The control center that holds the DNA
Nucleus
The type of transport that requires no energy.
Passive Transport
The organelle responsible for photosynthesis
Chloroplast
The type of respiration that does not require oxygen.
Anaerobic respiration
The main macromolecule that our cell membranes are made of.
Lipids (phospholipids)
The part of the cell that controls what enters and exits the cell. Key to maintaining homeostasis
Cell membrane
The type of transport that goes AGAINST the concentration gradient.
Active transport
The pigment in chloroplasts that absorbs sunlight.
Chlorophyll
The reactants of this process are the products of cellular respiration.
Photosynthesis
The type of solution when water flows in and out of the cell equally.
Isotonic
Responsible for transporting materials around the cell.
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
The type of transport that requires the help of protein channels, but requires no energy.
Facilitated diffusion
The two processes of photosynthesis.
Light reactions/light-dependent reactions and dark reactions/light-independent reactions/Calvin Cycle
Two ATP and two pyruvates are products of this process.
Glycolysis
The type of respiration that occurs during periods of heavy exercise when little oxygen is available.
Lactic acid fermentation
Processes, sorts, and packages materials for the cell.
Golgi Apparatus/Body
Osmotic solution where the solution contains more solute than the inside of the cell
Hypertonic
The correct CHEMICAL equation for photosynthesis.
6CO2 + 6H2O + light --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
The type of anaerobic respiration that plants and yeast undergo.
Alcoholic fermentation
The correct CHEMICAL equation for cellular respiration.
C6H12O6 + 6O2 --> 6H2O + 6CO2 + ATP
3 differences between plant and animal cells
Chloroplasts, cell wall, large central vacuole, shape (irregular/squareish)
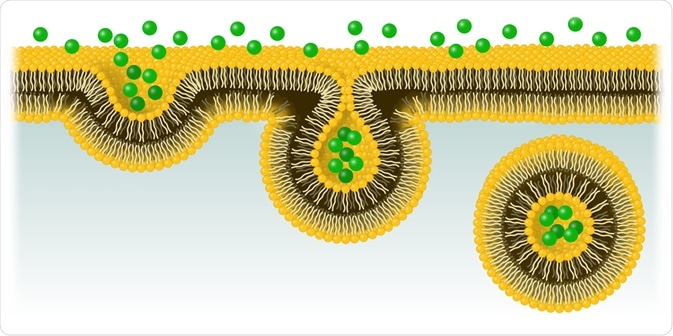
Endocytosis
The correct reactants and products for each step of photosynthesis (Reactants and Products of Light Reactions and Reactants and Product of Calvin Cycle).
Light Dependent: Reactants- water and light; Products- oxygen and ATP
Calvin Cycle: Reactants- carbon dioxide and ATP; Product- glucose
The 3 steps of respiration in the presence of oxygen.
1) Glycolysis, 2) the Krebs Cycle, and 3) the Electron Transport Chain
A correct explanation of the difference between the 3 types of passive transport.
Diffusion: molecules pass through the membrane without help
Facilitated Diffusion: molecules pass through the membrane with the help of a protein channel
Osmosis: the diffusion of water