The monomers of proteins.
What are amino acids?
The biomolecule found in foods like potatoes, bread, rice, fruits and vegetbles.
What are carbohydrates?
This organ contains protease and hydrochloric acid to help digest biomolecules.
What is the stomach?
These proteins act as biological catalysts, increasing the speed of reactions.
What are enzymes?
The biomolecule that is used for long-term energy storage as well as building cell membranes.
What are lipids?
The meaning of the terms monomer and polymer.
What are "one unit" and "many units"?
The biomolecules found in foods like meat, beans, nuts and seeds.
What are proteins?
This primary function of this organ in the digestive system is to absorb water.
What is the large intestine?
The part on an enzyme where molecules can attach and be changed.
What is an active site?
Jeopardy #2
Congratulations!
You have found a Jeopardy question!
Only you get to answer this question, and you can choose how much to bet... but be careful... if you get it wrong you will lose those points!
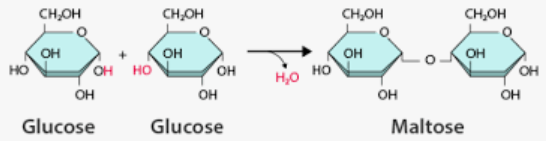
The term for two sugar molecules that bonded together.
What is a disaccharide?
The biomolecule found in foods like dairy, fish, avocaods, nuts and seeds.
What are lipids?
The upper section of the small intestine, just after the stomach, where many different enzymes act as catalysts to break down food into monomers.
What is the duodenum?
This enzyme is produced in the pancreas and helps to break down lipids into glycerol and fatty acids.
What is lipase?
The section of the large intestine that moves up along the right-hand side of the body.
What is the ascending colon?
The term for an enzyme that no longer functions due to a warped active site.
What is denatured?
The monomers of lipids.
What are glycerol and fatty acids?
This biomolecule is found in all foods and is used to create new strands of DNA.
What are nucleotides?
This gland produces amylase and lipase to be used in the duodenum.
What is the pancreas?
The name given to the molecule that binds with an enzyme.
What is a substrate?
The chemical formula of the following molecule:
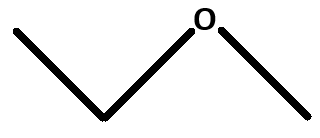
What is C3H8O?
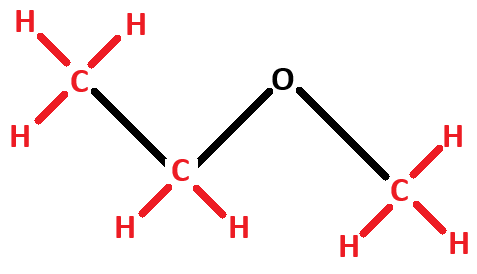
The name given to a fatty acid that does not contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms... it contains one or more double or triple bonds.
What is unsaturated?
Different forms of these polymers are used to build cells walls and exoskeletons as well as store energy for future use.
What are carbohydrates?
A lipid that is solid at room temperature and a lipid that is liquid at room temperature.
What are fats and oils?
The small, finger-like projections in the small intestine that help monomers to be absorbed into the bloodstream.
What are villi and microvilli?
Jeopardy #1
Congratulations!
You have found a Jeopardy question!
Only you get to answer this question, and you can choose how much to bet... but be careful... if you get it wrong you will lose those points!
The type of chemical reaction that occurs when two monosaccharides combine to form a disaccharide.
What is dehydration synthesis?
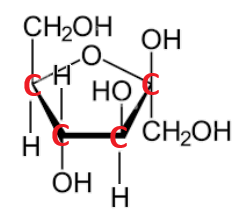
The name and formula of the following monomer.
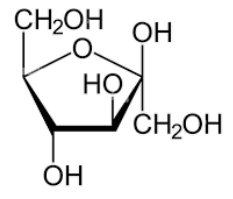
What is fructose? C6H12O6