This type of reaction uses water to break a polymer into smaller monomer subunits.
What is hydrolysis?
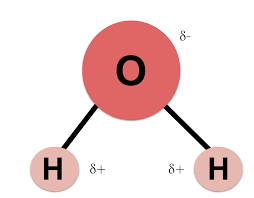
Draw a water molecule (including charges)
What is the difference between a monomer and a polymer?
A monomer is one small molecule or building block while a polymer is many/multiple molecules or building blocks forming a larger molecule.
This is the monomer of carbohydrates
What is simple sugars
or monosaccharides ?
This is the smallest unit of life
Cell
This type of reaction forms polymers from monomers and water is lost as bi-product
What is dehydration synthesis?
This is the term for the property of water being able to stick to itself:
This polymer is made from Amino Acids
What is Protein
These are considered the monomer of lipids
What is fatty acid?
Name any 3 properties of life
Cellular organization (at least one cell), reproduction/ heredity, response to stimuli, metabolism, homeostasis, growth and development, and adaptation through evolution
This reaction is shown below:

What is hydrolysis?
Capillary action or the ability of water to move up (against gravity) like in plants is possible because of these two properties of water:
Cohesion and Adhesion
This polymer forms ring-like structures from C, H, and O and is used for short term energy
What is a carbohydrate?
What are:
Phosphate group, 5-carbon sugar, nitrogenous base
These are the four most important elements for life on earth found in the highest abundance in living organisms
What are Carbon (C), Hydrogen (H), Oxygen (O), and Nitrogen (N) ?
Name the reaction shown below AND what type of polymer is being formed
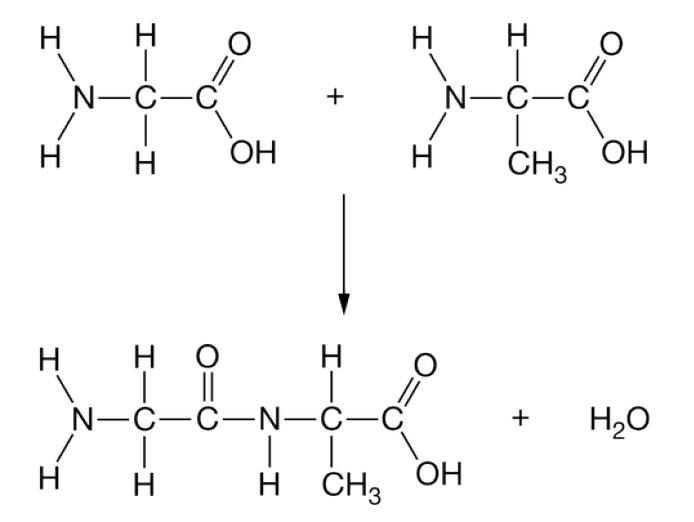
What is dehydration synthesis to form a polypeptide?
This is the chemical property that is a key factor in all of the emergent properties of water.
What is hydrogen bonding?
This is the only macromolecule that ALWAYS has phosphorus in addition to C, O, H, and N
What is Nucleic Acid
These are the two primary difference between an RNA nucleotide and a DNA nucleotide
What is a ribose sugar instead of a deoxyribose and a Uracil base instead of a Thymine base?
Give an example of a homeostatic set point in humans:
Body temperature (98.6 F or 37 C)
Blood Pressure
Heart Rate
Blood Sugar
This catalyst helps hydrolyze lactose into its monomer subunits
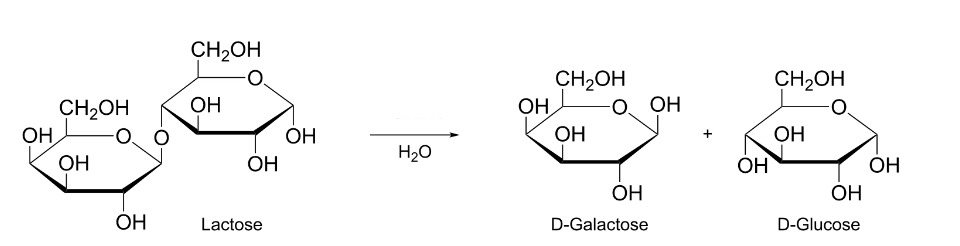
What is Lactase?
Explain WHY hydrogen bonds occur in water molecules.
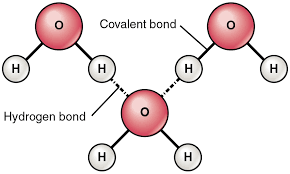
The partial - charge in the oxygen atom of one water molecule is attracted to the partial + charge of a hydrogen atom in another water molecule
This is the primary difference between a saturated and an usaturated fat which results in one being solid and one being liquid at room temp.
A saturated fat is linear with single-bonded carbons while an unsaturated fat has a double-bonded carbon which results in a kink or bend that prevents them from packing as closely together.
These are the 4 components of an amino acid (connected to the alpha or central Carbon)
What are:
Amino group, carboxyl group, R-group, hydrogen
Name 3 Properties of Life that viruses do NOT posses
Not made of one or more cells and don't have any of the following: the ability to maintain an internal environment (Homeostasis), process energy (metabolize), respond to stimuli, reproduce on their own.