This is the primary molecule that makes up the lipid bilayer
Phospholipid
This organelle is responsible for energy production
What is mitochondria
These are the reactants for photosynthesis
What are H2O, CO2, and Sunlight
This is the goal of Cellular Respiration
What is ATP (or energy) production
This is the chemical formula for Glucose
What is C6H12O6
This is the form of transport that moves molecules from an area of high concentration to low concentration WITHOUT the need of a protein channel
Diffusion
This organelle is responsible for protein synthesis
what are ribosomes
This is the goal of photosynthesis
What is the conversion solar energy into chemical energy?
This is the final stage of cellular Respiration that produces the most ATP
What is the Electron Transport Chain
This is the term for something that is dissolved into a solution
Solute molecule
Draw a phospholipid bilayer (including at least 6 phospholipids) and label your hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions
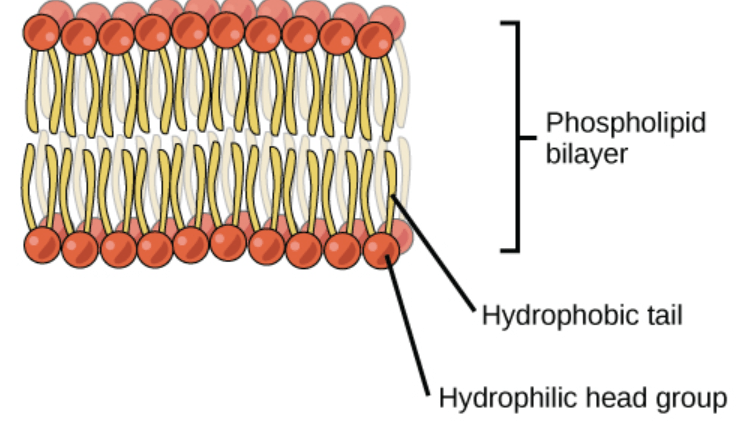
These are the 4 components that all cells have in common.
What are cell membranes, Ribosomes, cytoplasm, and DNA?
This is why plants are green
What is the reflection of green light?
Or: "Chlorophyll reflects green"
This is what happens to the mass of plants undergoing cellular respiration (faster than photosynthesis)
What is a decrease in mass
Is a virus alive? Why or why not?
No a virus is not alive because it lacks the ability to gain and process energy as well as other life functions (it does have DNA)
Would water moved towards side A or B? How do you know?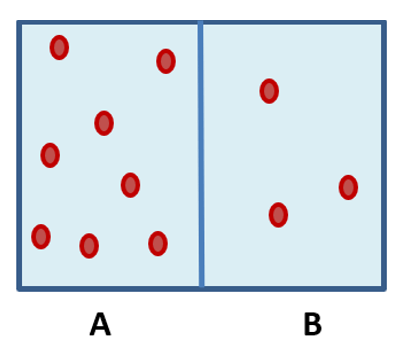
Towards side A because water moves from high water concentration to low water concentration meaning it goes towards an area with higher solutes
This cell type is likely to have a higher amount of Mitochondria - include a because statement!
What is a muscle cell because they require more energy and mitochondria are responsible for energy production.
Why are pigments like chlorophyl essential for plants?
Pigments absorb light energy which plants use for photosynthesis
These are the electron carriers used in cellular respiration:
What are NADH and FADH2
This is the location of the light dependent reactions of photosynthesis
what are thylakoids?
Explain the 3 pieces of evidence that tell you something is active transport.
Solute is moving from low concentration to high concentration, energy (ATP) is needed, and requires a protein channel
Prokaryotes are smaller/simpler, lack membrane bound organelles, don't have a nucleus (free floating DNA), are always unicellular, and include bacteria
The Oxygen that we breathe comes from this molecule
What is H2O (Water) ?
Explain how ATP is produced during the final stage of Cellular Respiration.
ATP is produced through the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis.
Electrons are passed giving the energy to move H+ ions from the matrix to the internal membrane space. Then H+ ions move from high concentration to low concentration through ATP synthase generating the energy require to transform ADP back to ATP.
Oxygen is the final electron acceptor and produces water as a bi product.
These are the 3 stages of Cellular respiration in order
(Honor's must also include the intermediate step)
Glycolysis, (Pyruvate Oxidation intermediate), Krebs Cycle, Electron Transport Chain