Sunlight, water, salinity
What are abiotic factors?
Element that can make 4 bonds and is important to organic compounds.
What is carbon?
Work was stolen by her lab mate.
Who was Rosalind Franklin?
Made of cells, cells come from other cells, cells are basic structure and function
What is modern cell theory?
Father of Genetics
Who was Gregor Mendel?
Traveled on the HMS Beagle and developed the theory of evolution.
Who was Charles Darwin?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
What are the domains?
Allows water to be drawn up through a plants root system.
What is capillary action?
Single helix strand with uracil
What is RNA?
No membrane bound organelles, plasmid ring, capsule
What is a prokaryote?
gamete chromosomes
What is haploid?
finches develop different types of beaks that are best adapted for their particular environments
What is divergent evolution?
The shark
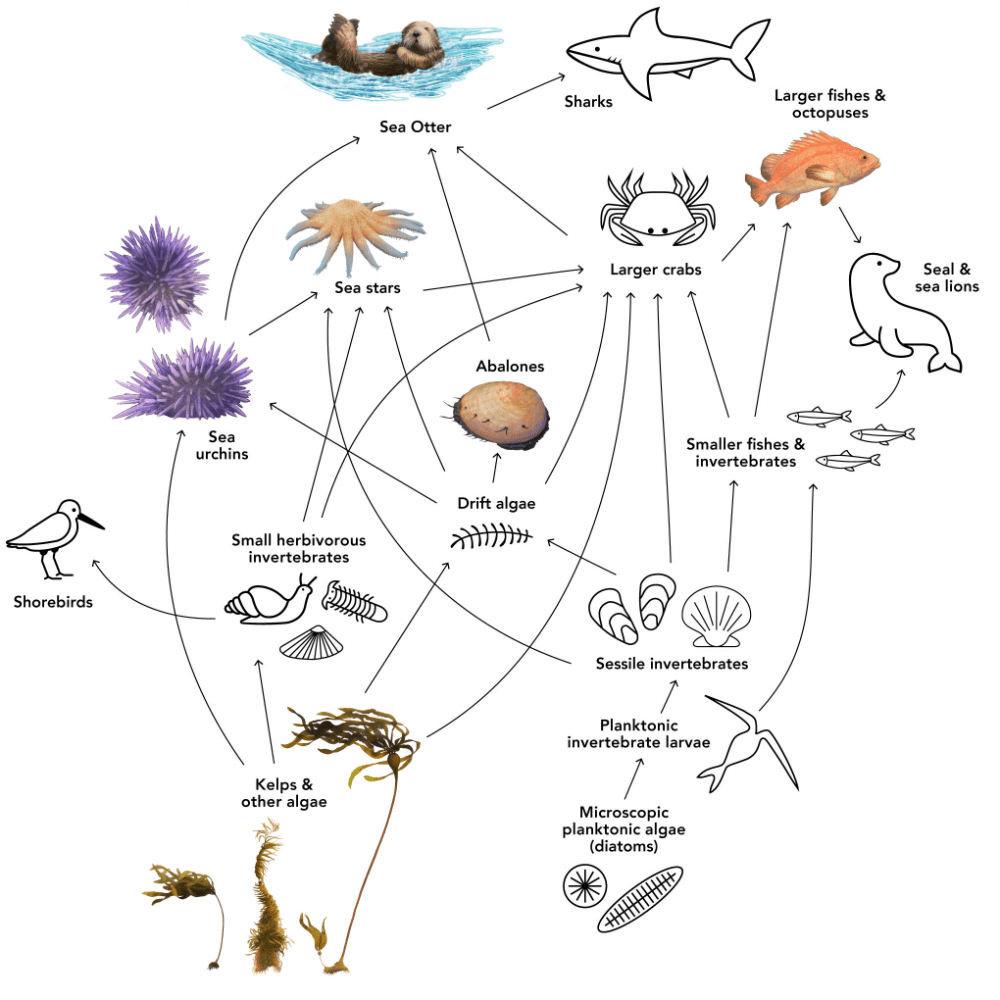
What is an apex predator or tertiary consumer?
Deforestation would increase carbon emissions.
What is the effect on the carbon cycle?
