These microscopes allow you to view 3D images in detail of the surface of things not able to be viewed with the unaided eye.
What are scanning electron microscopes?
The basis of the energy pyramid that gets its energy from the sun.
What is a producer?
The energy source that maintains the water cycle.
What is the sun?
A class of energy resource that has an environmental benefit of less greenhouse gas emissions.
What is a renewable resource?
The two factors that can cause populations to increase in size.
What is births and immigration?
The microscope that a group of science students used in order to view the vascular tissue of plants in order to determine if the cells were dehydrated from lack of water.
What is a compound microscope?
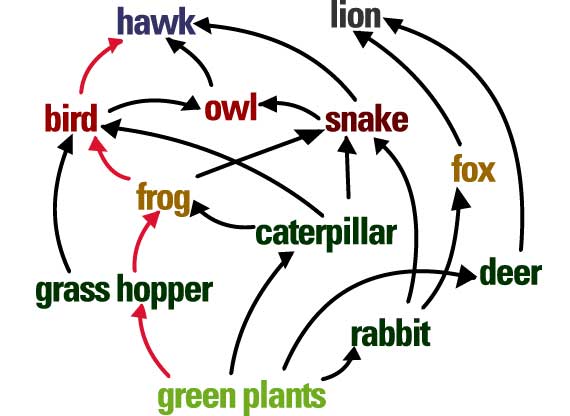
The primary consumers.
What are rabbits, deer, caterpillars, and grass hoppers?
The property of water that ensures that plants are able to transport the amount of water that they need from the roots to the leaves.
What is cohesion?
An organism that enters an area with no natural predators and competes with the native organisms.
What is an invasive species?
 Population of 2000
Population of 2000
What is carrying capacity?
These microscopes allow you to view 2D images in great detail of the inside of things you would not be able to view with the unaided eye.
What are transmission electron microscopes?
The amount of energy that is transferred from one trophic level ot the next.
What is 10%?
The process of the water cycle that plants do in order to add water into the atmosphere.
What is transpiration?
A class of energy resource that has an environmental benefit of less habitat loss in the development of necessary infrastructure.
What is a non-renewable energy resource?
In an ecosystem, which is the most likely reason for an increase in the producer population if there is an increase in the carnivore population?
A. fewer herbivores
B. higher temperatures
C. less food
D. more oxygen
What is A fewer herbivores?
The microscope used to form the image above.
What is a compound microscope?
The trophic level(s) that the robins would fall in.
What is the 2nd and 3rd trophic levels.
This process of the water cycle helps to cleanse the water in the water cycle.
What is evaporation?
The type of succession.
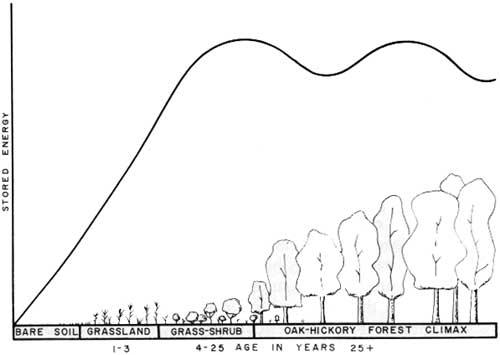
What is primary succession?
When an environment has reached its carrying capacity for a certain population, which of the following is true?
A. Birth and immigration rate is equal to death and emigration rate.
B. Birth and immigration rate is greater than death and emigration rate.
C. Birth and immigration rate is less than death and emigration rate.
D. Birth rate is exponential.
What is A. Birth and immigration rate is equal to death and emigration rate.
The microscope used to form the image below.
What is a dissecting microscope?

This causes the deer population to overgraze green plants.
What is the removal of the lion?
This property of water allows cells to transport vital nutrients into the cell and waste out of the cell.
What is versatile solvent?
This is necessary in order for an ecosystem to withstand an ecological disturbance without collapsing.
What is high biodiversity?
A cause for carrying capacity to increase.
What is an abundance in limiting factors? Example: more food in the area or, removal of a predator.