Nonliving and living factors together.
What is an ecosystem?
Lichen and moss are the first organisms of this succession.
What is primary succession?
An example of a Carbon Sink.
What are Fossil Fuels, plants, soil or the Ocean?
More of this gas would lead to more photosynthesis.
What is CO2?
The process that makes energy in cells.
What is cellular respiration?
The study of life.
What is biology?
At around 2000 organisms, this species reaches its
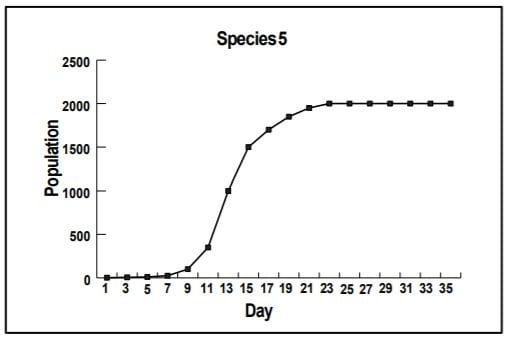
What is carrying capacity?
The ecosystem that is more resilient.
What is the high biodiversity ecosystem?
An example of a Carbon Source.
What is pollution, combustion or respiration?
The reactants of photosynthesis.
What are CO2 and H2O?
The type of organism that does cellular respiration.
What are all living things?
The type of energy turned into glucose in Photosynthesis.
What is light energy?
Where a species is around but is struggling.
What is stressed zone?
When two different species compete.
What is interspecific competition?
Solar, wind and nuclear energy.
What are solutions to pollution?
The products of photosynthesis.
What are Glucose and Oxygen?
The purpose of cellular respiration.
A negative of excessive greenhouse gases.
What is global warming, melting ice caps, sea levels rising, or climate change overall?
When a keystone species is removed, the effects it has on the rest of an ecosystem.
What is a trophic cascade?
When a seaside ecosystem recovers from a hurricane.
What is secondary succession?
Greenhouse gases interact with this type of radiation.
What is infrared?
The purpose of photosynthesis.
What is storing energy as sugar?
The place where cellular respiration takes place in the cell.
What is the mitochondria?
Each element of HIPCO.
What are Habitat Loss, Invasive Species, Pollution, Climate Change and Overharvesting?
When one species receives a benefit and the other is neither harmed or helped.
What is commensalism?
In community 1, the Species Evenness of the Blue stars.
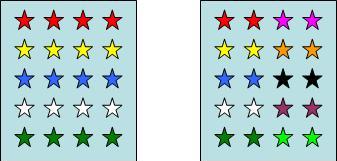
1 2
What is 20%?
One positive of the natural greenhouse effect.
What is allowing for life, protecting from objects or protecting from UV radiation?
The elements found in Glucose.
What are Carbon, Hydrogen and Oxygen?
The products of cellular respiration.
What are ATP, H2O and CO2?
A trophic cascade example from class.
What are otters indirectly helping help, or foxes harming plant growth, or bass helping reduce carbon?