of a Fact
of a Fact
the Know
Trouble!
Again!!
a Treat
Twisted Cyst-a
Name this pathology.
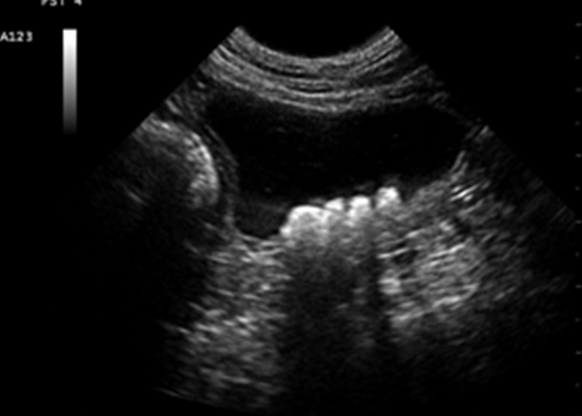
What are Bladder Stones?
this term is used to evaluate renal transplant rejection and medical renal disease
What is Resistive Index (RI)?
Most common cause of Acute Renal Failure (ARF)?
What is Acute Tubular Necrosis?
Results from bacterial invasion of the renal parenchyma.
What is acute pyelonephritis?
Name the two main benign tumors of the urinary system.
What is angiomyolipoma (AML) & oncocytoma?
Most common of all renal tumors.
What is Renal Cell Carcinoma (RRC)?
causes of nephronlithiasis
What is infection, elevated serum calcium levels, family hx, gout?
this term describes dilatation of the renal collecting system
What is hydronephrosis?
Name 3 categories of renal cystic disease.
What is acquired, congenital, or hereditary?
Name this pathology.
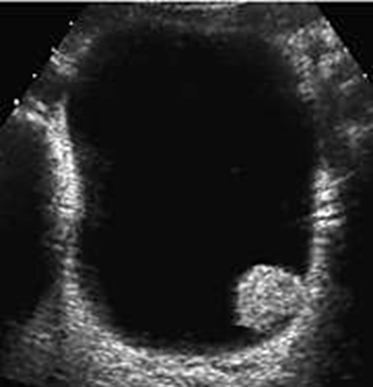
What is Bladder Papilloma?
Name the method of Renal Artery/Aorta Ratio (RAR)
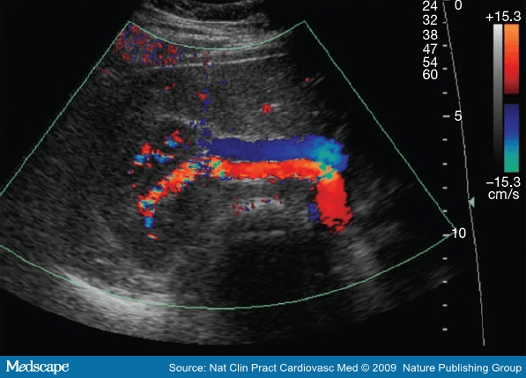
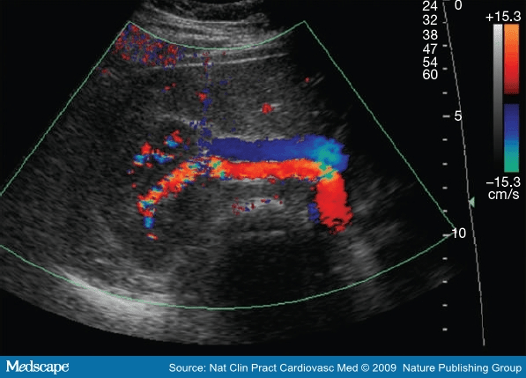
What is direct?
Three main stages of Acute Renal Failure.
What are Pre-renal, Renal(intrinsic) and Post-renal?
Name this pathology for a patient that presents with fever & leukocystosis:
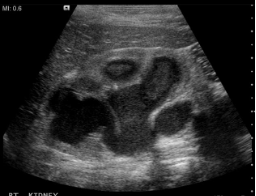
What is pyonephrosis?
Benign tumors that are found in the renal cortex.
What is angiomyolipomas (AML)?
The age group and gender affected most by Renal Cell Carcinoma.
What is 50 to 70-year-old males?
Term for a large stone that fills the pelvis and calyces
What is Staghorn calculi?
the congenital obstructive disease that is only seen in males
What is posterior urethral valves?
This age group is commonly affected by simple renal cysts.
What is half adults over 50?
Name this condition.
