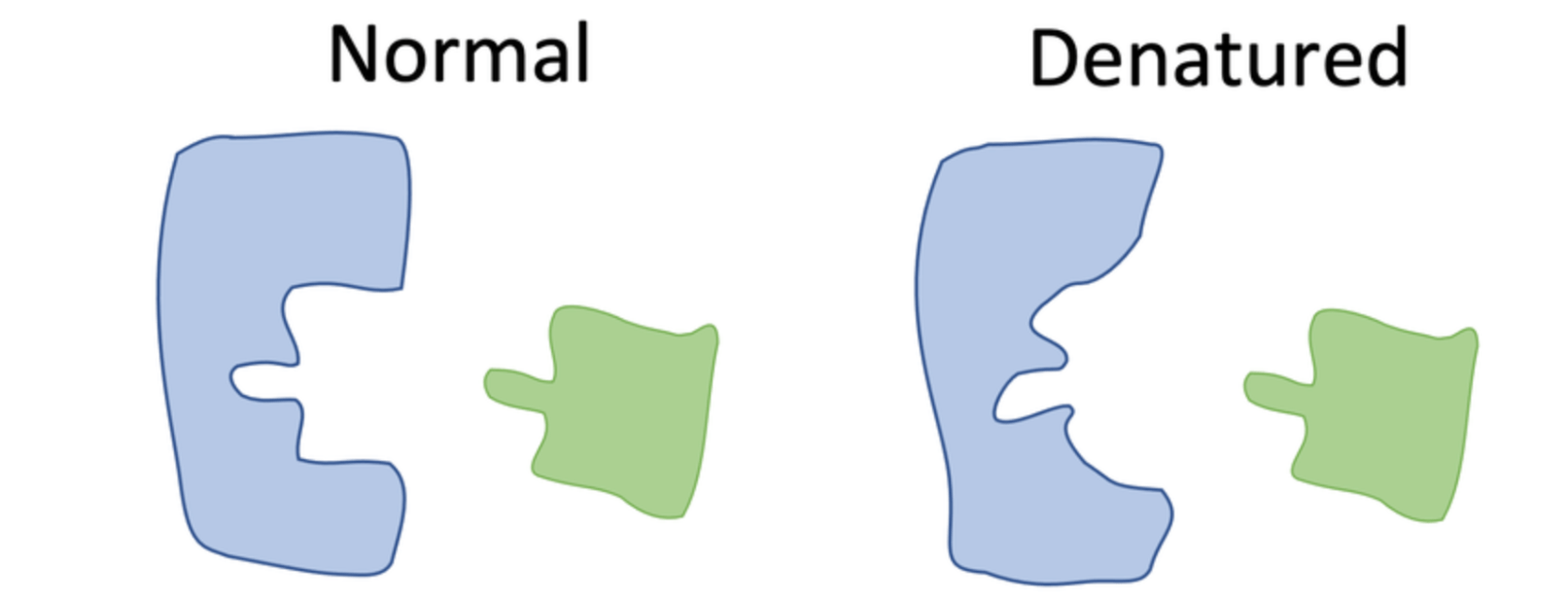
What is pH and Temperature
 The four nucleotide bases for RNA
The four nucleotide bases for RNA
Adinine (A), Guanine (G), Uracil (U), Cytosine (C)
The largest population supported by an environment long term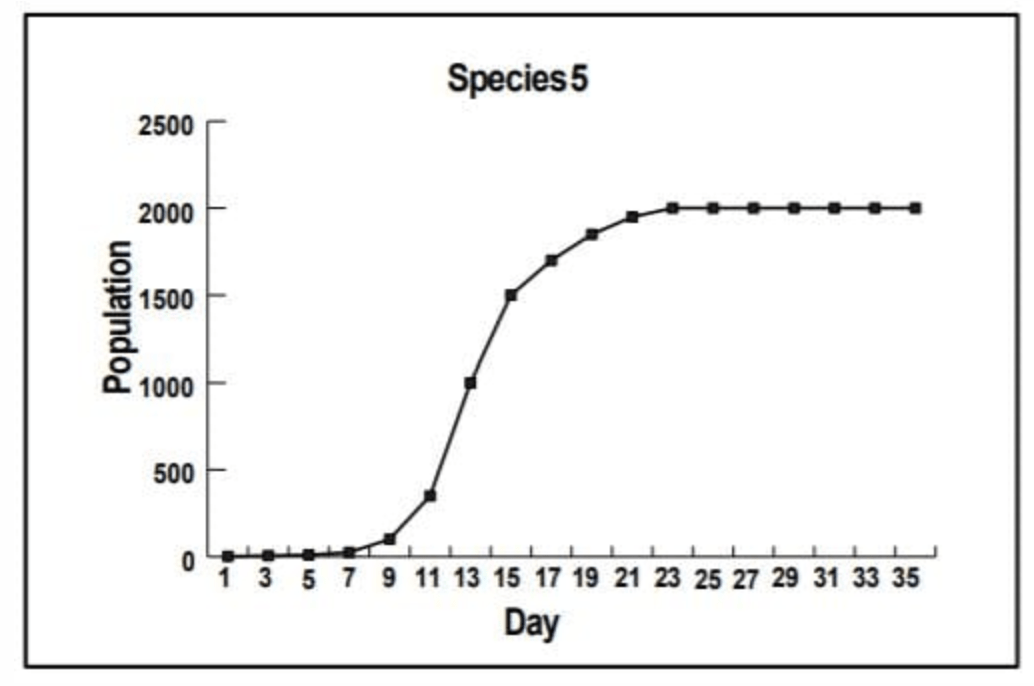
