What is the difference between food chains and food webs?
Food chains are linear and food webs are interconnected (multiple food chains).
What type of organisms make up the base of an energy pyramid?
producers
What are two substances that circulate throughout the biosphere?
water, nitrogen, carbon, phosphorus
(must name 2 of 4)
What is the difference between abiotic and biotic factors?
Biotic factors are alive and abiotic factors are not (and never have been).
What is the term that refers to one living thing?
an organism
Create a simple food chain using four of the organisms from the list below.
Big bluestem grass, Corn, Oak tree, Algae, White-tailed deer, Eastern cottontail rabbit, Grasshopper, Canada goose, American robin, Bluegill sunfish, Red squirrel, Leopard frog, Northern pike, Red-tailed hawk, Great horned owl
Many correct answers but should follow the format below.
producer -> primary consumer/herbivore -> secondary consumer/omnivore -> tertiary consumer/carnivore
In a kelp forest, place these organisms into correct trophic levels: sea otter, sea urchin, orca, kelp.
Kelp → Producer
Sea urchin → Primary consumer
Sea otter → Secondary consumer
Orca → Tertiary consumer
Name one way humans can influence the carbon cycle and explain its effect.
Burning fossil fuels adds carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, increasing greenhouse gases and contributing to climate change.
Identify one abiotic factor and one biotic factor in a kelp forest ecosystem.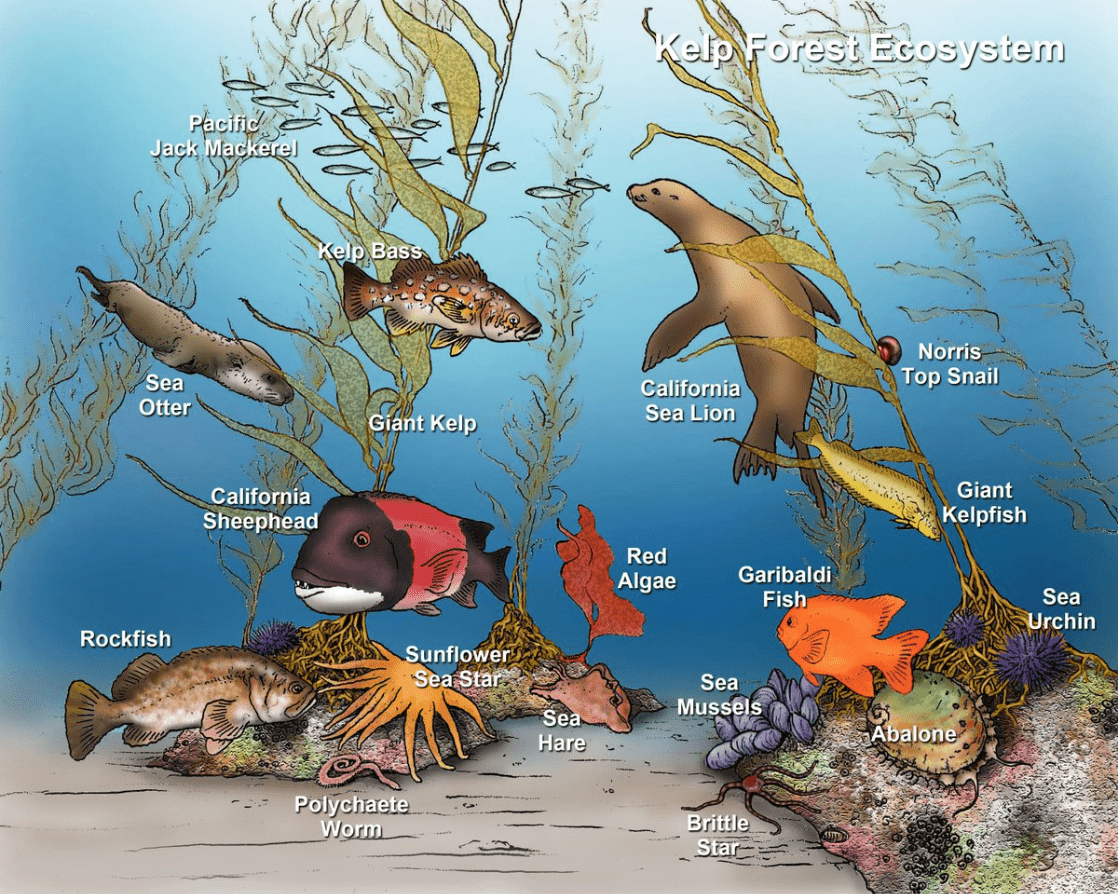
Abiotic factor: sunlight, cold ocean water, or nutrients.
Biotic factor: kelp, sea urchins, sea otters, or fish.
