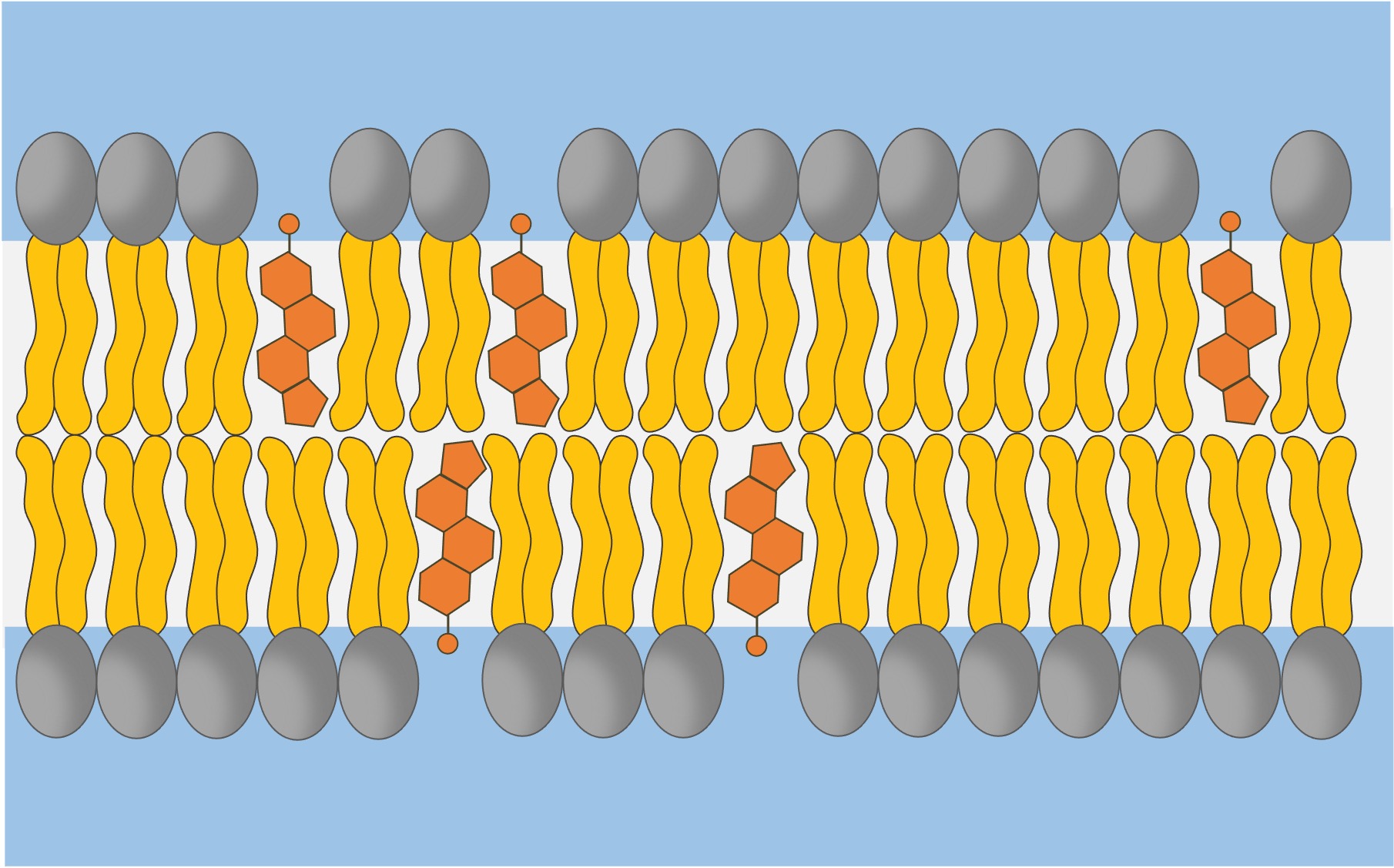
What is the name of the model that describes the structure of the cell membrane?
Fluid Mosaic Model
Define passive transport
The movement of molecules across a membrane without using energy from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration.
Define Osmosis
The diffusion of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high-water concentration to an area of low water concentration

Define Active Transport
The movement of molecules against their concentration gradient using energy.
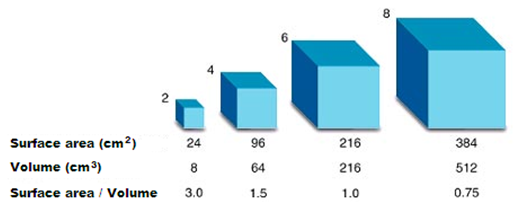
What happens to SA:V ratio as a cell increases in size?
It decreases
What type of molecule makes up the majority of the cell membrane?
Phospholipids

What type of molecules can move across the membrane via simple diffusion?
Bonus 100 points: Name an example
Small non-polar molecules
Bonus: oxygen and carbon dioxide
What happens to a cell if it is placed in a hypertonic solution?
Water leaves the cell, causing the cell to lose mass and potentially shrink.