What is Caring Capacity
Bottle neck and isolation on types of this, where allele frequency and diversity changes randomly over time
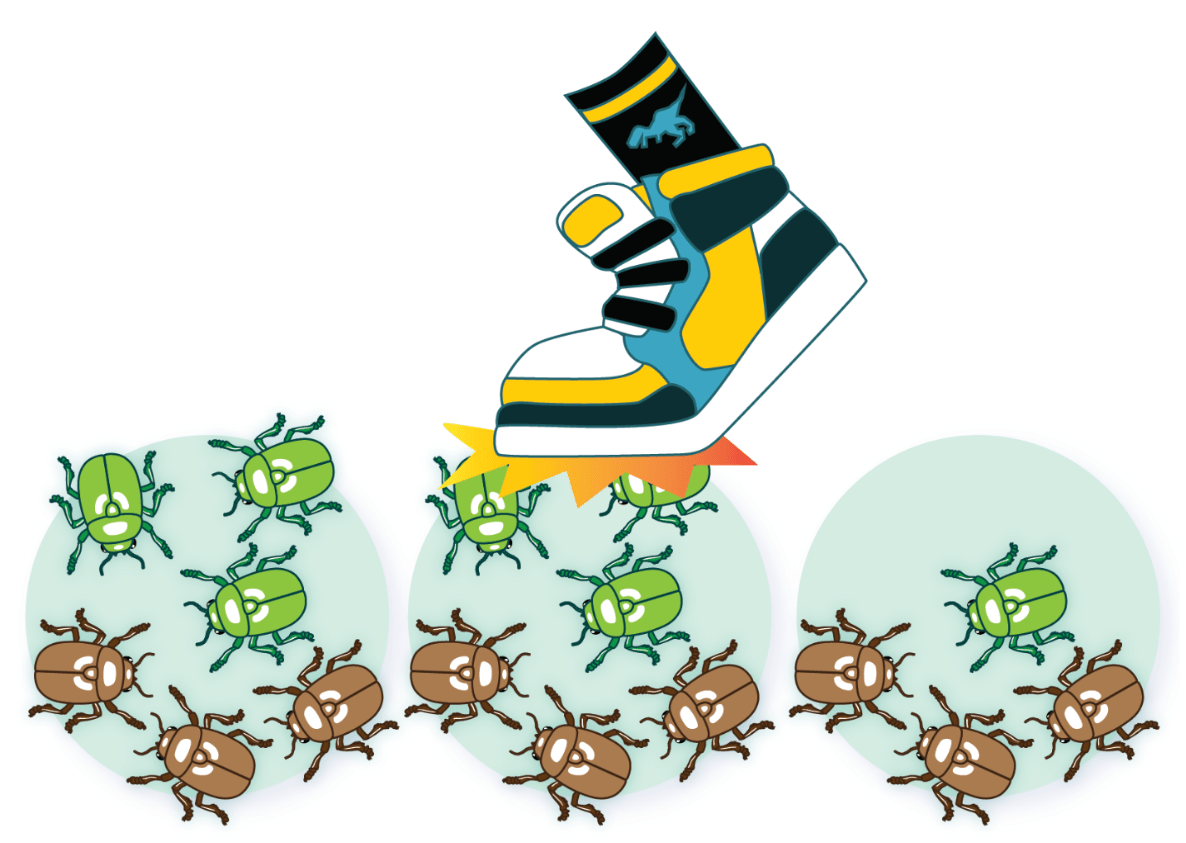

What is genetic drift
All things are connected, small changes to one organism = changes to all organisms