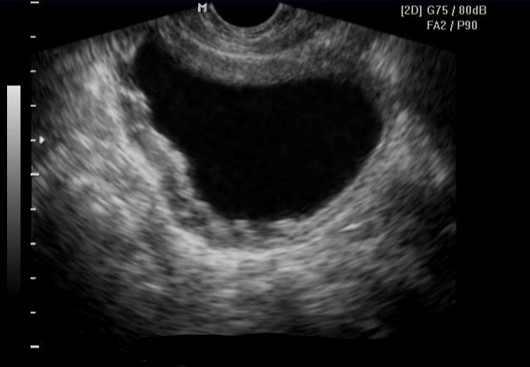
What is Cystitis?
Name the causes of renal artery stenosis
What is atherosclerosis and fibromuscular dysplasia?
Two types of Acute Tubular Necrosis.
What is Toxic and Ischemic?
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!Daily Double!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
Most commonly affects diabetics & can be caused from E. coli.
What is emphysematous pyelonephritis?
Name the malignant disease that Oncocytoma's sonographic appearance can mimic.
What is renal cell carcinoma?
This malignant tumor affects bladder and/or renal collecting system, often has multiple lesions and is commonly spread from the bladder.
What is Transitional Cell Carcinoma?
Name the X-ray exam performed to check function of kidneys and look for stones.
What is IVP (intravenous pyelogram)?
this obstructive disease grade is called the "bear-claw effect"
What is Grade II?
Nonhereditary renal dysplasia that usually occurs unilaterally & can be seen in utero.
What is multicystic dysplastic kidney?
Final Jeopardy!
A rare congenital renal cystic disease that is a nonhereditary cystic dilatation of the collecting tubules, is bilateral in 70% of cases and is associated with nephrocalcinosis and Caroli's disease of the liver.
What is Medullary Sponge Kidney?
Name this pathology.
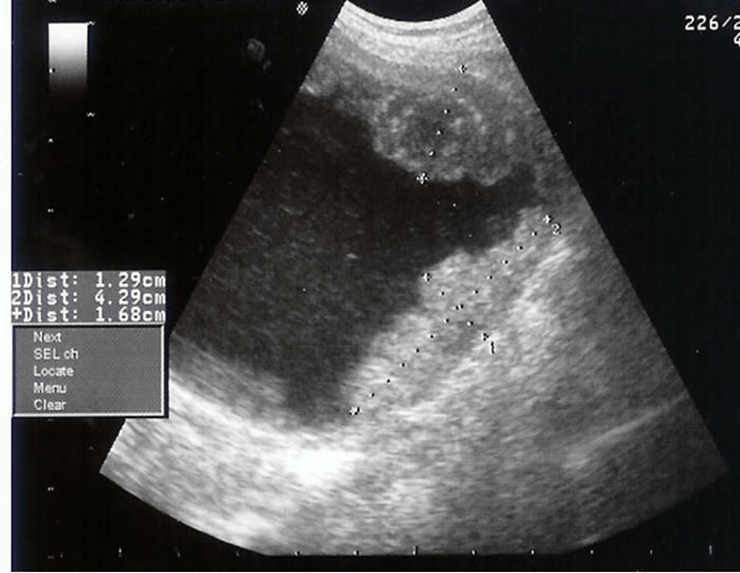
What is Transitional Cell Carcinoma (TCC)?
The gold standard test for renal artery stenosis
What is Renal Arteriography ("dye test")?
What three types of Chronic Renal failure?
Nephron, Vascular and Interstitial.
A deadly condition that requires immediate drainage.
What is pyonephrosis?
This age range & gender are associated with oncocytoma.
What is 60-70 yr old men?
Most common solid renal mass of childhood, common in ages 2-4yrs.
What is Nephroblastoma (Wilm's tumor)?
sonographic appearance of kidney stones
What is highly echogenic and shadowing?
Name the pathology
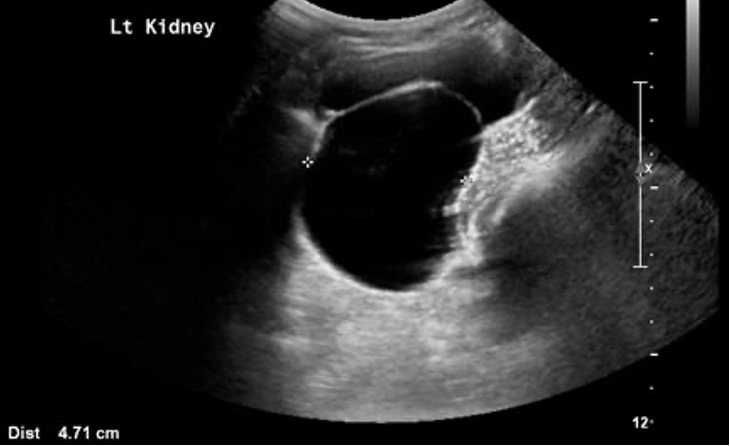
What is Ureteropelvic Junction Obstruction (UPJ)?
