What is DNA and where is it located? BE SPECIFIC!
DNA is the genetic material/coding instructions.
Inside the nucleus of Eukaryotic Cells.
Free flowing in the cytoplasm of Prokaryotic Cells.
Where is RNA located?
Both inside and outside of the nucleus (in the cytoplasm).
What are the monomers of Proteins?
Amino Acids
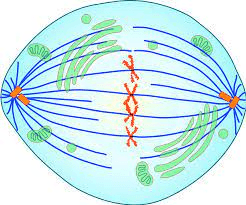
What step of mitosis is this?
What is probability?
Probability is the likelihood that something will happen.
Nucleotides.
Where does DNA replication occur?
In the nucleus of Eukaryotic Cells.
Nucleotides
The step going from DNA to RNA in protein synthesis is called _______.
Transcription
What type of cells do mitosis?
Nonsex cells
True or False.
Homozygous dominant, homozygous recessive and heterozygous are all examples of phenotypes.
FALSE!
What are the three parts of a DNA nucleotide? BE SPECIFIC.
Deoxyribose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen bases.
When does DNA replication occur?
In interphase, specifically S Phase.
Ribose sugar, phosphate group, nitrogen bases.
The step going from RNA to amino acids is called ______.
Translation
What are the three parts of interphase and what happens in each of them?
G1- Growth and development
S- DNA replication
G2- Prep for cell division
In people, freckles are dominant.
Use a Punnett square to determine allelic combinations among a woman who is heterozygous for freckles and a man who is homozygous recessive.
What is the probability of the offspring having freckles?
50%
What are the four nitrogen bases of DNA?
Adenine, Thymine, Cytosine, Guanine.
What is the final outcome of DNA replication?
TWO IDENTICAL DAUGHTER STRANDS.
What are the four nitrogen bases for RNA?
Adenine, Uracil, Cytosine, Guanine
Codon Wheel/Chart
What is the difference between the cells created by mitosis and the cells created by meiosis?
Meiosis cells are genetically diverse(different).
In sunflowers, fuzzy leaves are dominant over smooth leaves.
Cross a heterozygous sunflower for fuzzy leaves with a sunflower that is heterozygous for fuzzy leaves.
What RATIO of offspring will have fuzzy leaves?
What RATIO of offspring will have smooth leaves?
3/4 fuzzy leaves
1/4 smooth leaves
Using the base pairing rules, create the complementary DNA strand for.....
A T C G G C T A A C T G
T A G C C G A T T G A C
List the steps of DNA replication, be sure to name the enzymes involved.
1. DNA Helicase unzips the DNA helix.
2. Primase creates the starting line for DNA Polymerase.
3. DNA Polymerase builds the new nucleotides.
4. Ligase comes in to glue the DNA strands together.
FINAL OUTCOME: 2 identical semiconservative daughter cells.
What would the messenger RNA strand look like based on this DNA strand?
A T C G G C T A A C T G
U A G C C G A U U G A C
Translate the following mRNA into amino acids: AUG-ACA-UUC
Methionine-Threonine-Phenylalanine
What is the difference between mitosis, cell division and the cell cycle?
Mitosis is PMAT
Cell division is PMATC
Cell cycle is IPMATC
What is the relationship between genotypes, phenotypes and alleles?
Alleles are a variation of traits.
Genotypes are created by alleles.
Phenotypes are the physical representation of genotypes, the combination of alleles.