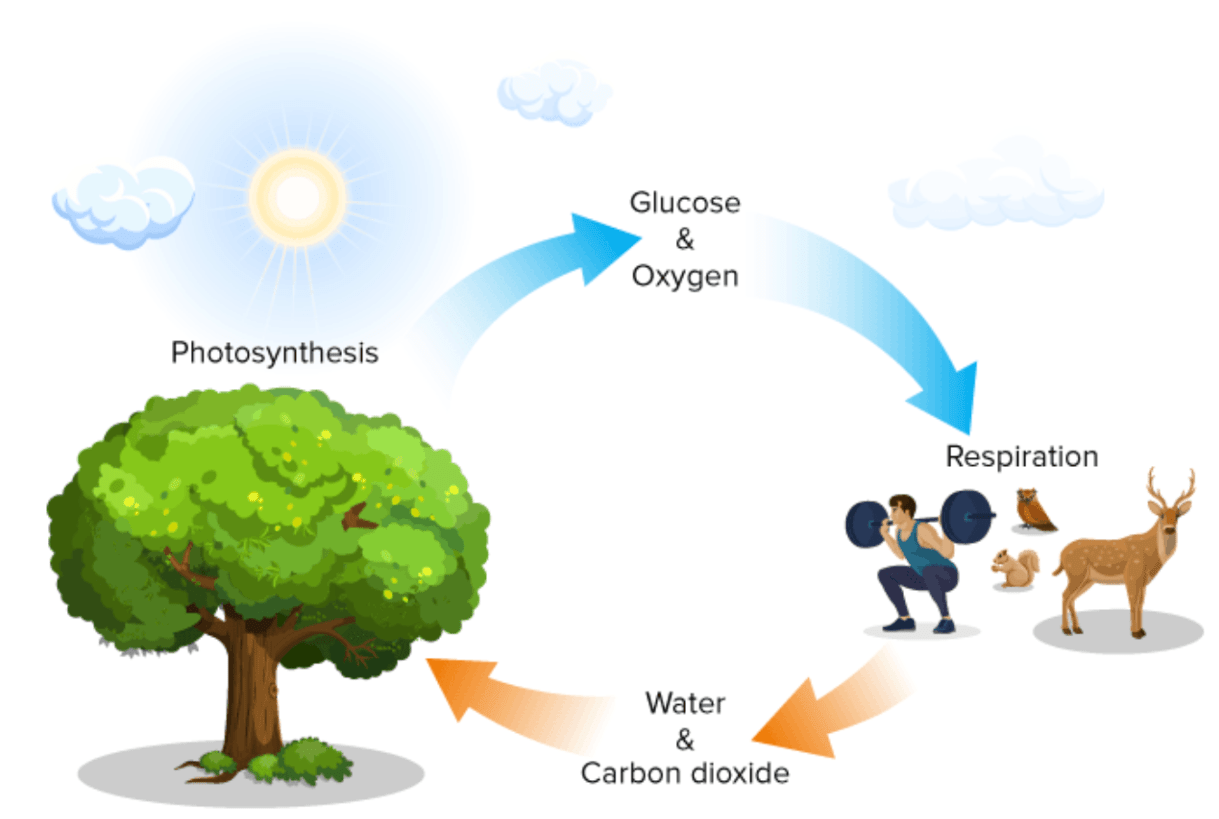
What is interdependence of life
Explain what the graph is illustrating
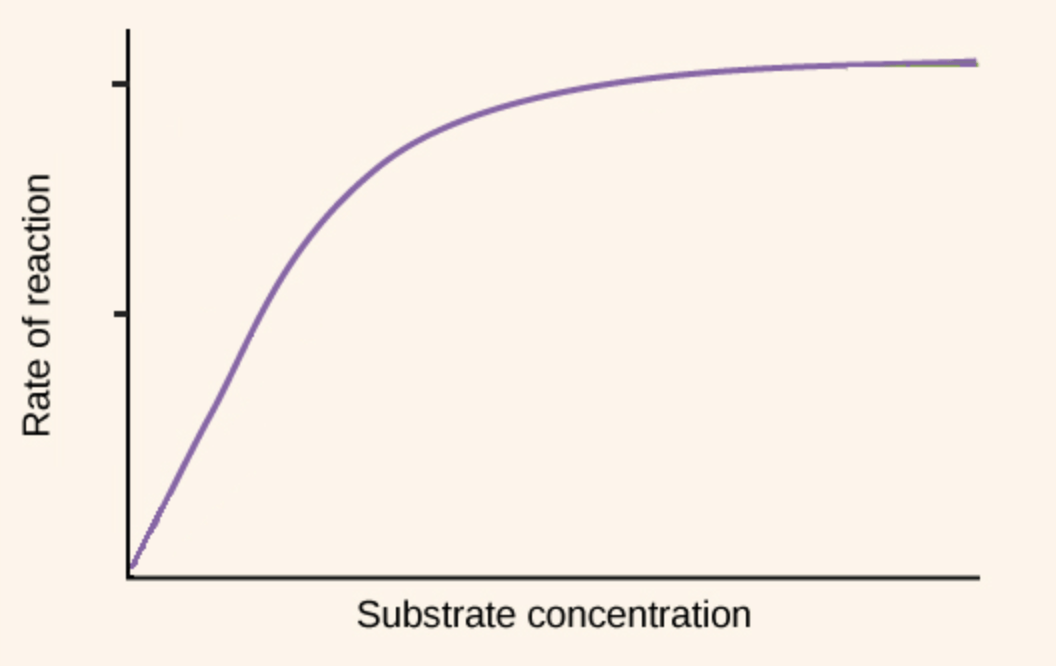
The graph is illustrating the reaction rate of enzymes as substrate concentration is