This system provides support and rigidity to the body and stores calcium.
What is the skeletal system?
Name this bone. 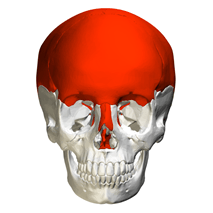
What is the cranium?
The two broad divisions of the skeletal system.
What are the axial and appendicular skeltons?
The name of the red muscles. 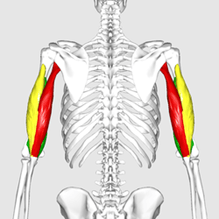
What are the triceps brachii?
The most freely movable joints in the body.
What are the ball-and-socket joints?
The flowering seed plants, which produce seeds that are covered by fruits.
What are angiosperms?
Water and dissolved minerals are transported from the roots to the leaves by this tissue.
What is xylem tissue?
The system rids the body of wastes.
What is the excretory system?
Name this bone. 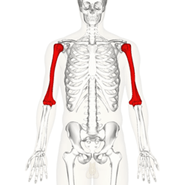
What is the humerus?
A small bone that covers the knee.
What is the patella?
The name of this muscle #51. 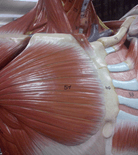
What is the pectoralis major?
Tissues are made of cells and this nonliving material.
What is matrix?
The part of a flower that produces pollen.
What is the anther or stamen?
The growth of a plant toward or away from a stimulus such as light, water, touch, gravity.
What is tropism?
This system carries materials to and from the cells.
What is the circulatory systeme?
Name this bone. 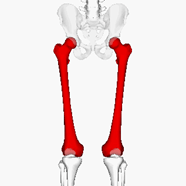
What is the femur?
A small bone that is shaped like the letter U.
What is an irregular bone?
The name of this muscle. 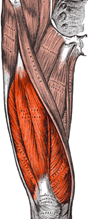
What is the quadriceps femoris?
A group of muscle cells connected to a single motor neuron.
What is a motor unit?
A leaf in which small veins extend outward from a single main vein.
What is pinnate?
The one-way diffusion of water through a semipermeable membrane.
What is osmosis?
This system coordinates the activities of the body.
What is the nervous system?
Name this bone. 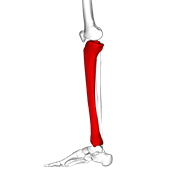
What is the tibia?
Vertebra connected to the skull.
What is the atlas?
Name of the muscle. 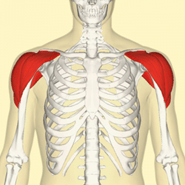
What are the deltoids?
Type of involuntary muscle that is not striate.
What is a smooth muscle?
Their characteristics are branching veins, petals in multiples of 4 or 5, and has a taproot system.
What are dicots?
An organism that obtains its nutrition from dead organisms.
What is a saprophyte?
This system protects the body from disease.
What is the immune system?
Name the bottom bone.

What is the ulna?
The long, straight shaft of a long bone.
What is diaphysis?
Name the red muscles. 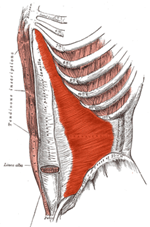
What are the rectus abadominis?
Bones are connected to other bones by these strong bands of fibrous connective tissue.
What are ligaments?
The part of a plant embryo that develops into stems and leaves.
What is the plumule?
Mosses and liverworts belong to these types of plants.
What are nonvascular plants?
This system is involved in pernicious anemia?
What is the digestive system?
Name this bone. 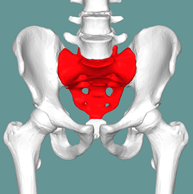
What is the sacrum?
Lightweight, porous bone that consists of an intricate network of tiny struts and girders.
What is spongy bone?
The name of this muscle. 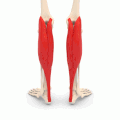
What is the gastrocnemius?
The tough, translucent sheath that surrounds a skeletal muscle and binds it together.
What is fascia?
Type of plant tissue responsible for the growth and repair of plant parts.
What is meristematic tissue?
Becuase the life cycle of a fern includes both asexual and sexual phases. they undergo this process.
What is alternation of generations?