What is biodiversity?
the variety of all life forms in an ecosystem: the different species of plants, animals, and microorganisms, their genes, and the ecosystems they inhabit
Why are keystone species important to an ecosystem? For example: What would happen if they were removed from an area?
The ecosystem would fall. Many species rely on the keystone and would either lose their food source, protection, or would lose population regulation.
For example: if the wildebeest left the Serengeti ecosystem... the lions/hyenas would lose their food source, zebras/gazelles would no longer be protected, and grass populations would grow out of control
What is a Carbon Sink?
an area that stores a lot of carbon (and energy from dead plants) that isn't going anywhere. Example: peat!
Who/what does cellular respiration?
all living things! (humans, plants, decomposers). they use it for energy
remember: cellular respiration and decomposition are not the same thing. decomposers break dead things down (their food!) to make energy. humans and plants do it by eating (or making) food for energy
In the Carbon Cycle, CO2 is always returned to the atmosphere. Why?
It is a gas!
If it was a solid = biosphere / geosphere
If it was a liquid = hydrosphere
What is a Keystone Species?
has multiple interactions within the ecosystem, other organisms rely on it
Explain what is happening to each population (& why!) in the following predator-prey graph:
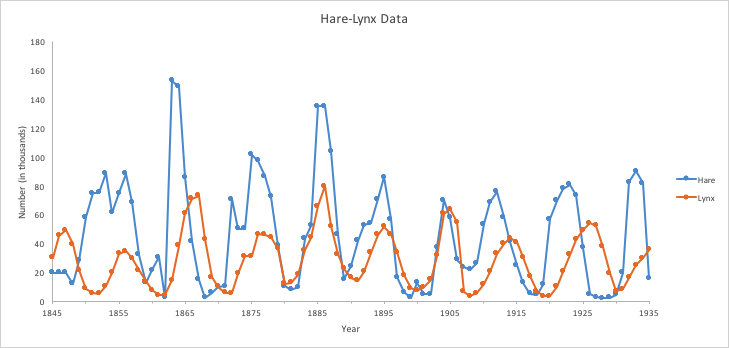
when the predator population increases, the prey population begins to decrease because they are being eaten. when the predator population decreases, the prey population can increase again due to less predators eating them
What is the difference between an independent variable and a dependent variable?
Independent: thing that the scientist is changing (cause)
Dependent: thing that changes based on the independent variable (effect)
What is the difference between photosynthesis and cellular respiration?
CR: makes energy, all living organisms do it
P: only plants do it, plants use it to make their own food
- formulas are the same, just in reverse!
Explain the color changes in BTB (blue, yellow, and green)
blue = increased oxygen
green = half oxygen, half CO2
yellow = increased CO2
What is carrying capacity?
the maximum number of organisms that can survive in an ecosystem based on the available resources
Give 4 examples of limiting factors
food/water, predators, space, weather, disease
The rate at which decomposers break down dead material is different with temperature and amount of surrounding oxygen. What is the relationship between temperature, oxygen, and decomposition?
higher temp = more decomposition
more oxygen = more decomposition. but remember, decomposition can still occur without oxygen! it is just slower and not as effective
Give 3 ways that CO2 is released into the atmosphere
Breathing (not a bad thing!), cellular respiration (humans + plants) and/or decomposition, fires, burning fossil fuels
resisting change to maintain normal conditions
examples: sweating/shivering to maintain the correct core body temp ; pancreas controlling blood sugar levels with insulin
What is a limiting factor?
an environmental condition that restricts the growth and survival of a population within an ecosystem
What did we learn about the importance of working in groups?
when there is a large group of wildebeest, it is harder for a predator to take them down (for example: in the game we played in Lesson 7: a group of WB will roll 3 dice when they go against a predator. however, if alone, it is only 1 dice. the more dice, the higher chance of survival
the same goes for predators. more lions can take down more prey = they work together!
What are the formulas for cellular respiration and photosynthesis?
cellular respiration: O2 + sugar -> energy + CO2 + H2O
photosynthesis: CO2 + H2O + sunlight (energy!) -> O2 + sugar
What conditions make carbon sinks more likely to burn? What are the consequences when they burn?
- have a lot of peat/materials that are compact and hold onto fire/heat so they are very hard to put out
- health (black sky) warnings, smoke can travel to different areas, burn homes and habitats
Give 4 ways humans increase CO2 in the air, leading to global warming
camp fires/BBQs, burning fossil fuels (cars, factories, heating our homes), deforestation, urban changes (creating farm land or making more space for homes)
breathing does not count! that does not lead to global warming lol
Explain the difference between a food chain, a food web, and a food pyramid (you can draw on the board if needed). Your answer must include the 10% rule
What are 3 ways we can conserve biodiversity?
Protecting natural habitats/resources from human interactions (example: deforestation)
Implementing practices so resources do not get overused
Promoting conservation education/communication
in the past: the Earth's tilt was larger, which lead to increased direct light and warmer temps. this caused higher rates of photosynthesis and decomposition (so there was not build up of dead materials!)
present(ish): the Earth's tilt is less, which provides less direct light and colder temps. this is why the Arctic is cold now! colder temps makes decomposition slower/stop so peat was able to build up and create carbon sinks. photosynthesis is less with less direct light
Explain how large fires affect each of the Earth's Spheres (hint: there are 4!). Give one example for each.
1) atmosphere (air): increased CO2, smoke, increased temps, heath warnings, low sun exposure
2) biosphere (land): burn scars, burning plants/habitats, hurting animals, changing migration patterns, destroying homes
3) geosphere (underground): peat holds onto fire/heat so it can create more fires through burn scars, may hurt living things in the ground/dirt
4) hydrosphere (water): melting, increased ocean levels, increased water temps, flooding, hurting animals/plants in water by habitiat/temp changes
List 5 fun facts you know about Ms. Hope
(answers may vary)