What are the four main classes of macromolecules found in living organisms?
Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids
Give one example of each level of organization:
Population
Community
Any group of same species in same area
Any group of more than one population in same area
DAILY DOUBLE:
Define mitosis AND give a reason why a cell may undergo it.
Nuclear division. To replace dead cells, to grow
What is the basic structural and functional unit of a living organisms?
Cells
Define natural selection. Give an example of natural selection in nature.
Survival of the fittest trait causes a change in a species. Example would be rock pocket mice changing colors based on their environment over time.
Which macromolecule is a catalyst, speeding up chemical reactions?
Enzymes (proteins)
Describe a biotic factor that can affect an ecosystem.
Any living thing that causes a change in an ecosystem. Example: an invasive species that outcompetes native animals, reducing their numbers.
State the four phases of mitosis AND give a brief description of what the chromosomes are doing in each phase.
prophase - chromosomes condense
metaphase - chromosomes line up in middle
anaphase - chromosomes pull apart
telophase - chromosomes uncondense in each nucleus
Explain the difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and provide an example organism for each.
eukaryotic - membrane bound organelles, animals
Describe the difference between homologous and analogous structures, and provide an example of each.
homologous - related, similar internal structure and different external structure. Humans and bat hands.
analogous - not related, evolved to have similar traits. dolphins and sharks with fins and torpedo body shape
For the DNA template below, identify the complementary strand of DNA.
ATC GAC TTA CCG
TAG CTG AAT GGC
Draw a graph showing logistic growth and carrying capacity of a population.
Should be an S shaped curve that oscillates at the top.
In humans, brown eye color (B) is dominant to blue eye color (b).
Identify what the homozygous recessive genotype would be.
Identify what the homozygous recessive phenotype would be.
bb
blue
Draw a picture of the rough ER. Identify its function.
function: to fold and package proteins to send throughout the cell
Explain how the fossil record provides evidence for evolution. Identify one limitation of using fossils to study evolutionary relationships.
Shows a sequence of life forms that have existed and changed over time, with simpler organisms found lower and more complex organisms found in younger rock layers.
limitation: not all organisms become fossilized, so we sometimes have incomplete records.
Fill in the blanks in the picture shown:
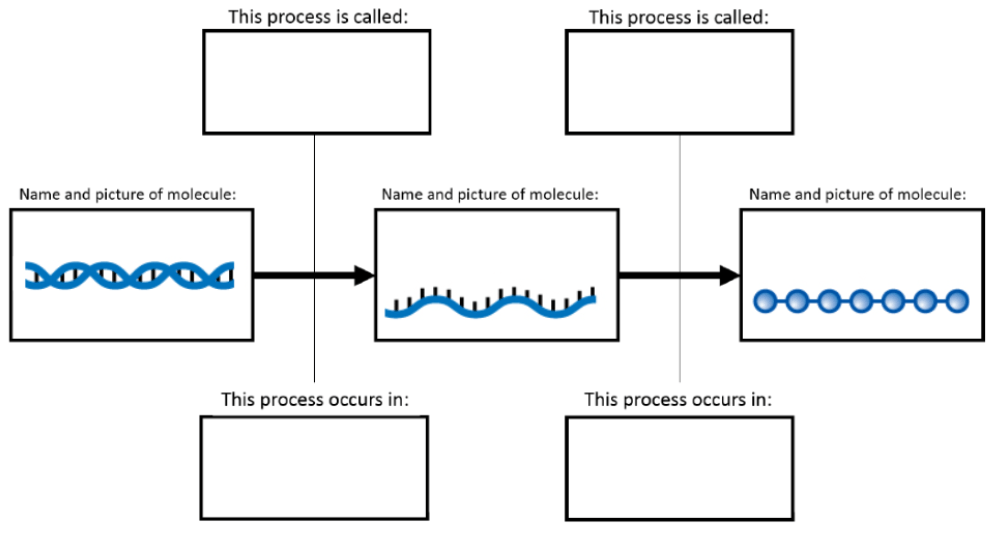
transcription translation
DNA RNA Protein
Nucleus Ribosome
According to the food web, what does the sea nettle eat?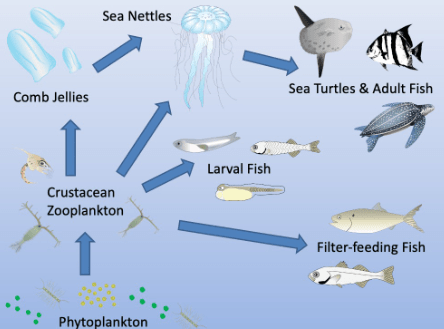
In pea plants, the gene for flower color has two alleles: purple (B) and white (b). If a homozygous purple flowered plant is crossed with a heterozygous purple plant, what percentage of the offspring are white?