increased. Eventually the reaction rate evens out due to all of the enzymes being used.
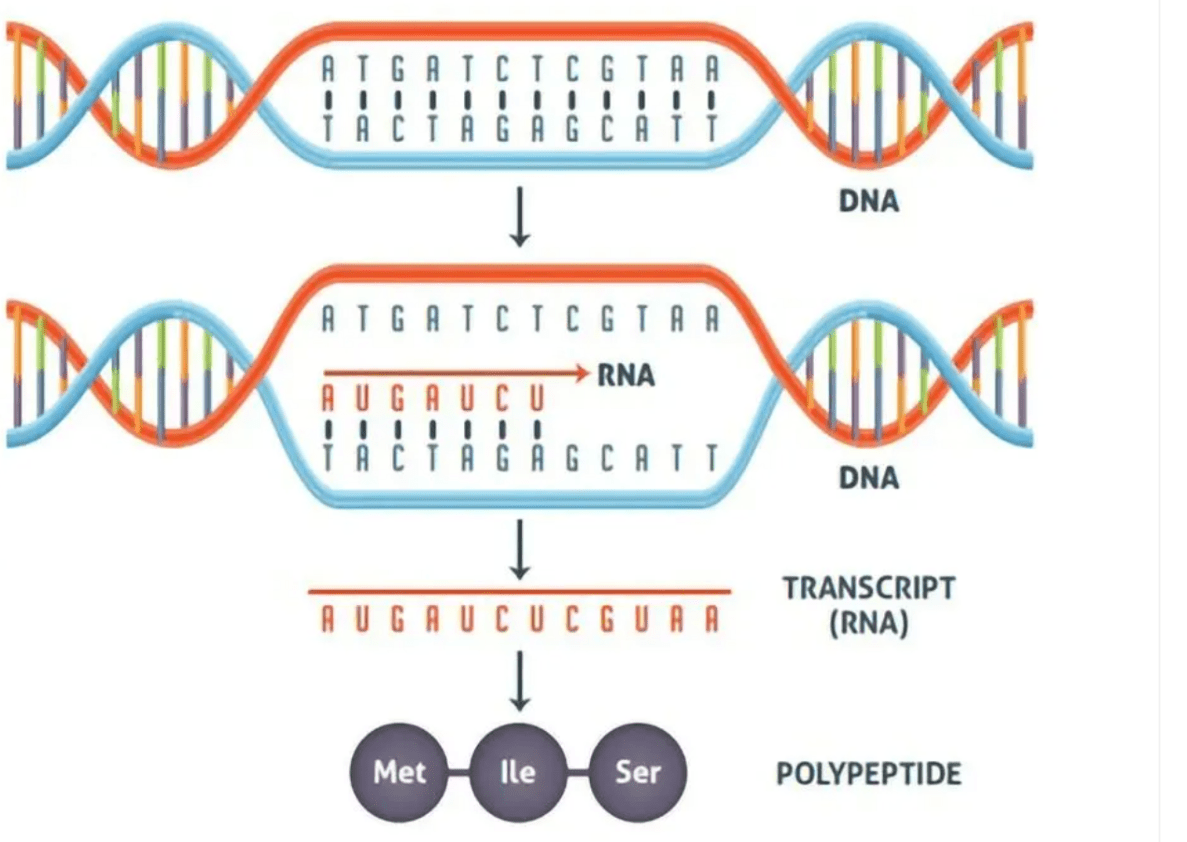 The two steps of protein synthesis where DNA is copied into mRNA that leaves the nucleus to meat a ribosome and tRNA to make proteins. Order Matters.
