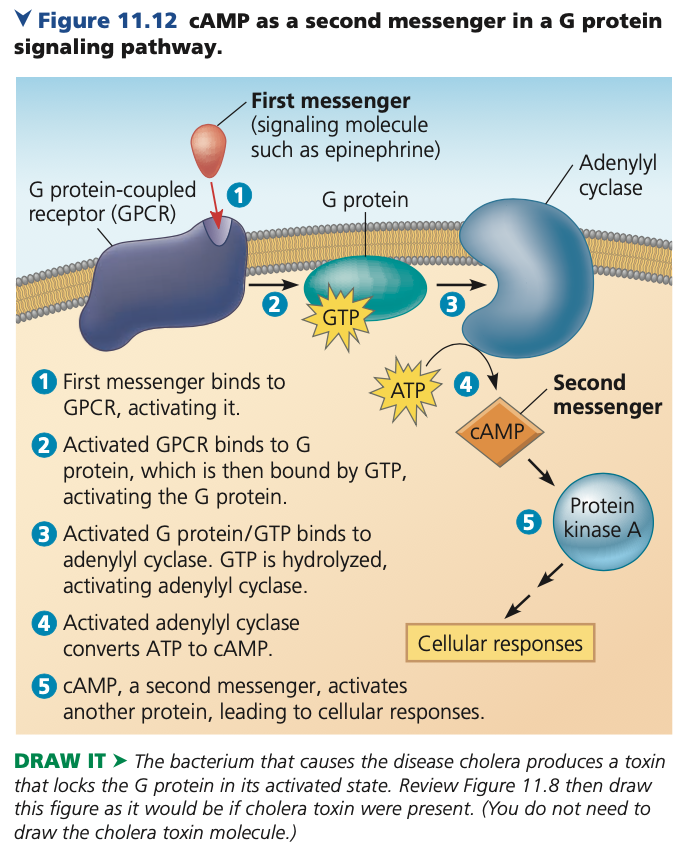
What is the role of cAMP in signal transduction?
cAMP is a second messenger or cellular activator.
How are DNA and RNA polymerases different?
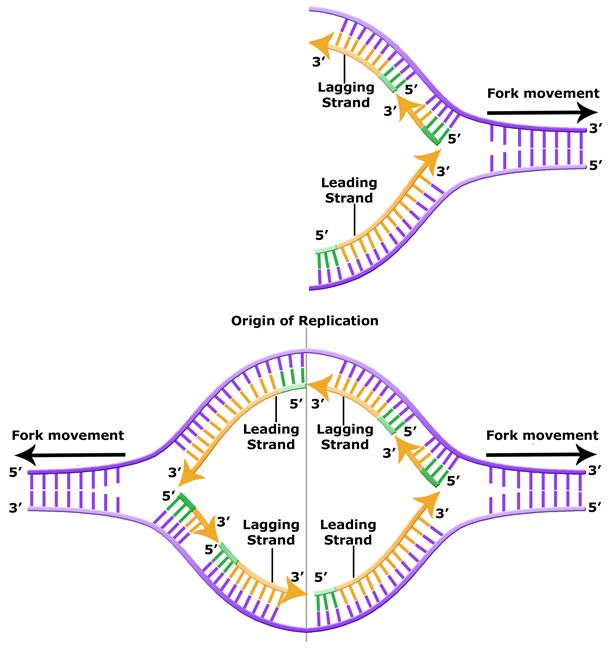
How do new and old strands of DNA interact during DNA replication?
DNA replication is Semi-Conservative
![]()
What happens if a cell fails to pass cell cycle checkpoints?
The cell attempts to either complete DNA replication or repair the damaged DNA. If the damage is too great, apoptosis (automated cell death) occurs.
If one of your parents has blood type AB and your other parent has blood type B, what are your possible blood types (include genotypes)?
A -> I^A i
B -> I^B I^B or I^B i
AB -> I^A I^B
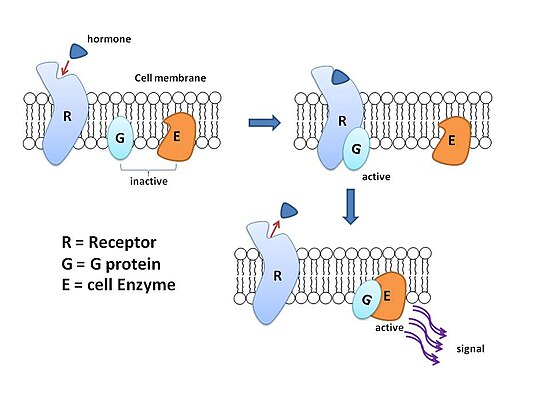
Explain how epinephrine release leads to increased blood glucose by way of a signaling cascade
What is an intron? An exon?
Introns: non-coding gene material that "stays IN" the nucleus because they do not code for functional proteins
Exons: coding sections of RNA (or DNA that codes for the RNA) that "EX-it" the nucleas to be coded into proteins
In which direction does DNA polymerase function? How does this relate to leading and lagging strand synthesis?
