In a scientific investigation, this variable is deliberately changed by the researcher.
What is the independent variable?
These large molecules include carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What are organic molecules/biomolecules.
These cells lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
What are prokaryotic cells (or prokaryotes)?
DNA is composed of repeating units called these.
What are nucleotides?
This cell structure is selectively permeable and helps maintain homeostasis by controlling what enters and leaves the cell.
What is the cell membrane?
(Accept: plasma membrane)
This group or setup is used as a basis for comparison and does not receive the independent variable.
What is the control group?
This type of molecule serves as is a monomer of proteins.
What is an amino acid?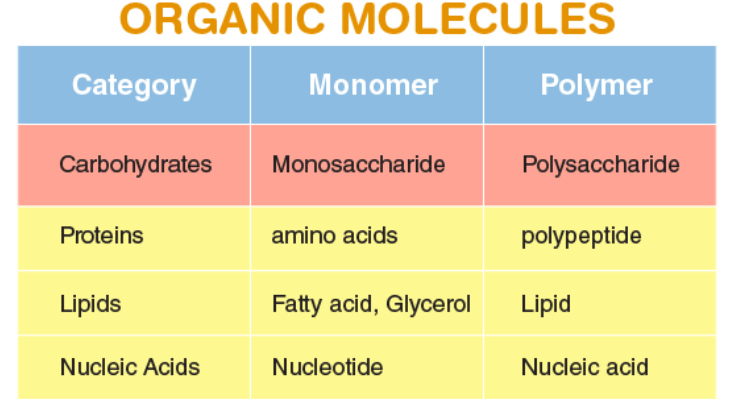
This organelle is the site of cellular respiration and ATP production.
What is the mitochondrion? (Accept plural version also: mitochondria.)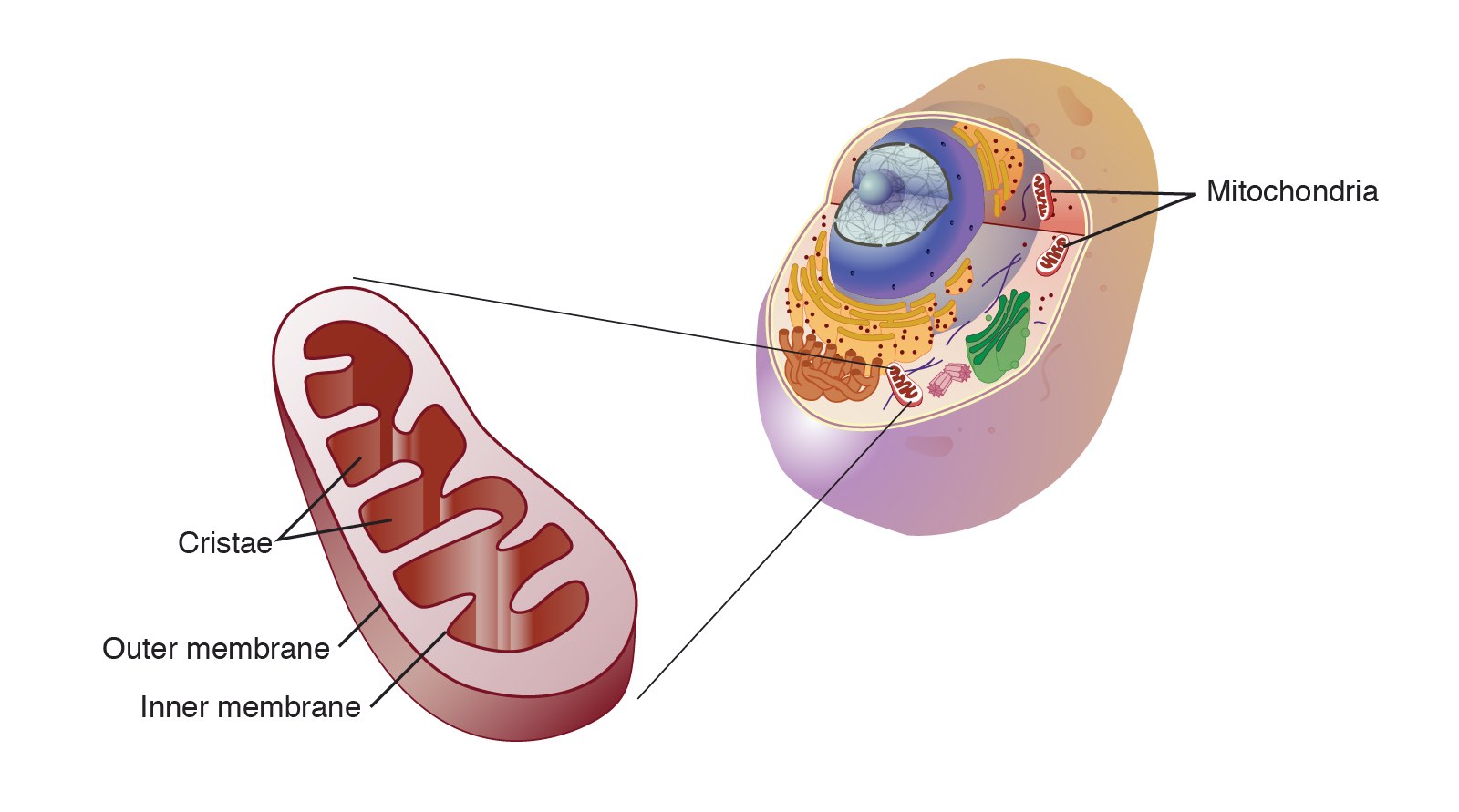
During DNA replication, adenine always pairs with this base.
What is thymine?
Alterations to the shape and function of an enzyme exposed to extreme temperatures and/or pH are described by this term.
What is denaturation? (Accept denature)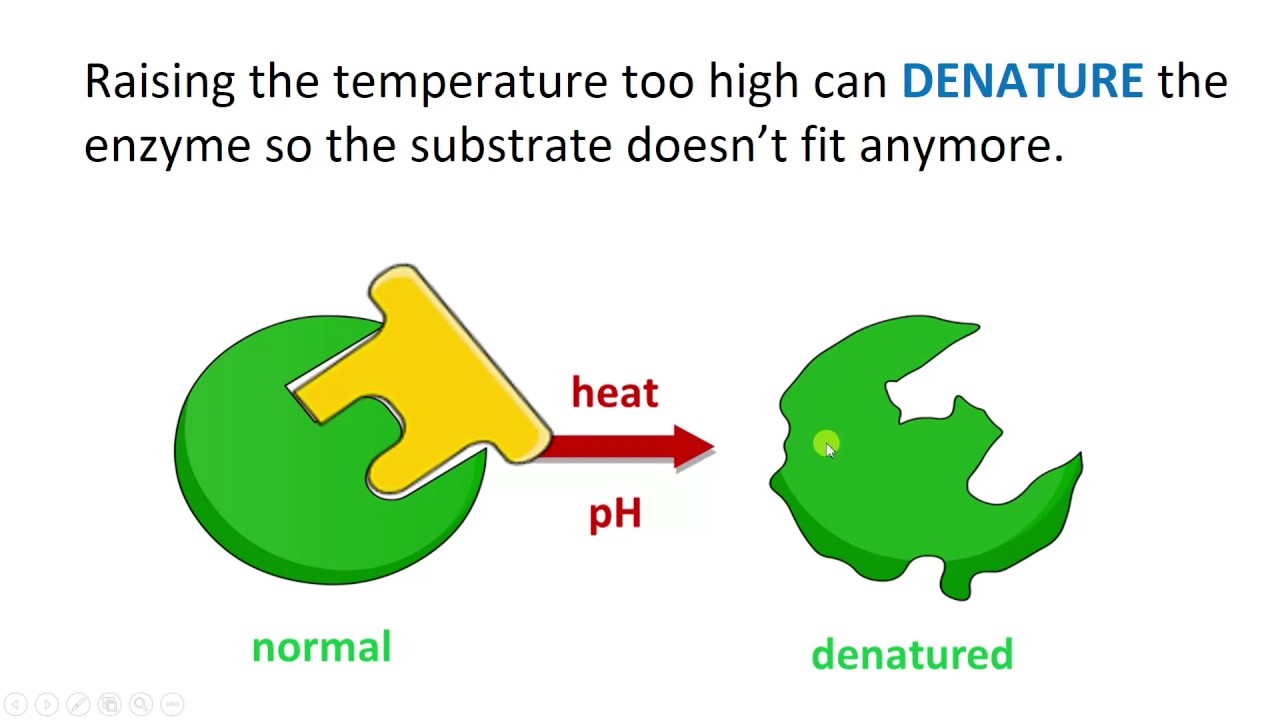
