What structure is 1.5 cm lateral and1.5 superior to the lateral canthus and is a consistent landmark to identifying the nerve proximity?
Sentinel vein
Describe which muscle causes each line

Transverse head of corrugator- vertical glabellar lines
Procerus- transverse dorsal lines
Oblique head of corrugator (depressor supercilii, medial fibers of orbicular oculi) - oblique glabellar lines
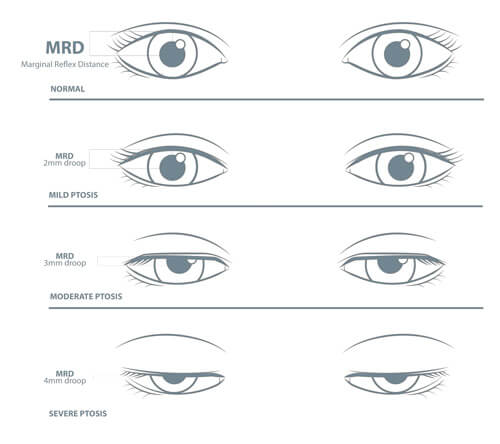
What is the marginal reflex distance 1 (MRD1) used for? Name the grading and corresponding distances for +100 points
Assess eyelid ptosis. Measurement of the distance from the margin of the upper eyelid to the light reflex on pt's cornea
*Mild 1-2mm
*Moderate 2-3mm
*Severe >4mm
What compartment must you not overreact to maintain an aesthetic balance of the upper eyelid in an upper aleph?
Central compartment
Postmenopausal women on HRT have a 70% higher risk for this type of complication after blepharoplasty
Dry eye
How many orbital fat compartments are in the upper and lower eyelids? Name them all for +100.
Two for the upper eyelid and three for the lower eyelid.
Upper: central & medial/nasal.
Lower: lateral, central, and medial/nasal
What causes festoons?
attenuation and laxity of the orbicularis oculi muscle retaining ligaments
What is the eyelid squint test and what does it assess?
Patient will squint eyes to assess for improvement in fullness
If there is a decrease in fullness, this suggests the fat herniation is behind the orbicularis oculi muscle (OOM) and the fullness be due to fat pad pseudoherniation. Surgical excision may improve appearance if so
What lower bleep approach decreases the risk of lid malposition?
Transconjunctival approach
What is most commonly injured in a lower blepharoplasty?
Inferior oblique muscle
What is arcus marginalis?
This is a confluence of the orbital septum with the periosteum at the orbital rim
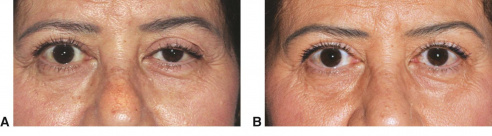
Inn the before pictures, what do you see and what is your assessment?
Frontal hyperactivity compensating for brow ptosis
Where is the zone of adhesion?
6 mm wide zone medial to the superior temporal fusion line of the skull
Extends to include the orbital ligament
Incomplete release tethers the transposition of the forehead flap and prevents repositioning
What nerve is particularly predisposed to injury in a brow lift?
Supraorbital nerve (deep division)
What is the name for the deep continuation of the levator muscle?
Mueller's muscle or superior tarsal muscle
At the fornix, the levator muscle splits into a deep and a superficial layer
What might a high supratarsal fold indicate?
Levator dehiscence
What is the frontalis relaxation test?
Gently support of the upper lid margin to assess whether frontalis recruitment is compensating for lid or brow descent
In an endoscopic brow lift, through what anatomical plane is dissection commonly performed to mobilize forehead soft tissue?
Subpeeriosteal
Lockwood's ligament in the upper eyelid corresponds to this ligament in the lower eyelid
Whitnall's ligament
The deep branch of the supraorbital nerve passes through which layers
Galea and periosteum
Describe the ideal eyebrow positioning
Medial border in line with medial canthus and ala
Peak at a vector connecting the alar base and lateral limbus. Females have a peak 5-10 mm superior to the lid margin, males have a gentle curve
Lateral border at a vector connecting the lateral canthus and the alar base
When the brow is held in its natural anatomic position and the upper lid still appears heavy, this condition is confirmed.
Dermatochalasis
Describe the Loeb procedure and what is addresses
Fat transfer from the medial orbital compartment to the tear trough to address tear trough deformities
When the brow is held in its natural anatomic position and the upper lid still appears heavy, this condition is confirmed.
Galea