The two steps of protein synthesis where DNA is copied into mRNA that leaves the nucleus to meat a ribosome and tRNA to make proteins. Order Matters.
Transcription and Translation
During this phenomenon ecosystems change due to extreme factors, carrying capacity change for all, and eventually new equilibrium is reached.

What is disequilibrium
Allele frequencies should remain constant unless a change is caused by 1 or more of 5 factors
Nonrandom mating (sexual selection)
Small population size (genetic drift)
Gene flow from immigration or emigration example
Mutations (new alleles are added to the gene pool)
natural selection
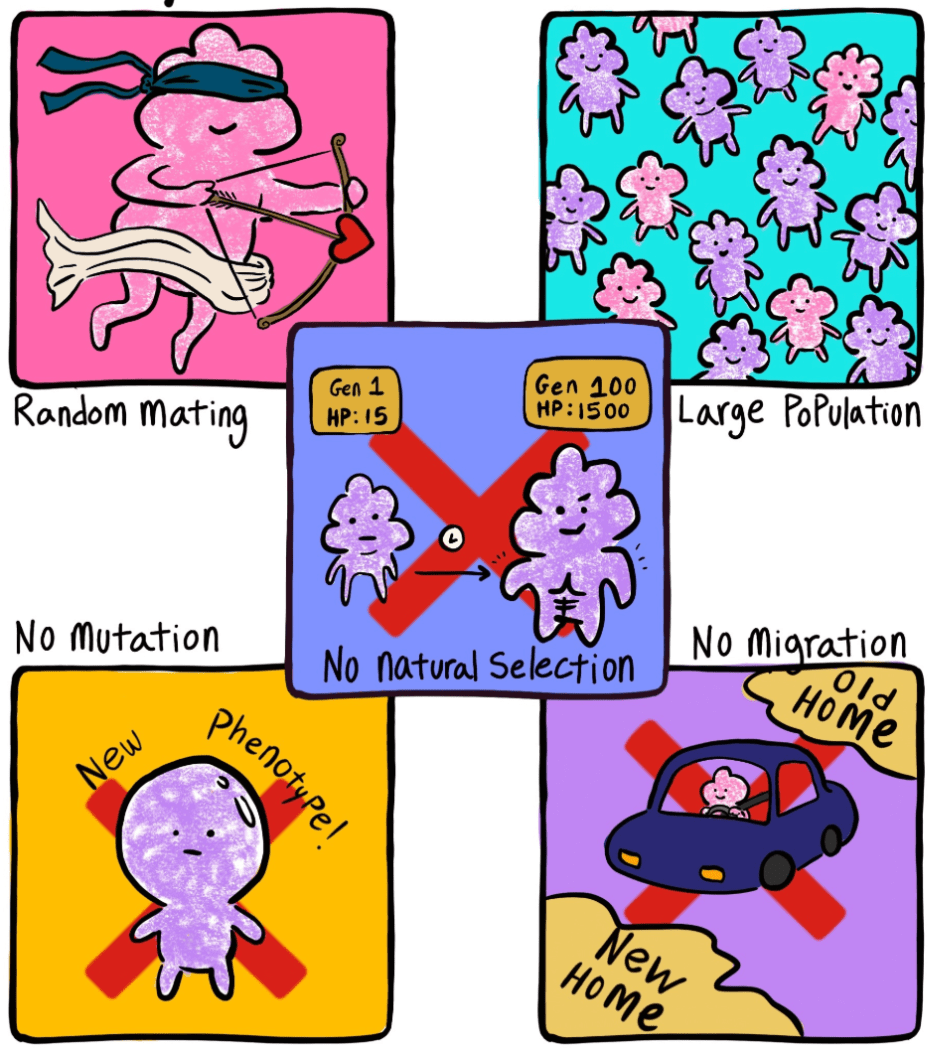
What is the Hardy-Weinberg Principle
A hydrophilic head, and two hydrophobic tails make up this macromolecule that creates cell membranes.
