What type of Growth Model is this?
Exponential Growth model
Define sustainability.
Sustainability is the ability of the biosphere to maintain its balance indefinitely, keeping lifeforms in check.
Define Eutrophication.
Eutrophication is an overload of nutrients in a body of water that causes uncontrolled algal growth.
What is primary succession and when is it required?
When plants must grow a new habitat beginning with rock. This happens after volcanic eruptions.
Name 3 or more greenhouse gases.
1) water (H2O)
2) carbon dioxide (CO2)
3) ozone (O3)
4) methane (CH4)5) nitrous oxide (N2O)
6) chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs)
What type of Growth Model is in the shape of an S and includes a carrying capacity?
Logistic Growth model
Define limiting factors.
Limiting factors hinder the growth of a population.
True or False: Chemical fertilizers and dish detergents can enter lakes and oceans causing eutrophication from excess nutrients.
True.
What is secondary succession and when is it required?
Secondary succession is starting a new habitat beginning with soil. It occurs after a landslide or abandoned field regrows new plants or trees.
Define climate change.
Climate change includes global temperature and weather pattern changes over a long period of time.
What is carrying capacity?
Maximum population size that an area can sustain.
Name two major ways populations increase.
1) Increase birth rates
2) Immigration
Why do fish die from eutrophication?
The algae uses up all the dissolved oxygen in the water and the fish cannot breathe.
What is a pioneer species?
These are the first plants and animals that tend to return after an area is disturbed. They tend to be fast-growing and hardy, but short-lived.
Define ecological footprint.
An ecological footprint model compares an area's used natural resources (cropland, fisheries, forest, and pasture) to the amount of natural resources it generates.
What type of growth model only occurs under ideal environmental conditions?
Exponential growth model
1) More deaths than births.
2) Increase emigration.
Define biodiversity.
Biodiversity refers to the number of different species (richness) in an area and the proportionality of all population species (evenness).
What is a climax species?
These species are stable, long-lived plants and animals that mark the end of succession.
Define bioremediation.
This is a technique that uses organisms to remove or neutralize hazardous materials. An example is the oil eating bacteria found in the Mariana Trench that helped with an oil spill clean up in the Gulf of Mexico.
Which population concept does this map represent?
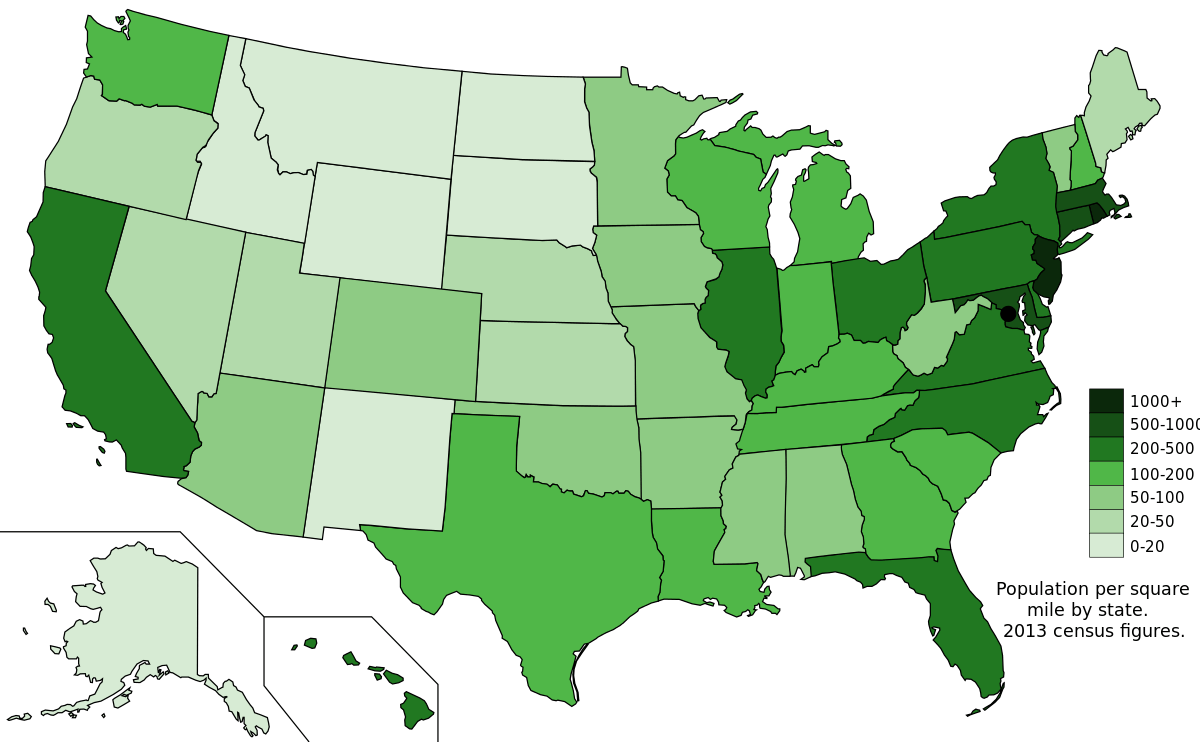
Population Density - the number of individuals in a given space
Give 3 examples of limiting factors.
1) Predation
2) Disease
3) Lack of food
Name 3 reasons humans cause a decrease in biodiversity.
1) Habitat loss
2) Over using resources (water, minerals, wood...)
3) Invasive species being introduced
4) Overuse of chemical fertilizers in farming
Can pioneer species and climax species live in the same habitat? If so, why?
Yes, because succession is a gradual process where various species fade in and out as the dominant species. Just because the dominant species is a climax species doesn't mean the pioneer species are entirely gone.
Why are invasive species problematic?
These organisms rapidly reproduce and overtake native species, lowering biodiversity.