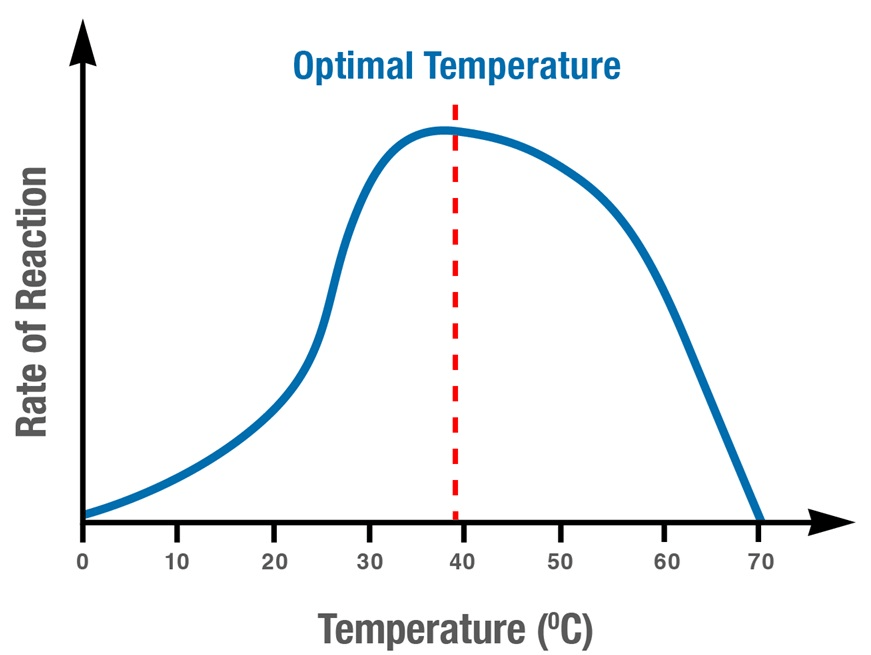
Identify the dependent variable represented in this graph.
What is the rate of the enzyme-controlled reaction?
This chemical reaction joins monomers together by removing a molecule of water.
What is a condensation reaction (or dehydration synthesis)?
Diffusion, osmosis, and facilitated diffusion are all examples of this type of membrane transport.
What is passive transport? (Accept transport that doesn't involve energy expenditure.)
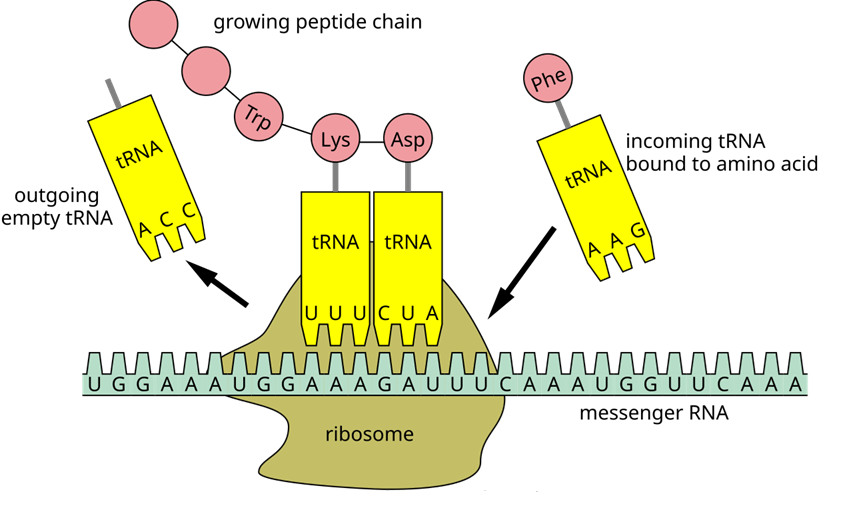
In the Central Dogma of Biology, this process occurs when information is used to build a protein from RNA.
