What part of a flower produces pollen?
anther (stamen)
What is the primary purpose of fruit?
enclose and disperse seeds
What is the inactive xylem at the center of a woody stem called?
heartwood
What is the tiny baby plant inside the seed called?
embryo
Ginger comes from an underground structure known as a rhizome. Which of the following best describes the rhizome?
A. root
B. stem
C. fruit
B. stem
What is the primary purpose of flowers?
seed production
Which is not a simple fruit?
A. peanuts
B. pineapple
C. papaya
D. peaches
B. pineapple
_______ is to wood as ______ is to bark.
(xylem, phloem)
xylem, phloem
Which is the first step in the process of seed germination?
A. the root begins to grow
B. the seed begins to absorb water
C. the shoot begins to grow
D. the leaves begin to perform photosynthesis
B. the seed begins to absorb water
Why does high salt content in the soil kill plants?
the salt sucks the water out of the plant's roots and the plant wilts
What determines when a flower forms and opens?
light / length of day and night
What cuts a fruit from the stem?
A. dissection layer
B. hormonal layer
C. abscission layer
D. endospermal layer
C. abscission layer
What is the tough outer part of a monocot stem called?
BONUS: What is the outer part of a dicot called?
rind
BONUS: epidermis
What is the function of the endosperm?
BONUS: What structure in the seed stores the endosperm?
Provide food for the developing plant.
BONUS: cotyledons
The tiny, tube-like projections that extend from the epidermal cells of roots to absorb water from the soil are ______ ______.
root hairs
A flower without true petals is a ______ flower.
A. monoecious
B. dioecious
C. incomplete flower
D. complete flower
C. incomplete flower
What part of the flower develops into the fruit?
ovary / receptacle
How is the structure of an herbaceous monocot stem different from that of an herbaceous dicot stem? Give two differences.
dicot: vascular bundles in ring, contains pith, no rind
Reproductive cells, such as egg cells and sperm cells, that unite to form an embryo in a plant seed, are known as _______.
A. pollen
B. seeds
C. gametes
D. cotyledons
gametes
Which is not one of the factors that drives the sap stream?
A. capillarity
B. transpiration pull
C. root pressure
D. root growth
D. root growth
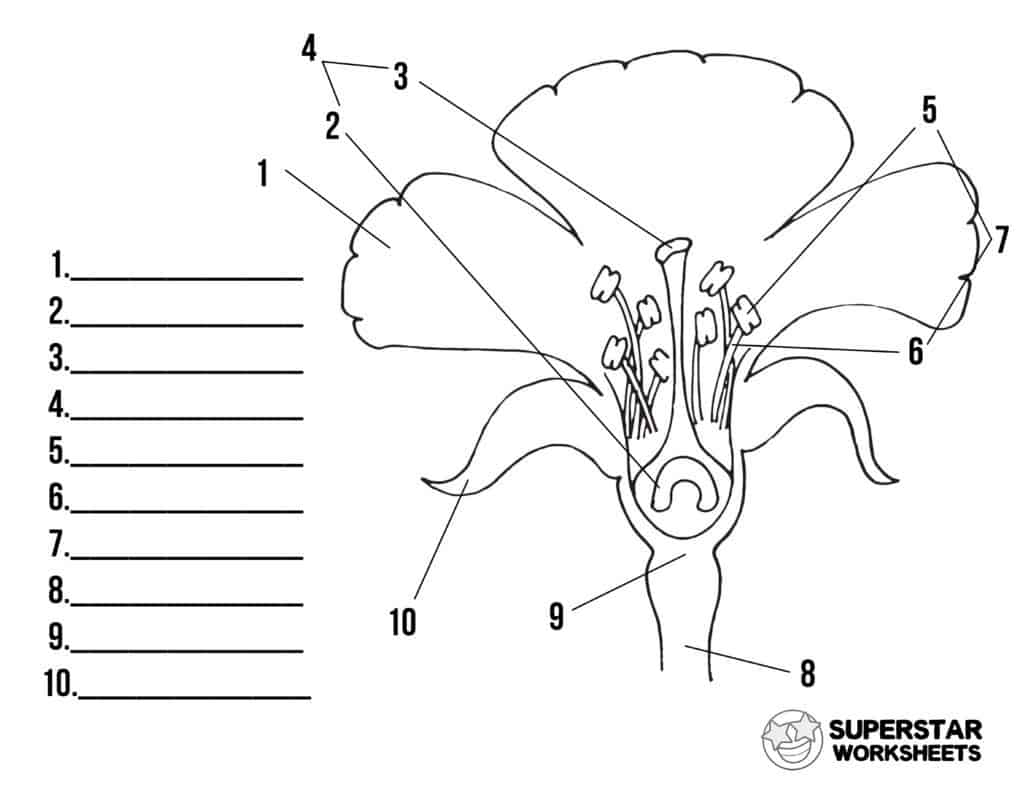
Identify structures 1-10
Which is a true nut?
A. walnut
B. peanut
C. hickory nut
D. cashew
C. hickory nut
What are the small openings in a stem's bark that allow air to enter the stem?
lenticels
Give four examples of agent dispersal.
wind, water, man, animals
_____________ roots sprout from the stem of a plant.
adventitious