What do we call a group of the same species living together in the same area?
population
If a disease drastically reduced the white-tailed deer population, explain how that could affect both plants (like corn or oak trees) and predators (like red-tailed hawks).
If white-tailed deer decline, plants such as corn or oak may increase because fewer deer are eating them. Predators like red-tailed hawks could decline because their prey (rabbits, squirrels, or other small animals) may shift populations due to changes in plant growth and ecosystem balance.
Other answers may be reasonable-determine as a group
What would likely happen to the sea urchin population if sea otters were removed from the kelp forest ecosystem?
Sea urchin populations would increase rapidly, which could overgraze and damage the kelp population.
How does the water cycle help move materials like nutrients or soil from one place to another?
Rain and runoff can carry nutrients into rivers, lakes, and oceans, while floods or erosion can move soil and minerals across landscapes.
How do sea otters (a biotic factor) indirectly affect the abundance of kelp?
Sea otters eat sea urchins, which prevents urchins from overgrazing the kelp. Without otters, sea urchin populations explode and kelp forests disappear.
A kelp forest includes the living organisms and also nonliving factors like sunlight, water, and nutrients. What level of organization does this describe?
ecosystem
Compare the roles of the red squirrel and the grasshopper in a food web. How are their positions similar, and how are they different?
Both red squirrels and grasshoppers are primary consumers because they eat plants (acorns and leaves for squirrels, grasses and crops for grasshoppers). However, squirrels can also act as secondary consumers when they eat insects or bird eggs, while grasshoppers remain strictly herbivores.
Other answers may be reasonable-determine as a group
Compare the amount of available energy at the producer level to the tertiary consumer level in an energy pyramid. Why is there such a difference?
Producers capture the most energy from the sun, and only about 10% of energy transfers to the next level. By the time energy reaches tertiary consumers, much has been lost as heat, so they receive far less.
Why are cycles like water, carbon, and nitrogen essential for life on Earth?
They recycle important substances so organisms can reuse them; without these cycles, resources like water or carbon would quickly become unavailable for living things.
Explain how changes in abiotic conditions, such as rising ocean temperatures, might contribute to the loss of kelp forests.
Warmer water stresses kelp and reduces their growth, making them less able to recover from grazing or storms, which speeds up kelp forest decline.
Other answers may also be considered correct.
A kelp forest is home to sea otters, sea urchins, kelp, fish, and many other species. What level of organization do all of these species living together represent?
community
Construct a food web that includes at least 8 of the listed organisms. Then identify:
One producer,
Two primary consumers,
Two secondary consumers, and
Two tertiary consumers.
Big bluestem grass, Corn, Oak tree, Algae, White-tailed deer, Eastern cottontail rabbit, Grasshopper, Canada goose, American robin, Bluegill sunfish, Red squirrel, Leopard frog, Northern pike, Red-tailed hawk, Great horned owl
Producers: Big bluestem grass, Corn, Oak tree, Algae
Primary consumers: Grasshopper, Eastern cottontail rabbit, Red squirrel, Canada goose, White-tailed deer
Secondary consumers: American robin (eats insects), Leopard frog (eats insects), Bluegill sunfish (eats algae and small animals)
Tertiary consumers: Northern pike (eats fish and frogs), Red-tailed hawk (eats rabbits, squirrels), Great horned owl (eats rabbits, squirrels, birds)
Use the kelp forest to explain why top predators like orcas are more vulnerable to ecosystem disruptions than producers like kelp.
Top predators depend on long food chains, so any disruption at lower levels (like loss of kelp or sea otters) reduces their food supply. Producers can often recover faster, but tertiary consumers have smaller populations and need large amounts of energy, making them more at risk.
Explain how the water cycle creates a natural phenomenon such as a thunderstorm or a lake-effect snowstorm.
Evaporation moves water vapor into the atmosphere, condensation forms clouds, and rapid cooling or rising warm moist air leads to heavy precipitation. In lake-effect snow, warm lake water evaporates, cold air causes condensation, and snow falls downwind of the lake.
Other answers may be considered correct- discuss as a group.
Disappearing kelp forests are influenced by both abiotic and biotic factors. Explain how these factors interact to create the decline.
Abiotic factors like warming waters and stronger storms weaken kelp, while biotic factors like unchecked sea urchin populations (due to fewer sea otters) overgraze kelp. Together, these pressures cause rapid loss of kelp forests.
Kelp forests are sometimes called “ecosystem engineers” because they create habitat for many other species. At which levels of organization would the loss of kelp have the greatest impact, and why?
The loss of kelp would most strongly affect the community and ecosystem levels, because kelp provides food and shelter for many species, and its decline disrupts both living interactions and abiotic conditions across the whole system.