Name 3 clinical symptoms of autosomal-dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD).
What is HTN, headache, flank pain, hematuria, UTI, kidney stones, cyst rupture or renal obsturction?
Name the two pathologies in this image. 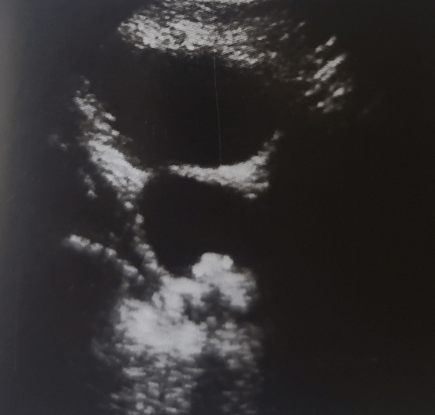
What is a bladder stone within a diverticula?
Determine whether this flow pattern is normal or abnormal
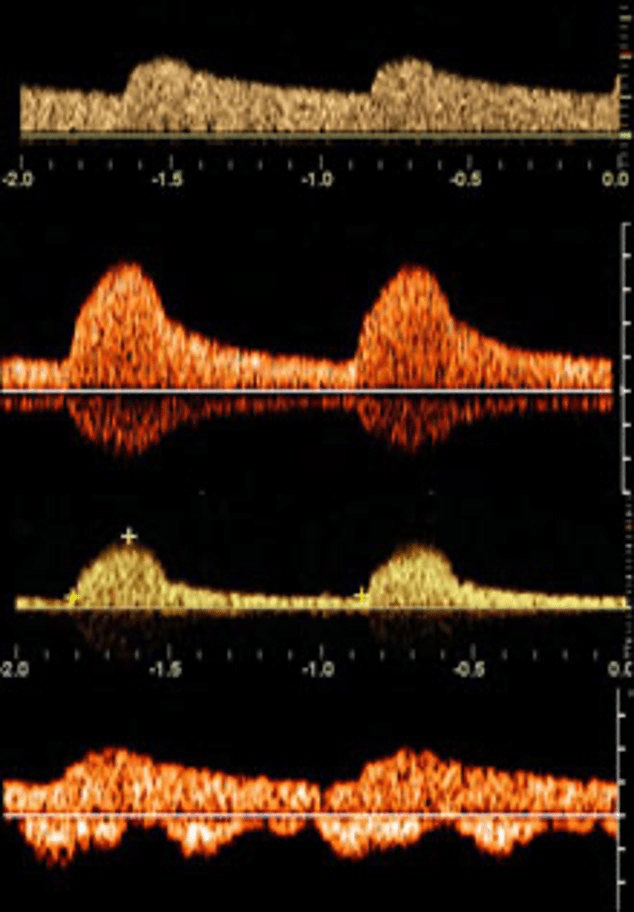
What is Abnormal?
Loss of renal function due to disease, most commonly parenchymal disease.
What is Chronic Renal Failure?
Rounded echogenic material that does not shadow and is seen in the dilated renal pelvis.
What is Mycetoma or Fungal disease (fungal balls)?
Anigomylipomas are made up of these 3 structures.
What are blood vessels, smooth muscle, and fat cells?
The syndrome associated Nephroblastoma (Wilm's tumor).
What is Beckwith-Widemann syndrome?
Term that describes small calculi or calcium salts deposit in the renal parenchyma
What is Nephrocalcinosis?
Sonographic appearance for Posterior Urethral Valves
What is massively distended bladder, tortuous dilates ureters, and dilated pelvicalyceal region?
Name this pathology that presents as a spherical structure that does not communicate with the renal collecting system.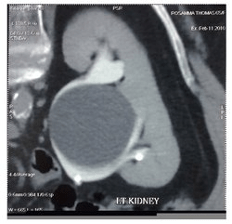
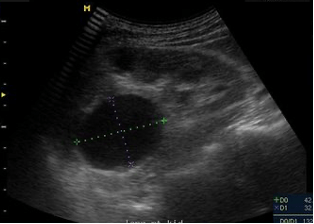
What is a parapelvic cyst?
