What is another word for enzymes?
catalyst
What is it called when an enzyme’s active site loses its specific shape, causing a loss in biological activity
denaturation
What is the purple arrow representing?
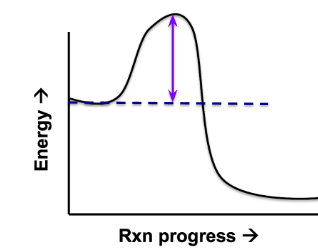
activation energy
If the food you eat is like a check, ATP is like _____
cash
What macromolecule can your body NOT get ATP from?
in other words, what macromolecule can you not break down
nucleic acids
What do enzymes do to the activation energy?
lower/decrease it
What kind of reaction is photosynthesis?
(endothermic or exothermic)
What kind of reaction is this energy diagram for?
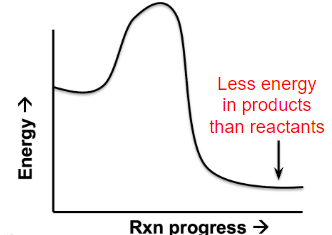
exothermic
What are the names of the three parts that make up ATP?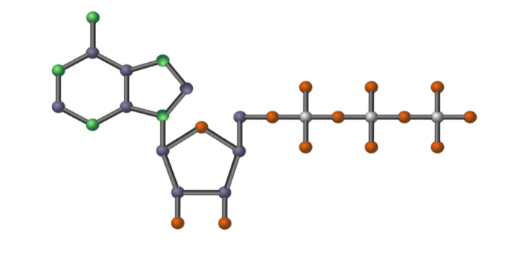
Adenine, Ribose, Phosphates (3)
All of the following parts make up an ADP molecule EXCEPT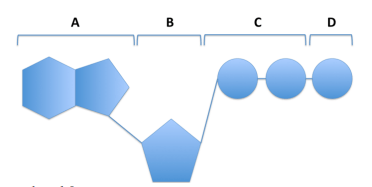
D
What macromolecule are most enzymes?
proteins
What kind of reaction is cellular respiration?
EXOthermic
What is the second arrow on the right referring too?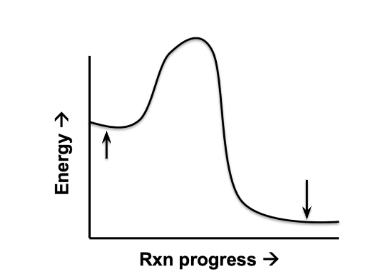
products
What is the only thing recycled during the ATP-ADP cycle?
ADP
What is the second picture trying to tell us?
or in other words..what is the enzyme doing to the substrate?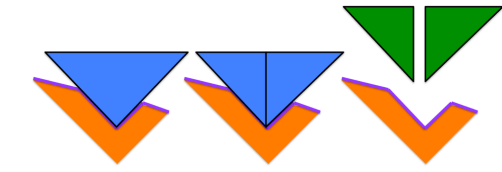
breaking bonds
creating 2 products
Q: Where do substrates (reactants) bind to enzymes?
A: On the active site
If the activation energy is lowered, then the reaction will....
(happen faster or happen slower?)
happen faster
what kind of reaction is this energy diagram for?
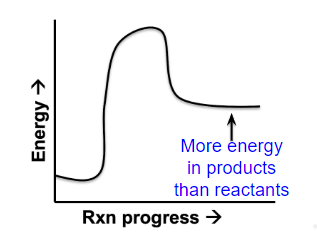
endothermic
Energy is released from an ATP molecule for cellular processes when it
loses a phosphate group
What is an example of something the energy from ATP is released for?
Cellular processes like active transport, cell division (to help grow), or muscle contraction
Have to get all 3 parts
what is the orange representing, what is the purple representing, and what is the blue representing?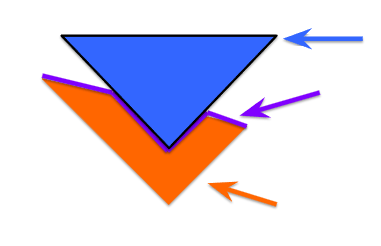
orange=enzyme
purple=active site
blue=substrate/reactant
Identify the products in this reaction:
6H2O + 6CO2 ---> C6H12O6 + 6O2
C6H12O6 + 6O2
There are 5 factors that affect the rate of a chemical reaction: temperature, pH, substrate concentration catalysts, and competitive inhibitors
Describe how 2 will specifically affect the rate of a chemical reaction
temperature: temperature increases, the rate increases (to a degree) due to molecules moving faster and colliding more.
enzymes: Enzymes work in specific pH ranges. They can lose function outside of that range and not be able to speed up the reaction.
substrate concentration: As substrate concentration increases, the rate increases, due to more particle collisions.
Catalyst/coenzyme: Catalysts (like enzymes) speed up reactions by lowering the activation energy needed.
Competitive inhibitors: Competitive inhibitors lower the rate by competing with substrate for the enzyme’s active site.
Which of the following phrases best describes the function of an ATP molecule
absorbs energy?
increases energy?
stores energy?
creates energy?
stores energy
What is the name of the process in which ATP is made?
AND
Where does that process happen in a cell?
Cellular respiration in the mitochondria