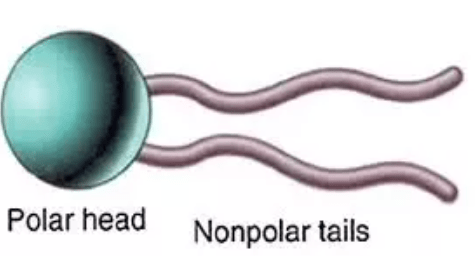
What is a phospholipid
Membrane bound organelles such as a nucleus, endoplasmic reticulum, and golgi body are not present in these primitive cells. Instead you will find free floating DNA, cell walls, ribosomes, a cell membrane, and appendages (cillia and flagella) to help movement.
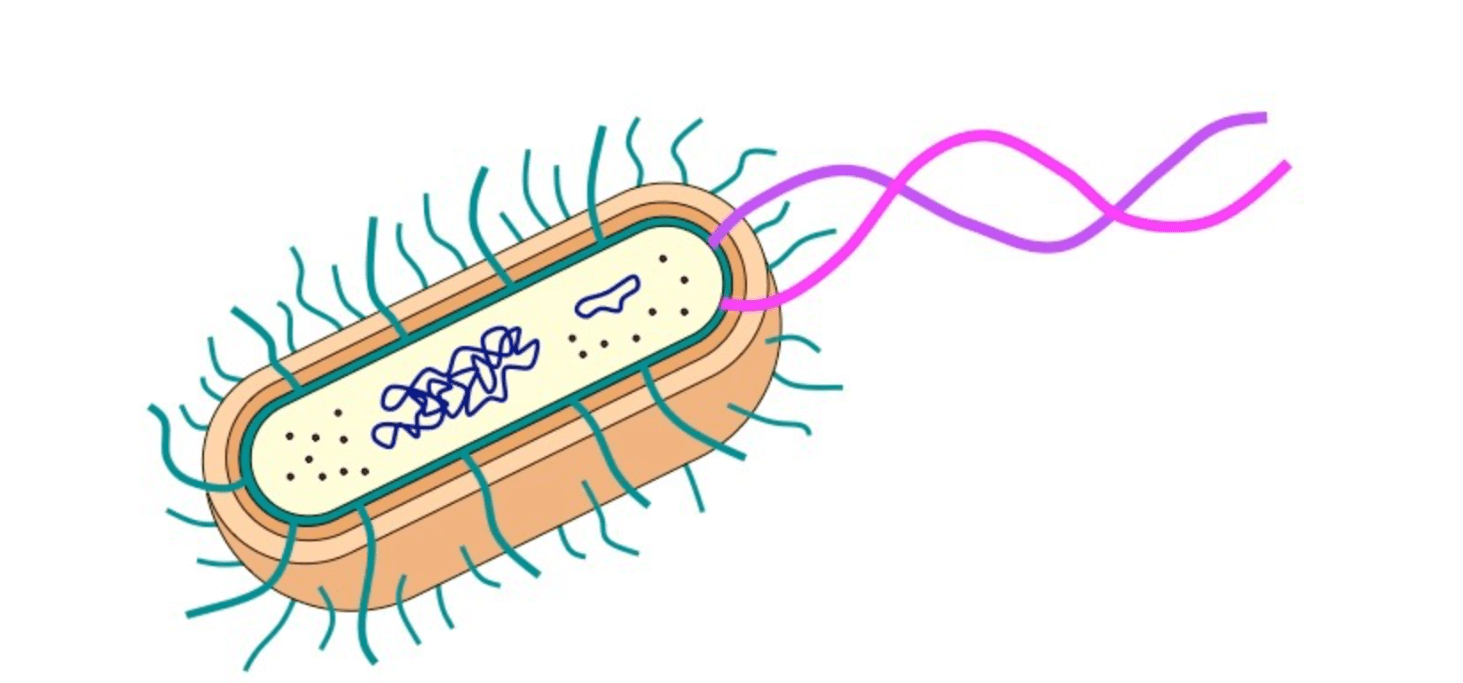
What is a prokaryote
 Three types of mutations. 1) Could result in a silent mutation, replacing one nucleotide with another. 2) Results in a frame shift shortening the protein sequence 3) Results in a frame shift elongating the protein sequence.
Three types of mutations. 1) Could result in a silent mutation, replacing one nucleotide with another. 2) Results in a frame shift shortening the protein sequence 3) Results in a frame shift elongating the protein sequence.