What is translation?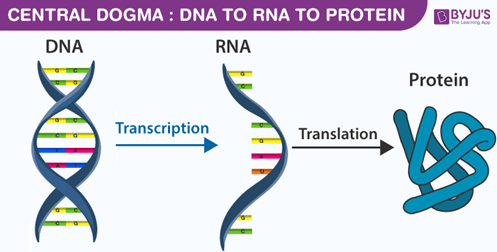
Certain proteins in the plasma membrane of liver and muscle cells allow glucose to move into the cell without using ATP. This type of transport is occurring.
What is facilitated diffusion?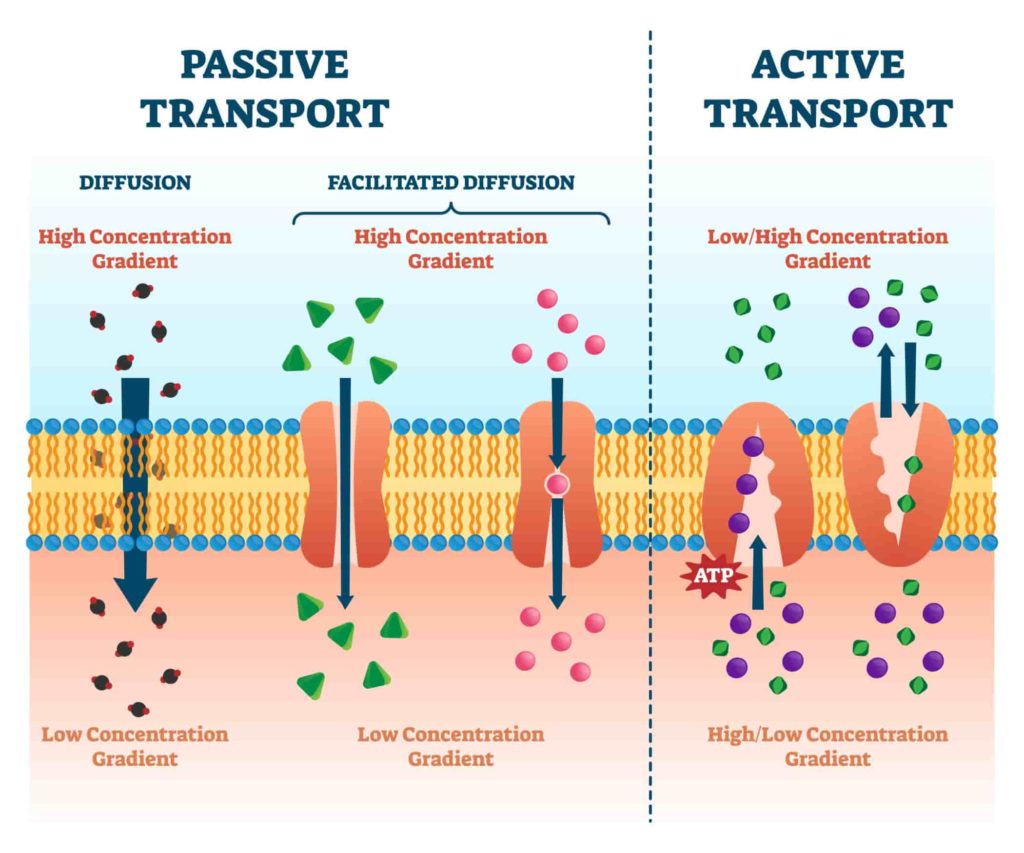
Repeating an experiment multiple times increases this aspect of the results.