Draw two pictures of molecules moving INTO a cell: one showing diffusion, the other showing facilitated diffusion.
for diffusion there should be small solutes. for facilitated they should be larger molecules with a transport protein in it
Plants and fungi are often compared to each other. Identify the following for each kingdom.
Autotroph or heterotroph
What is in their cell wall?
How do they obtain food?
fungi plant
heterotroph autotroph
Chitin cellulose
External digestion photosynthesis
(consuming)
DNA: TAC GCA GGT TCA ACT
Transcribe and translate the DNA strand above into the correct amino acids. Use the chart to help.
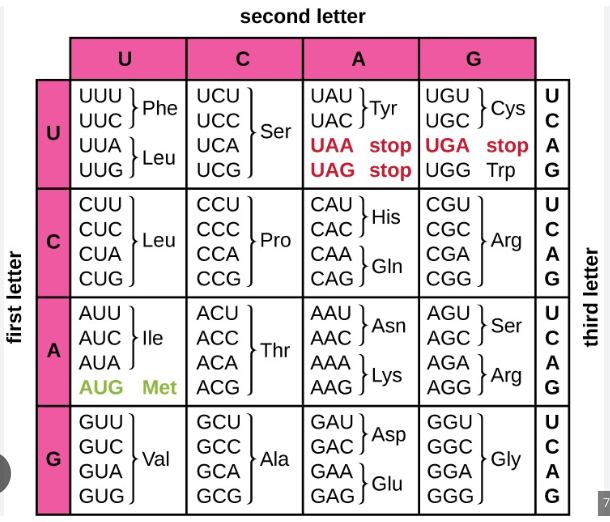
rna: AUG CGU CCA AGU UGA
protein: met - arg - pro - ser - stop
Design an experiment (give me IV, DV, control group, and constant) that would investigate the impact of invasive species on native species in an environment.
Answers will vary. But it could be:
area 1 has no invasive species but native organisms. Scientists count number of each organism at the end
area 2 has invasive species and native organisms. scientists count number of each organism at the end.
IV: invasive species
DV: number of organisms
Control: area 1
contestants: time, same starting environment
In guinea pigs, coat color is determined by two genes: black (B) is dominant over white (b), and rough (R) is dominant to smooth (r). If a guinea pig has the genotype bbRr, what is its phenotype?
white and rough
Write the chemical formula for cellular respiration.
C6H12O6 + O2 --> H20 + CO2 + ATP
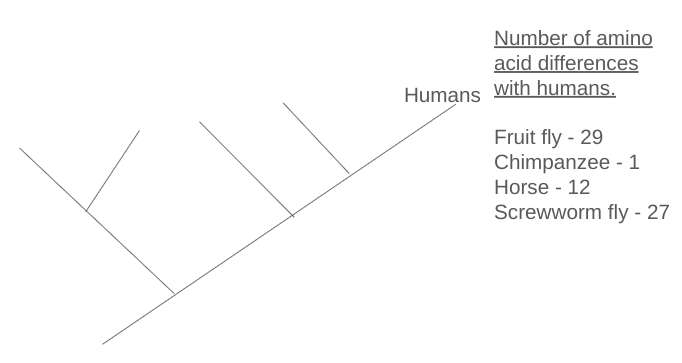
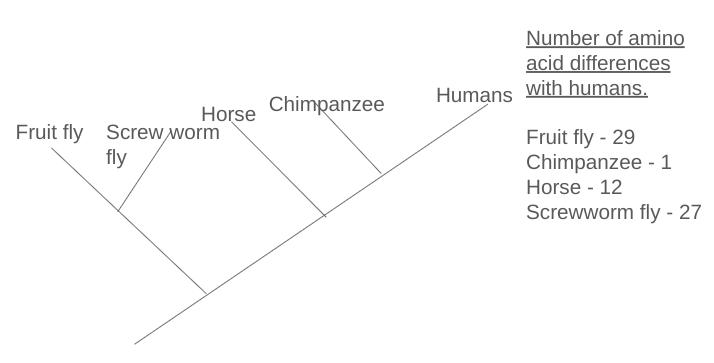
Fill in the cladogram with organisms names at the top based on the data given.