What is 1) substituion 2) deletion 3) insertion
The following describes what phenomenon:
Human activity creates greenhouse gases
Extra gas traps more heat
Increase in global temperature
Rising ocean levels
More dramatic weather
Melting glaciers and polar ice caps
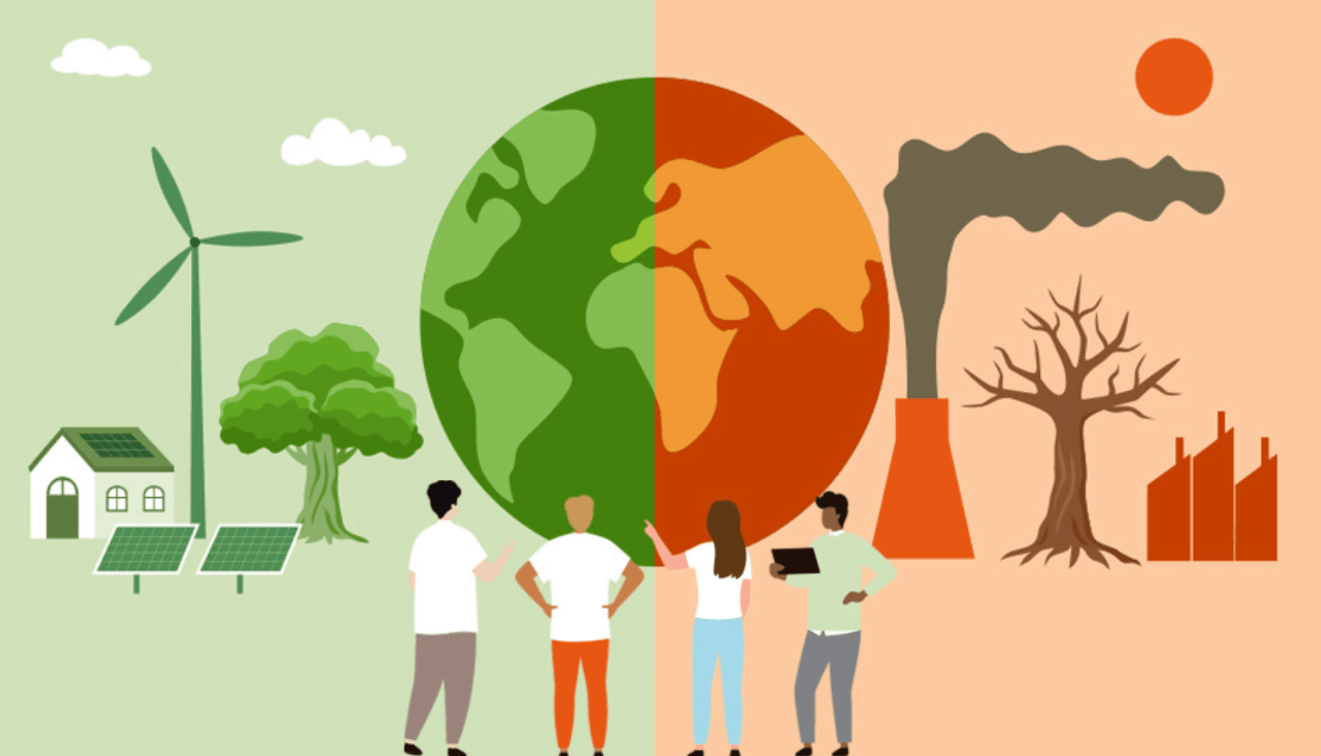

What is climate change
