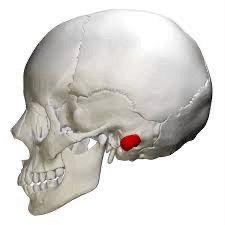
Name 2 muscles that attach here
Mastoid process:
1. SCM
2. posterior belly of digastric
3. splenius capitus (block 1 throwback)
Which nerve provides motor innervation to the buccinator muscle?
Bonus: what's the action of the buccinator?
buccal branches of CNVII (facial nerve)
Bonus: buccinator acts to compress the cheeks (ex = playing trumpet)
A patient can't wink/forcefully close their eye - which nerve is affected?
Bonus: If it were ptosis/drooping eyelid, which nerve would be affected?
CNVII (facial nerve) = orbicularis occuli
Bonus: CNIII (oculomotor) = levator palpebrae superioris
A baseball player is hit on the side of the head (near their temple) with a fastball. They lose consciousness, wake up briefly, then become comatose on the way to the ER. CT scan shows a lemon/lens shaped accumulation of blood on the right side compressing the cerebrum. What blood vessel is the bleed coming from?
Bonus: what area on the skull did the ball likely hit/fracture?
Middle meningeal artery - this is a classic epidural hemorrhage
Bonus: the skull likely fractured at the pterion - weak point where the parietal, frontal, temporal, and sphenoid bones meet - middle meningeal artery runs right under it
What bones/articulation points take part in the TMJ?
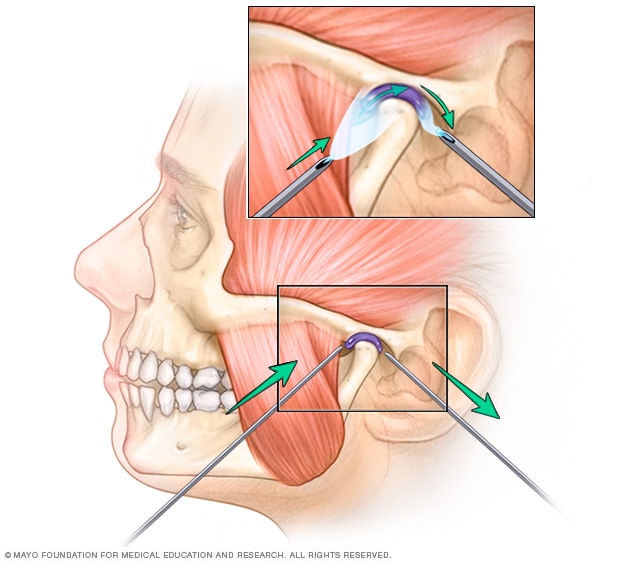
the condylar process of the mandible and the mandibular process of the temporal bone
What nerve innervates stapedius?
Bonus: what symptom would you see with a lesion/palsy here?
CN VII = facial nerve - nerve to stapedius
Bonus: stapedius activation/contraction decreases sound transmission in the middle ear (think protective) - so if it's not working, patient will be hypersensitive to sound/sounds are overly loud for them
remember also that tensor tympani has a similar action - but it's innervated by CNV3
What does mydriasis mean? What branch of the autonomic nervous system causes mydriasis?
Mydriasis = dilated pupils - this is mediated by the sympathetic nervous system (don't care about reading fine print when you're running from a bear)
Miosis = constricted pupils - this is mediated by the parasympathetic
Where does CNVIII (vestibulocochlear) exit the skull?
Bonus: what else travels with it?
Internal acoustic meatus
Bonus: CNVII (facial nerve) travels with it
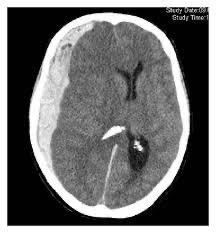
What kind of bleed is this?
Bonus: What vessels cause it?
This is an acute subdural hematoma - banana shaped/crosses suture lines - white on CT (will darken with time)
Bonus: Caused by ruptured bridging veins
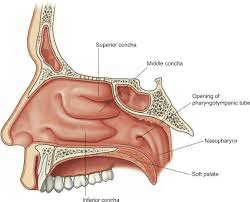
The middle nasal concha is part of what bone?
ethmoid
What innervates the infrahyoid muscles?
Bonus: What other nerve runs alongside it?
Ansa cervicalis = nerve loop of anterior rami from C1-C3
Bonus: CNXII (hypoglossal) runs alongside the superior aspect
A patient presents with inability to elevate and abduct the eye after a head injury - pupil is dilated - mild ptosis is observed. What cranial nerve is affected?

CNIII (oculomotor) - this is a "down and out" sign - often caused by uncalled herniation which puts pressure on/compresses CNIII
With superior oblique (CNIV/trochlear) and lateral rectus (CNVI/abducens) left unopposed, eye pulls down and out
Where does CNIX (glossopharyngeal) exit the skull?
Bonus: what travels with it?
Jugular foramen
Bonus: CNIX, CNX, CNXI, and jugular vein all exit together
Infection in the sinuses or nasal cavity can spread up to the meninges via the olfactory nerve fibers + bulb
Where does it enter the cranial cavity?
Cribiform plate
remember this is the ethmoid bone
What attaches to the crista galli?
The falx cerebri - separates the cerebral hemispheres
What nerve provides taste to the anterior 2/3 of the tongue?
