These are the 4 macromolecules
What are proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids?
This is the smallest unit of life
What is a cell?
These are the 3 domains.
What are archaea, eukarya, and bacteria?
This is the MAIN difference between eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus, prokaryotic cells do not.
This organelle is found in ALL cells and surrounds the cell.
What is the cell membrane?
This is the longest stage of the cell cycle. During this phase, the cell copies its DNA and grows.
What is interphase?
These are the building blocks of a macromolecule
What is a monomer?
This means to break down food for energy
What is metabolism?
The kingdom fungi belongs to this domain.
What is eukarya?
What are the chloroplast and cell well?
This organelle is found in ALL cells. It is the fluid that fills the cell.
What is the cytoplasm?
During this process, the cell's nucleus divides into two new nuclei, each with a complete set of DNA.
What is mitosis?
These are functions of lipids (name at least two)
What is insulation, long term energy storage, protection
In order to be considered living, organisms must react to things around them. This is known as _____________.
What is "responding to stimuli?"
This kingdom consists of eukaryotic organisms that are autotrophs. Their cells have cell walls with cellulose.
What is plantae?
The DNA in a prokaryotic cell is found here.
What is the nucleoid/floating in the cytoplasm?
This organelle synthesizes energy for the cell. It is in all eukaryotic cells.
What is the mitochondria?
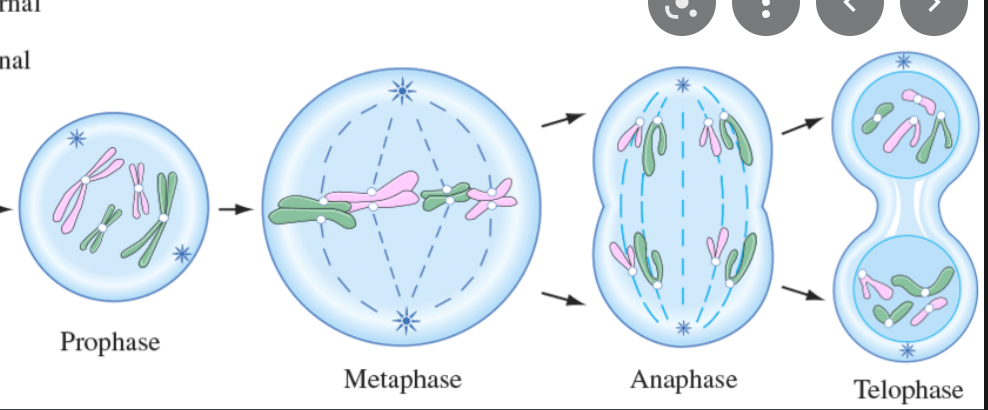
These are the 4 stages of mitosis in order.
What is prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase?
What are...
Protein: amino acids
Lipids: fatty acid and glycerol
Carbohydrates: monosaccharides
Nucleic acids: nucleotides
This means a stable set of internal conditions (heart rate, temperature, CO2/O2 levels, etc.)
What is homeostasis?
This kingdom is known as the "catch all kingdom." It is difficult to classify an organism in this kingdom because it does not have any defining characteristics.
What is protista?
This organelle, responsible for making proteins, is found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
What are ribosomes?
This organelle packages and ships materials out of the cell. It is considered the "ups" of the cell.
During this stage of the cell cycle, the cytoplasm splits, completing cell division.
What is cytokinesis?
These three elements are found in ALL macromolecules
What are carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
organs, cells, organism, organ system, tissue
cells-->tissue-->organ-->organ system-->organism
Plantae are autotrophs, fungi are heterotrophs. Plantae have cellulose in the cell walls, fungi have cell walls with chitin.
What is "Animal cells lack a cell wall"?
This organelle captures sunlight and uses it to create sugar molecules that the cell can break down for food/energy. It is only in plant cells.
What is the chloroplast?
Draw mitosis. Include a picture for each stage showing where the chromosomes are/what is happening.