The name of the diagram below shows evolutionary relationships/common ancestors is...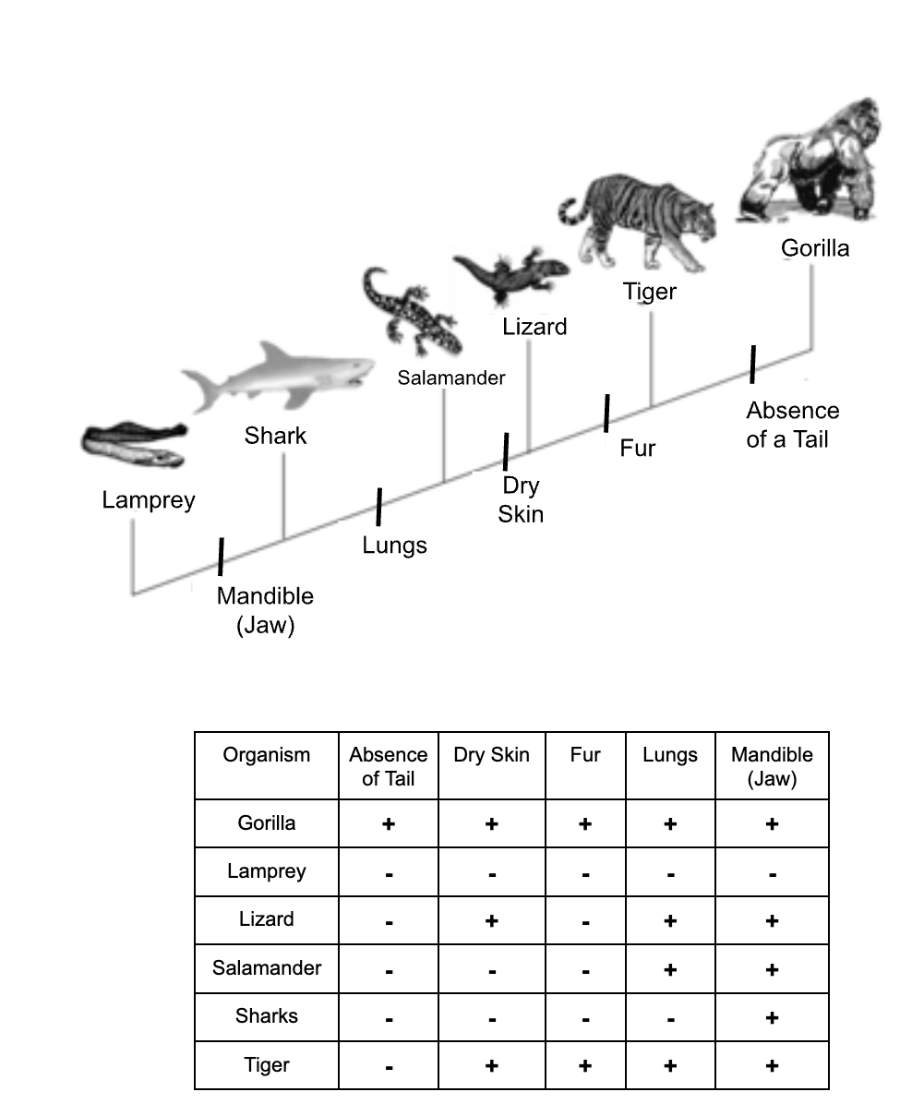
What is a Cladogram
When coding for proteins, the mRNA strand is broken up into groups of nucleotide bases of three. This chart is then used to determine which amino acid makes up the protein.
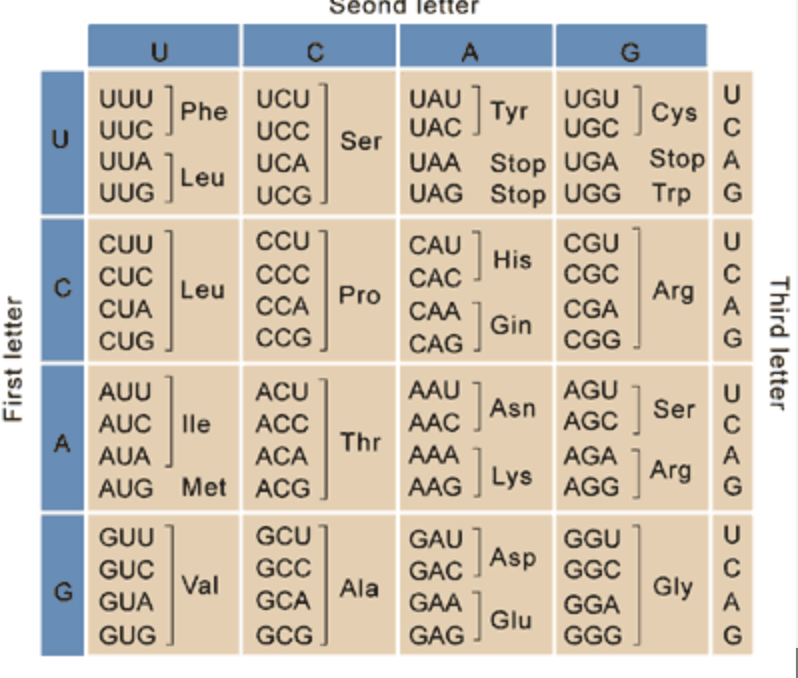
What is a codon chart