What is the most common form of oral cancer?
What is Squamous Cell Carcinoma?
What muscle does CN VI innervate?
What is the Lateral rectus?
Which antidepressant medication can lower the seizure threshold?
What is Bupropion?
What protein makes up Lewy bodies?
Bonus (200): What is a key clinical feature of Lewy Body Dementia?
What is Alpha-synuclein?
Bonus: halluciations w/ Parkinson's-like symptoms
Where does the dorsal column-medial lemniscus pathway decussate?
What is the medulla oblongata?

What is the part of the auditory pathway in the midbrain called?
What is Inferior Colliculus?

What cranial nerve lesion results in a “down and out” palsy?
What is Oculomotor nerve (CN III)?
What is the name of the heart condition that can be found in children of pregnant women who take lithium in the first trimester of pregnancy?
What is the Ebstein’s Anomaly/Atrialization of the right ventricle?
What cells maintain and make up the blood-CSF barrier?
Bonus (100): BBB
What is Ependymal cells (and Choroid Plexus Epithelial Cells)?
Bonus (100): Astrocytes
A 78 y/o female presents to the ED with room-spinning for the last few hours. A HINTS exam reveals vertical nystagmus. What is the most likely diagnosis?
What is a central lesion (possibly cerebellar origin, like a stroke)?
Where along the cochlea oscillates in response to high frequencies?
What is the Base?

What muscle is at risk of entrapment with an orbital floor fracture/blowout fracture?
What is the Inferior rectus?
What medication is used to treat severe cases of serotonin syndrome?
What is Cyproheptadine?
Which physical exam maneuver tests both the motor and sensory pathways?
Bonus (100): What are the main ones, and what locations do they test for (in terms of numbers)?
What are Reflexes?
Ankle (S1-S2), Knee (Patellar) (L3-4), Brachial (C5-6), Radial (C6-7)
What is the inheritance pattern for Duchenne muscular dystrophy?
What is x-linked recessive?
What is the embryological origin of the stapes?
What is the Second Pharyngeal Arch?
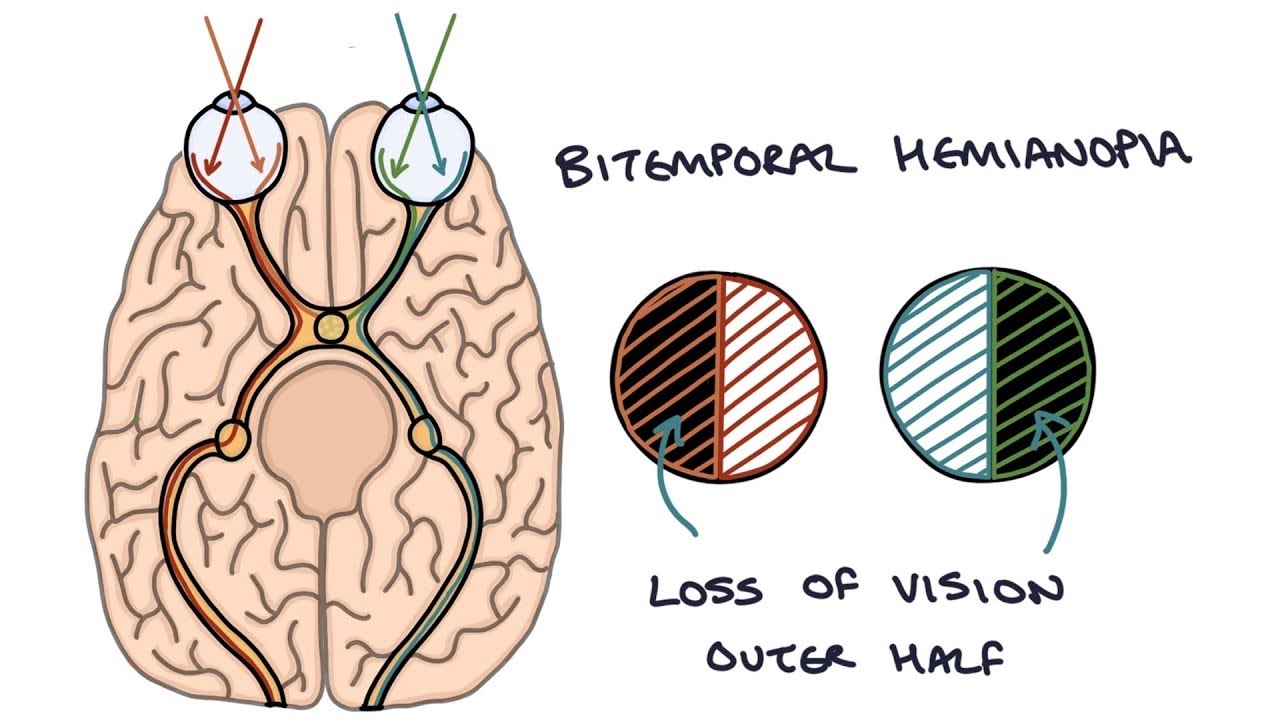
A pituitary adenoma compresses the optic chiasm and causes which visual field defect?
What is Bitemporal hemianopsia?
Which medication can be used to treat depression and can also stimulate the appetite?
What is Mirtazapine (Remeron®)?
What neurocutaneous syndrome is associated with pheochromocytomas, optic nerve gliomas, and renal artery stenosis?
What is Neurofibromatosis Type 1 (aka Von Recklinghausen Disease?)
A 75 y/o male with a 1-year history of urinary frequency presents to the ED with severe back pain and left leg numbness and weakness. What medication should you administer? Name one consulting service you should page immediately.
This patient likely has spinal cord compression from metastatic prostate cancer, causing chronic urinary symptoms and acute radiculopathy. You should give steroids to decrease edema and consult neurosurgery, radiation oncology, and oncology.
What is the muscle responsible for abducting the vocal cords?
What is the Posterior Cricoarytenoid?
What nerves are in /travel through the cavernous sinus?
CN III, IV, V1, V2, and VI, plus postganglionic sympathetic pupillary fibers?
What is the treatment for Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome (NMS)? (2 answers)
Bonus (300): What is the mechanism of action?
What are Bromocriptine & Dantrolene?
Bromocriptine is a DA agonist; Dantrolene is a muscle relaxant that prevents calcium release from the muscle sarcoplasmic reticulum, inhibiting the RYR channel.
What is the next best step in management for a patient presenting with fever, nuchal rigidity, and photophobia that began a few hours ago?
If you encountered this patient in the NICU (Neonatal Intensive Care Unit), what specific agents would you use to manage the condition?
What are IV Antibiotics?
What are Ampicillin, Gentamicin, Cefotaxime, and Dexamethasone?
A 54 y/o man comes to your clinic presenting with/ 7-month history of progressive weakness in his right hand, with difficulty grasping small objects and buttoning shirts. Over the last several months, he's been having muscle wasting of his right forearm and hand, accompanied by muscle cramps and visible fasciulations. Physical exam shows marked atrophy of the intrinsic hand muscles, +3 reflexes of the right hand, and mild spasticity. There's no sensory loss. He also reports mild dysarthria (slurred speech) but denies dysphagia or respiratory symptoms.
Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS)
Key Feature:
-UMN (hyperreflexia, spasticity) & LMN (fasciculations, muscle atrophy) signs
-No sensory involvement
-Some bulbar (= facial) signs (dysarthria)