DNA Pol III adds nucleotides to the 3' end, moving 5'-3' on the new strand and 3' -5' on the template strand.
What is the G0 phase? What are cells doing when they are in this phase?
The resting or working phase. The cell is neither dividing or prepareing to divide, but doing whatever other jobs the cell has. Cells like nuerons spend most of their lives in this stage.
What happens when zygote implantation fails, or occurs outside of the uterus? Are these events common?
Misscairage or Ectopic Pregnancy (1/3-1/2 of fertilizations)
Why might two cells respond differently to the same chemical signals?
The same ligand may bind to different receptors on different cells, triggering different pathways and therefore different responses. For Example, epinephrine triggers increased blood glucose in some cells and relaxation in smooth muscle cells along airways.
What is a promoter and how does it interact with RNA polymerase?
A DNA sequence that lets RNA (or helper proteins) attach to the DNA and begin transcribing
What are telomeres and how are they related to aging and cancer? What is the function of telomerase?
-Telomeres are a repetitive string of non protein coding nucleotides at the end of chromosomes
-They are cut a shortened each time the DNA is replicated
-Telomerase lengthens and repairs telomeres
-Many organisms (including humans) produces less telomerase overtime
-As telomeres get shorter, the coding DNA is damaged and the organism ages. If enough damage is done in the right places, the organism can get cancer
Explain how a predisposition to cancer can be hereditary
In a variety of ways!
One of which is mutated tumor supressor genes
Another is a dysfunctional copy of a redundant gene, leaving only one copy of it still functional and therefore more vulnerable to mutation
You mate a rooster with gray feathers with a hen of the same phenotype. Among their offspring, 15 chicks are gray, 6 are black, and 8 are white. What is the most likely explanation regarding heritance of these colors in your chickens? What offspring would you predict from mating a black hen and a gray rooster?
Incomplete dominance
Punnett Square Time!
Explain how a how signal, receptors, G proteins, and effector proteins are related.
What do we mean by saying the genetic code is redundant or degenerate? How does that offer an evolutionary advantage?
A single amino acid may be coded for by more than one codon. This allows some mutations to have little to no effect, making replication mistakes that much less likely to kill (and prevent reproduction by) the organism.
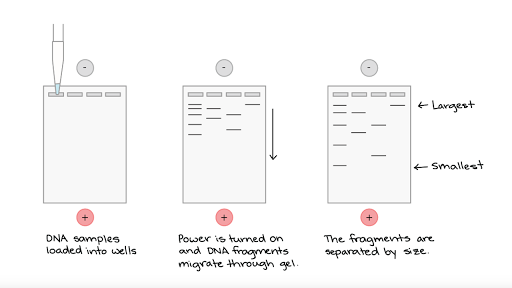
How is gel electrophoresis used to separate molecules?
DNA is negatively charged and therefore runs towards the strong positive charge at one end of the gel. Smaller peices of DNA move faster (and farther) than larger ones, allowing us to identify unique patterns.
Give an example of a phenotype affected by X-inactivation. Does X-inactivation occur in XY individuals?
Calico cats!
it does not because you can't healthily inactivate a X when you only have 1 copy
What is the difference between accuracy and precision?
Accuracy is how "true" your measurements are, Precision is how consistent your measurements are. Remember the bullseye diagrams!
How does phosphorylation affect molecules in a signal transduction pathway?

Given the following mRNA sequence, determine the template DNA and coding DNA
CCG AUG UGC UUA GAC UAA
template: GGC TAC ACG AAT CTG ATT
coding: CCG ATG TGC TTA GAC TAA
Do it on the board!
Draw and explain/describe the steps of DNA replication starting with points of origin and the replication fork.
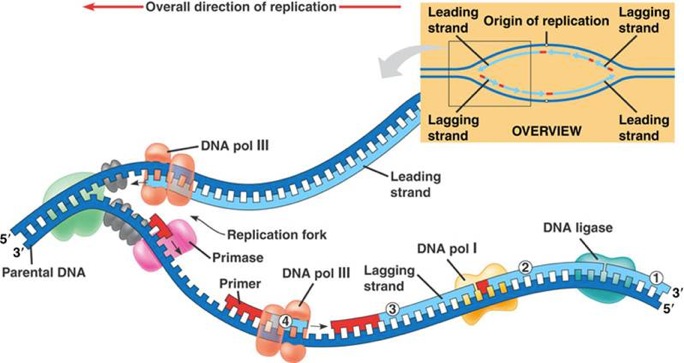
Describe the 4 ways that genetic variation occurs. Which 2 occur during meiosis, and in which stages do they occur?
mutation
random assortment (meiosis metaphase 1)
random fertilization
crossing over (meiosis prophase 1)
List all of the possible different alleles that could result in games if an individual with the genotype: AaBbCc.
AaBbCc
ABC aBC
AbC abC
ABc aBc
Abc abc