What is the energy source for active transport?
ATP: Adenosine Triphosphate

Why is a high SA:V ratio beneficial for a cell?
It allows for efficient diffusion of nutrients and waste exchange

What is the function of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
It maintains membrane fluidity and stability
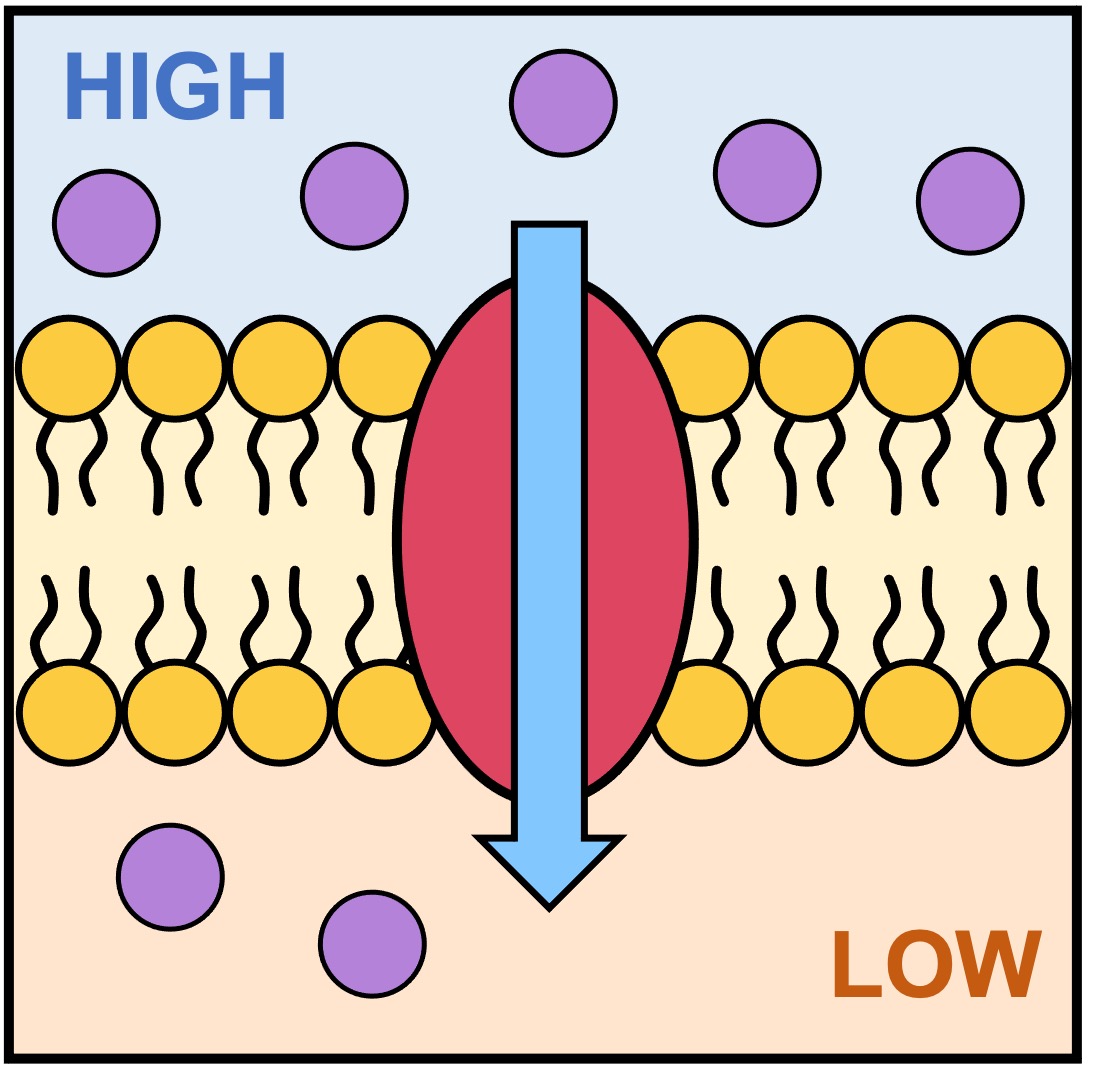
How do protein channels facilitate diffusion?
They provide a passage for larger or charged molecules to pass through the membrane.