What is reliability? (Also accept validity.)
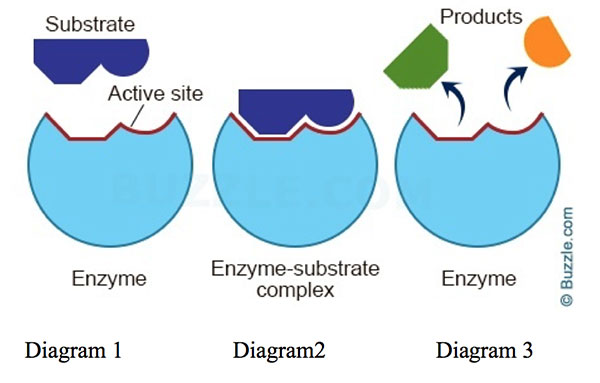
This explains why enzymes are specific for only certain substrates.
What is the shape of the active site? (Also accept: enzyme–substrate specificity)
Water moving across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to low water concentration is called this.
What is osmosis?
In humans, this type of inheritance occurs when both alleles are equally expressed in the phenotype.
What is codominance?
The reduction of multiple toes into a single hoof in modern horses is an inherited trait that increased survival over time. This is an example of this.
What is an adaptation?
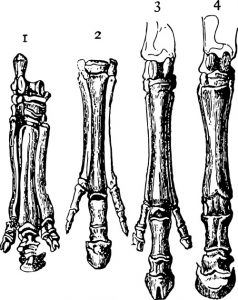
An investigation produces unexpected data in addition to data that partially supports the original hypothesis. Scientifically, the most appropriate next step is to do this.
What is revise the hypothesis & retest? (Also accept: reevaluating & revising the investigation.)
Cells require this molecule, which can combine with a phosphate group to form an energy-rich compound used to power cellular processes.
What is ADP (or Adenosine Diphosphate)?
Maintaining proper concentrations of sodium and potassium ions across a cell membrane requires ATP and a membrane protein that moves sodium ions against their concentration gradients.
What is active transport?
Brings amino acids to ribosomes to be assembled into proteins.
What is a transfer RNA? (Also accept tRNA.
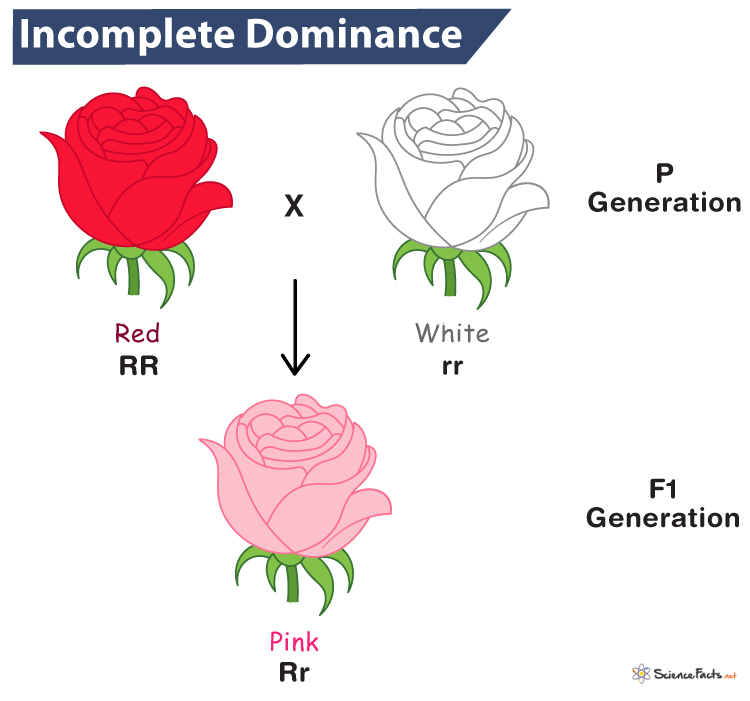
In snapdragons, crossing red-flowered plants with white-flowered plants produces pink offspring. This inheritance pattern best describes this situation.
What is incomplete dominance?