Bonus: what else does this nerve do?
chordae tympani from CN VII = taste
general sensation of tongue = lingual nerve from CN V3 - chordae tympani runs with it
Bonus: chorda tympani also innervates secretory function of sublingual and submandibular glands
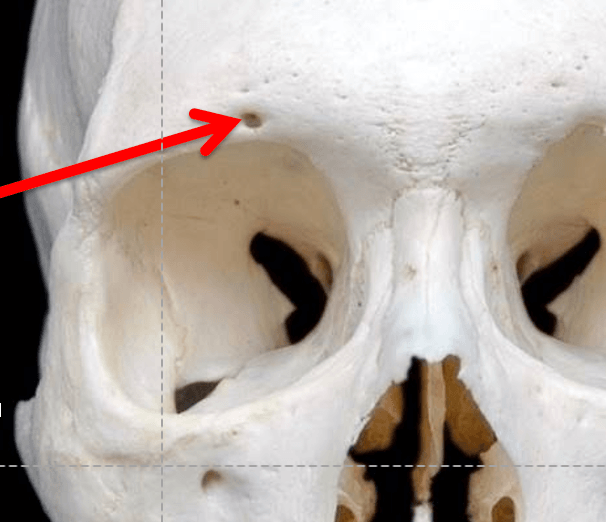
What passes through that opening?
supraorbital nerve (branch of CN V1) and supraorbital artery
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_sm.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/foramen-rotundum/yvTmzU0WG5KrgyMa90o0Vg_Foramen_rotundum.jpg)
What runs through this foramen? (in green)
A newborn presents with their head tilted to one side, what is the name for this condition and what nerve is impacted?
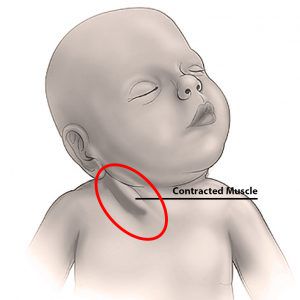
Torticollis ("wry neck") - CNXI (spinal accessory nerve) is compressed, causing the SCM to be shortened/hyper-contracted on the affected side
In what bone does the pituitary gland live? What the area called?
Sella turcica = nook of sphenoid bone where pituitary sits
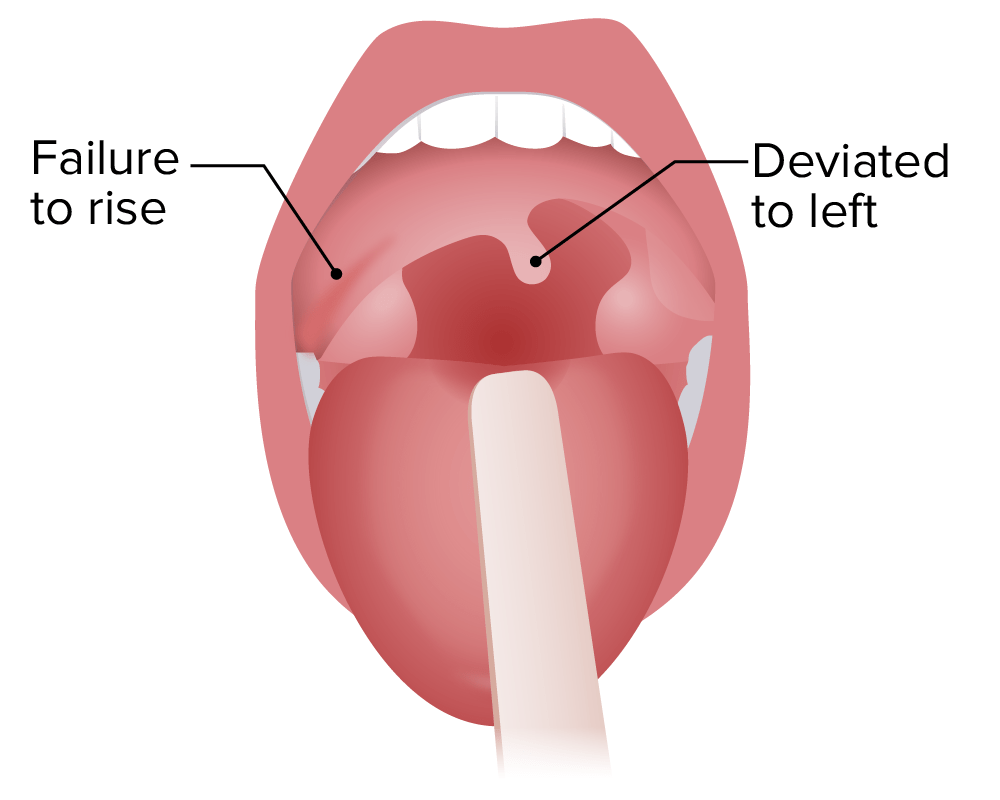
Uvula is deviated to the left - what cranial nerve is affected, and on which side?
How would you test the integrity of the CNIV/trochlear nerve (what direction do you want the patient to look)?
Ask the patient to look in (toward the nose) and down - testing superior oblique
What foramen does the middle meningeal artery run through?
Foramen spinosum
Shortly after a thyroidectomy (which required ligation of the inferior thyroid artery), a patient presents with hoarse voice and isn't breathing well. What nerve was injured?
recurrent laryngeal nerve (branch of CNX/vagus) - handles all intrinsic muscles of the larynx except for cricothyroid
cricothyroid is innervated by superior laryngeal nerve