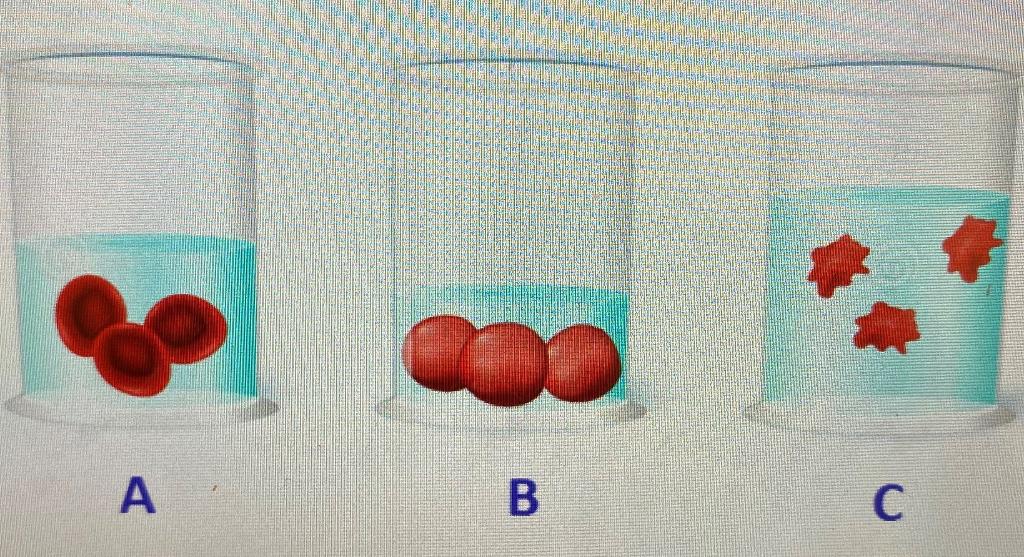
Blood cells were put in different solutions.
Identify which solutions were isotonic, hypertonic and hypotonic given that beaker A's blood cells are a normal shape.
A: Isotonic
B: Hypotonic
C: Hypertonic
Why is active transport necessary for cells? Why not have passive transport for all cells?
It allows cells to move substances against their concentration gradient, which is essential for maintaining homeostasis and proper cell function.

Why do large organisms consist of many small cells instead of a few large ones?
Smaller cells have a higher SA:V ratio, allowing for more efficient nutrient uptake and waste removal.
How do glycoproteins contribute to cell membrane function?
They play a role in cell recognition, communication and adhesion.

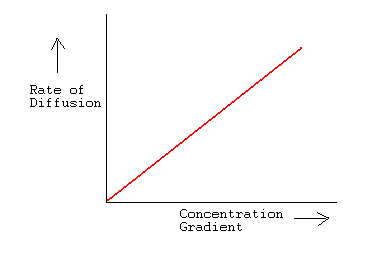
How does the steepness of the concentration gradient affect the rate of simple diffusion?
Bonus 100 points: Name one other factor that increases rate of simple diffusion
A steeper concentration gradient increases the rate of diffusion, as molecules move more rapidly from high to low concentration.
Bonus: temperature, SA:V ratio, cell size, membrane permeability, molecule size
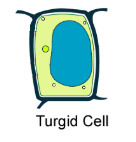
Why do plant cells not burst when placed in a hypotonic solution?
The cell wall prevents excessive expansion leading to high pressure in the cell.
Name an example of a pump involved in active transport
Sodium (Na+)/Potassium (K+) pump (ATPase)

How does shape affect the SA:V ratio?
Bonus 100 points: How else can you change SA:V ratio (excluding size)
Flattened or elongated shapes increase surface area without significantly increasing volume
Bonus: Folding of the membrane
Describe how the chemical composition of phospholipids contributes towards membrane structure.
The hydrophilic phosphate head faces outwards towards the water while the hydrophobic tails face inwards, forming a bilayer.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/lipid_bilayer-5b96eddf46e0fb0025509dde.jpg)
A scientist measures the movement of glucose into a cell and finds that it stops when a specific transport protein is blocked, even though glucose is still present in high concentration outside the cell. What type of transport is occurring, and why does it stop?

Facilitated diffusion. It requires a transport protein to allow glucose to pass through, even though no energy is used.
Using your understanding of osmosis - why might salty foods make you feel thirsty?

Salty foods increase the solute concentration in your blood, causing water to leave cells by osmosis, triggering thirst to restore balance.
Compare endocytosis and exocytosis
Similarity, Difference, Significance of the difference
Similarity: Both use vesicles, use energy for transport
Difference: Endocytosis allows substances to enter the cell, exocytosis allows substances to exit the cell
Significance: This allows for bulk movement of substances both in and out of the cell through the membrane
Desert Foxes have longer ears than arctic foxes. Explain why this trait has evolved using your knowledge of SA:V ratio.

Having longer ears results in a higher SA:V ratio which means the ears are more efficient at losing heat (beneficial in hot environment). This is the opposite for a cold environment where animals want to conserve heat.