These biological catalysts speed up all metabolic reactions
What are enzymes?
These are the inputs for cellular respiration.
oxygen and glucose
An organic molecule contains both of these elements.
Carbon and Hydrogen
The substrate in the catalase enzyme lab
What is hydrogen peroxide?
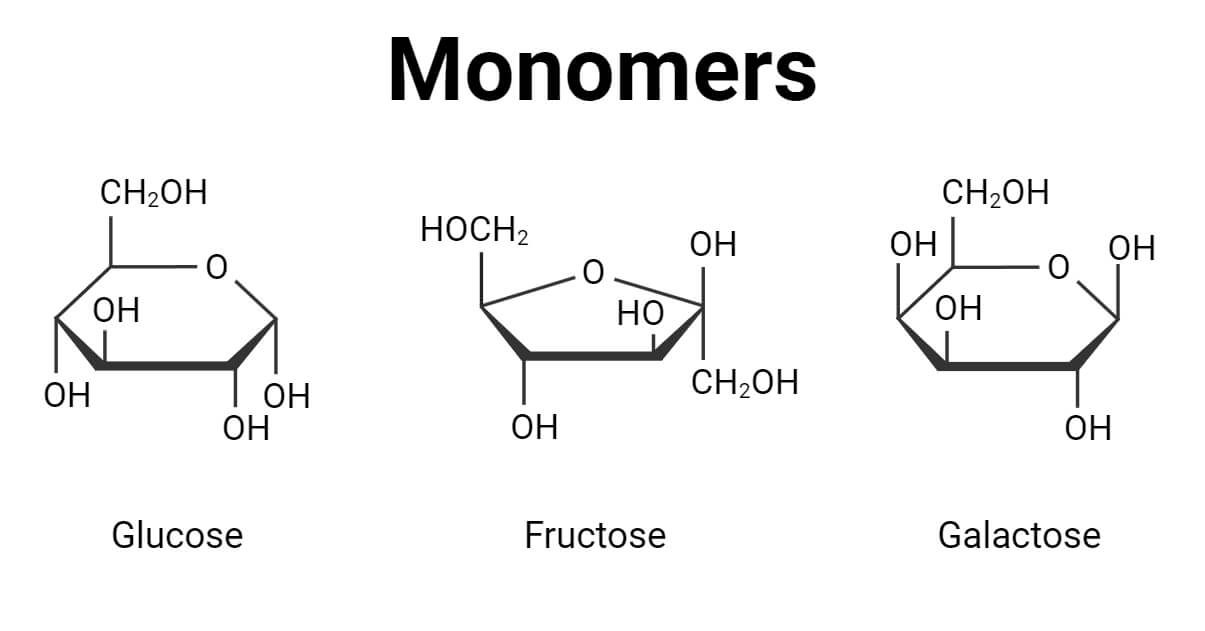
The name for the single building blocks needed to create polymers.
What are monomers?
This reaction type creates polymers from smaller subunits
What is dehydration synthesis
The products of photosynthesis
What are oxygen and glucose?
What elements are in carbohydrates?
Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen
Where the substrate binds the enzyme
Active site
The name for the carbohydrate monomer?
Simple sugar
Solar energy is transformed into the chemical energy of an organic molecule in this process
What is photosynthesis?
There are this many carbons in a molecule of glucose.
What is 6?
Protein shape determines...
Function
Monomer of nucleic acids
What are nucleotides?
Chemical energy is converted into usable energy for the cells in this process
What is cellular respiration ?
Carbon recycled from the biosphere to the atmosphere in this process?
What is cellular respiration?
Factors that affect enzyme activity
Temperature, pH and concentration
These parts make up this larger molecule
What is a starch? or polysaccharide?
The addition of _____________ causes biomolecules to break apart into smaller subunits.
What is water?
The carbon from the atmosphere enters plants here
What are Stomata?
Carbon is captured from the atmosphere is this process
What is photosynthesis?
When the enzyme changes shape and becomes in active.
Denature
Enzymes, Hormones, Antibodies and cell receptors are important molecules that are made of these subunits
What are amino acids?