Connects the nitrogen bases together in a DNA molecule.
What is a hydrogen bond?
folds proteins into their 3D shape
What is the rough endoplasmic reticulum?
Gender
Bat wing, human arm, and a whale fin
What are homologous structures?
Golden jackals, once expelled from the pack, will trail a tiger and feed on the remains of its catches.
What is commensalism?
glycogen
What is a carbohydrate polymer?
Cytosine, Thymine, and Uracil
What are pyrimidines?
Cell shrinks in this solution.
What is a hypertonic solution?
Cross two heterozygous tall (T) pea plants. Percent of short (t) offspring is ____.
What is 25%?
Breeding corn to make it sweeter with more kernals
What is artificial selection?
Population grows almost exponentially until resources become limited in the ecosystem.
What is carrying capacity?
High temperature or changes in pH disrupt the secondary and tertiary structure of an enzyme.
What is denature?
DNA --> RNA --> Protein
What is the central dogma of biology?
Prophase takes care of this problem
What is removal of the nuclear membrane?
Type of inheritance
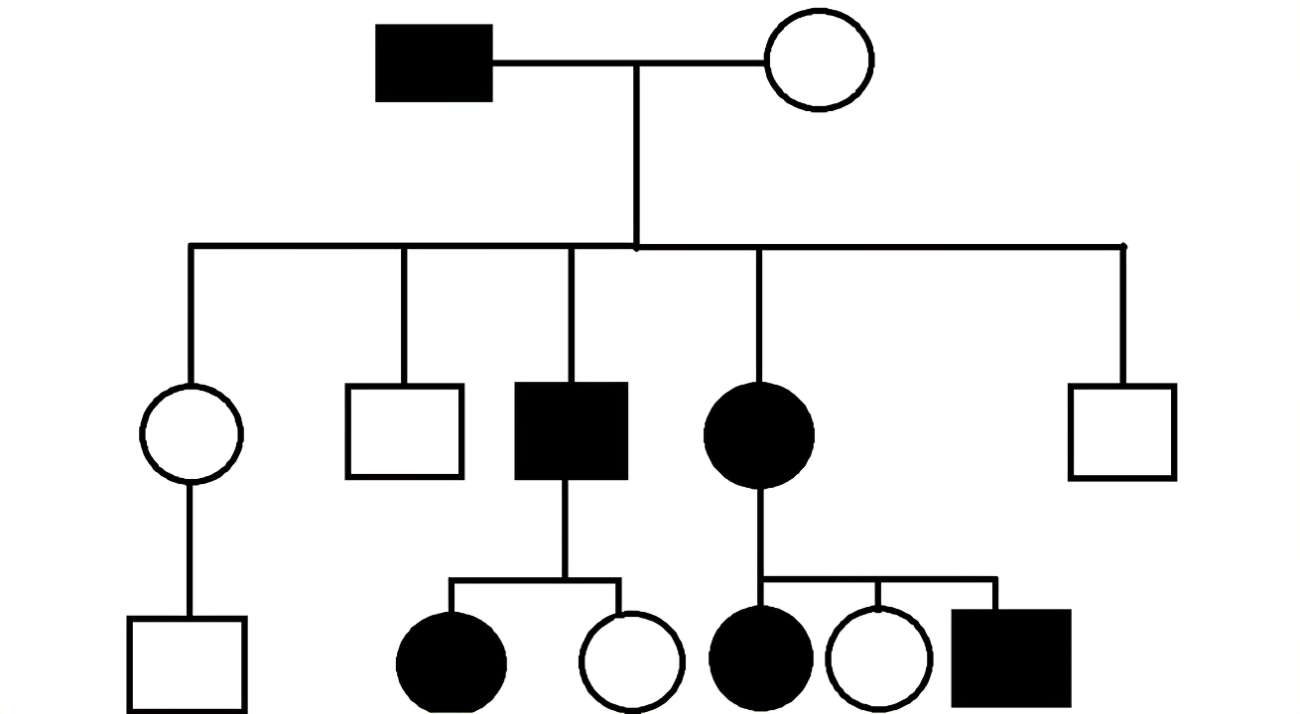
What is autosomal recessive?
Usually caused by geographic isolation
What is speciation?