Name the bladder condition and two types. 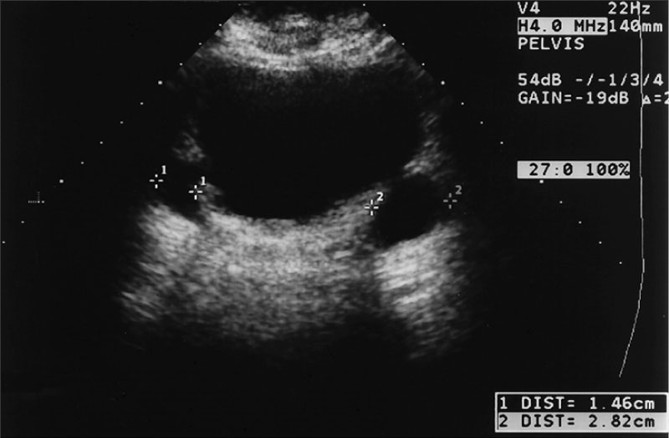
What is Diverticula, acquired or congenital?
Name clinical symptoms of renal vein thrombosis (RVT)
What is flank pain, proteinuria, and hematuria?
This term is used to describe a decrease in normal function of the kidneys due to varying disease processes.
What is Medical Renal Disease?
An autosomal-dominant genetic disorder that causes hemangiomas, cysts, and other tumors in areas all over the body.
What is Von Hippel-Lindau Disease?
A cystic disease that is associated with Angiomyolipomas (AML).
What is Tuberous Sclerosis?
The staging of Renal Cell Carcinoma and structures involved (name at least 2).
What is stage I.-confined to renal capsule, stage II.-invasion of the perinephric fat, stage III.-involves regional lymph nodes, renal vein, and/or IVC, stage IV.-adjacent organs or distant metastases (lung, liver, bone, adrenal glands)
Determine the two different forms of nephrocalcinosis.
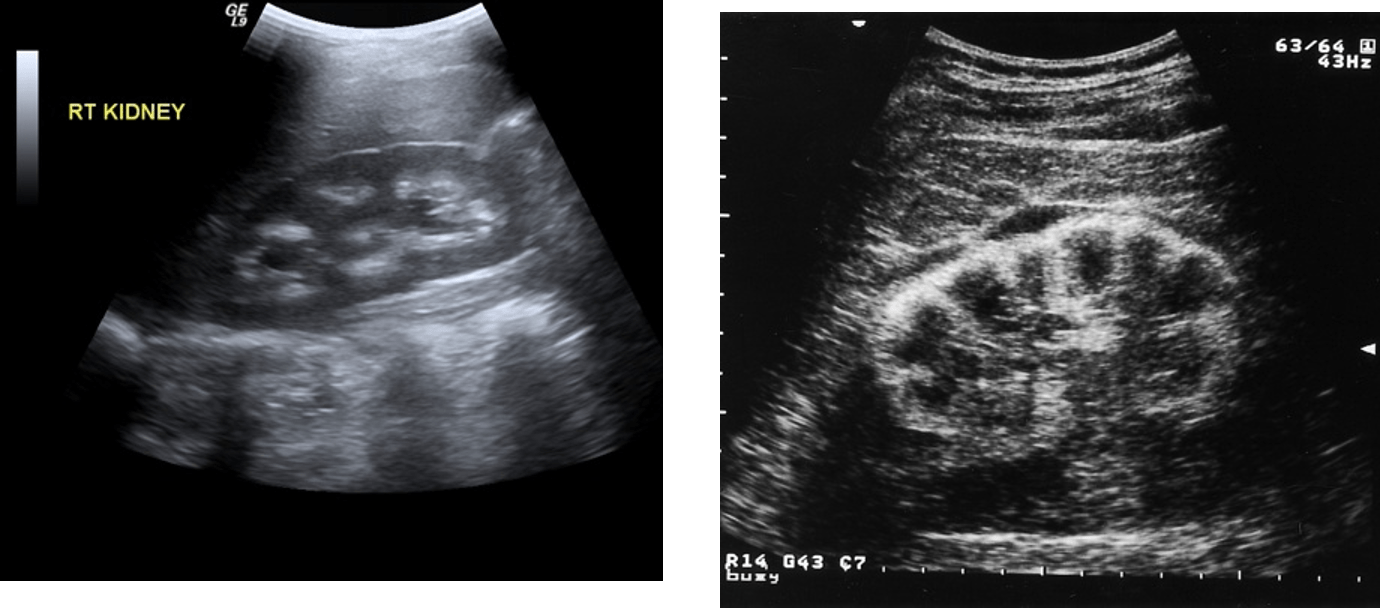
What is medullary nephrocalcinosis (left) and cortical nephrocalcinosis (right)?
Causes of hydronephrosis
What is pregnancy, urethral stricture, calculi, masses, bladder outlet obstruction, surgery, ureterocele, UPJ obstruction?
An autosomal-dominant genetic disorder associated with epilepsy, facial lesions, benign tumors in varies parts of the body, and angiomyolipoma's of the kidneys.
What is tuberous sclerosis?