What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus is the storehouse for most of the genetic information, or DNA in the cells.
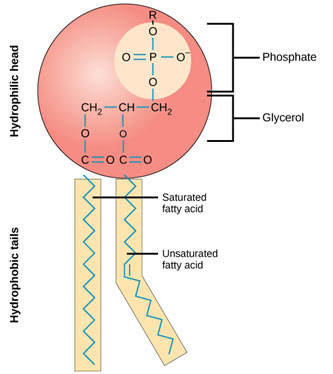
What is the phospoplipid looks like?
The relationship between monomer and polymer.
Each smaller molecule is a subunit called a monomer, and the monomer will form the polymer.
All living thins and all the place can be found in the Earth.
Biosphere
The different between Active transport and Passive transport?
The passive transport is opposite, and it does not need to spend energy.
What is the function of cytoskeleton?
The function of cytoskeleton is the network of proteins that is constanly changing to meet the needs of a cell.
What is the function of the cell membrane?
The cell membrane forms a boundary between a cell and the outside environment and controls the passage off materials into and out of the cell.
How are carbohydrates and lipids similar? How are they different?
They both are the polymer, but they have different monomer.
What is the Homeostasis?
The maintenance of constant internal condition in an organism.
What is the facilitated diffusion?
The diffusion of molecules across a membrane through transport protein.
The major principles of the cell theory.
All organisms are made of cells; All existing cells are produced by other living cells; The cell is the most basic unit of life.
What is the phospholipids layers embedded with other molecules?
Proteins, carbohydrates and cholesterol.
Describe the monomers of nucleic acids and proteins.
Nucleotides and Amino acids
How are structure and function related to adaptation?
Structural adaptations are physical features of an organism. Functional adaptations are those that help the organism to survive, the difference being that they are innate functions.
What is the isotonic, hypotonic, and hypertonic for the cell?
Isotonic is equal solute between cell and environment.
Hypotonic is more solute than the outside
Hypertonic is less solute than the outside
What is the different of Prokaryotic cells and Eukaryotic cells?
Eukaryotic cells have a nucleus and other membrane-bound organelles, and Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or other membrane-bound organells.
What is the receptor to transmit across the cell membrane?
Portein
Four main types of Carbon-based molecules are found in living things.
Carbohydrates, Lipids, Protein, Nucleic acid
How does biodiversity depend on a species' ability to reproduce?
It ensures that the species will continue to be present over the next generation.
The cell membrane engulfs large particles
Phagocytosis
The organelles that only plants have, and the organelles that only animals have.
Plants: Chloroplast, Central Vacuole, Cell Wall.
Animals: Centriole, Lysosome
What is the fluid mosaic model?
To describe the arrangement of the molecules that make up a cell membrane.
Why might fatty acid, amino acids, and amino acids increase the hydrogen ion concentration of a solution?
Because fatty acids, amino acids and nucleic acids are acids that produce hydrogen +
Do you think homeostasis is necessary at the level of a single cell?
Cells are alive and all living things must maintain homeostasis.
Ions are in low concentration outside a cell. They move rapidly into the cell via protein molecules. What term describes this action? Does it require energy?
This process do not need energy.