what type of mutation happens when two nonhomolgous pairs cross over?
translocation 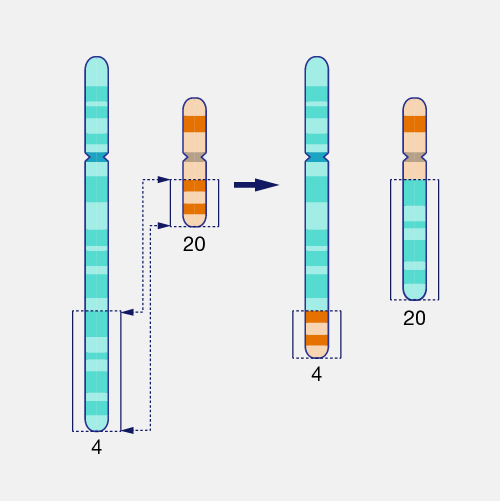
These simple molecules form the basis of all proteins
What are amino acids?
An organism that makes its own food.
What is an autotroph?
A biomolecule that serves as a fast source of energy.
What are carbohydrates?
The process by which water moves through the cell membrane to balance out a high concentration of solutes.
What is osmosis?
The grouping of cells that contain DNA, cytoplasm, ribosomes, and a cell membrane, but no other membrane-bound organelles.
What is a prokaryote? (or prokaryotic cell)
What is activation energy
A students observes a cell where the chromosomes appear to be pulled apart by spindle fibers. These two final steps would come after this.
What are telophase and cytokinesis?
This is the process by which organisms break down glucose, without the use of oxygen, to create ATP
What is anaerobic cellular respiration?
The first stage of cellular respiration in which glucose is split to form two molecules of pyruvate.
What is glycolysis?
This RNA is transcribed from a section of DNA and later leaves the nucleus in order to be translated into an amino acid chain.
What is mRNA?
movement of ions, and molecules across cell membranes without the need for energy input
What is passive transport?
Water molecules have attractive forces to one another and are held together by these types of weaker bonds
What are hydrogen bonds?
The stage in meiosis 1 where crossing over occurs to create genetically different chromosomes from the originals
What is prophase 1?
The process in which genetic instructions in mRNA are "read" to synthesize a protein with the help of tRNA.
What is translation?
What are Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, and Cytosine?
This process produces four genetically unique cells, each with half the number of chromosomes as in the parent
What is meiosis?
Name 6 things needed to be classified as a living thing.
What are responds to environment, grows and develops, produces offspring, maintains homeostasis, has complex chemistry, and consists of cells?
When both alleles are present they will mix to create a new phenotype/trait
What is incomplete dominance?
The three organelles found in a plant cell but not an animal cell
What are cell wall, large central vacuole, and chloroplast?
These are the products of cellular respiration
What are water, carbon dioxide, and ATP?
6CO2 + 6H2O —> C6H12O6 + 6O2
What is photosynthesis?
What is the difference between Primary and Secondary succession? give one example of each
Primary: starting from soil, pioneer species. volcanic eruption, iceberg melting
Secondary: soil and species already astablished. forest fire, land development, hurricane, tornado
Find the Amino Acids
TAC - AGT - CTC
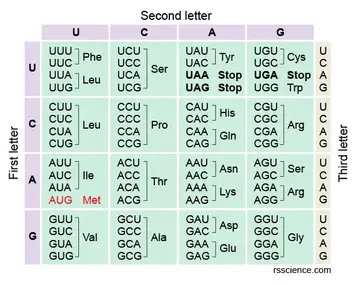
DNA: TAC - AGT - CTC
RNA: AUG - UCA - GAG
Amino Acids: MET - Ser - Glu
Sickle cell anemia is a recessive disease. If you cross two parents with the alleles Aa x Aa, what are their children's chances of having sickle cell anemia?
What is 25% have sickle cell?