Where do 90% of nosebleeds originate from?
Bonus (400): What are the tributaries to this area, and where do they originate from?
What is Kisselbachs plexus?

Anterior & Posterior Ethmoidal a. (V1)
Sphenopalatine a. & Greater Palatine a. (V2)
Superior Labial a. (Facial CN VII)
What ocular muscle is innervated by the trochlear nerve?
What is the Superior oblique?
At what age should a child know 2-word phrases, throw a ball overhand, have a 50-word vocabulary, parallel play, and be able to turn a single page in a book?
When is 2 years old?
When taken in excess, this drug causes analgesia, euphoria, pupillary constriction, and respiratory depression.
What is Opioid Intoxication?
What are the 3 main signs of Horner syndrome?
What are Ptosis, Anhidrosis, and Miosis? (aka “PAM”)
A 22 y/o male is brought to your clinic with a significant other with a history of obesity and migraines. The patient's partner says that he has had two separate episodes of tense muscles all over, jerking movements, and passing out. Both were accompanied by tongue bites and feeling out when woken up. What drug from the class of anti-epileptics may be useful to manage his conditions?
What is Topiramate?
A patient comes to the office with a midline neck mass that moves with swallowing. What is this?
What is a Thyroglossal duct cyst?

What optic nerve disease is this demonstrating?
Bonus: Why is checking the eye essential, especially in acute cases?
What is Papilledema (or blurring of the optic disc margins from increased ICP)?
Want to assess for papilledema before doing an LP. LP with evident increased cranial pressure tends to cause herniation of brain parenchyma into/through the foramen magnum and compress the brain stem (Not good or fun).
What is the most common form of child abuse?
What is (Child) Neglect?
This toxidrome involves cocaine, amphetamines, or caffeine, producing mydriasis, hyperactivity, diaphoresis, and tremors. Patients are typically hyperalert, agitated, and sweaty.
What is sympathomimetic Toxidrome?
One of the key ways to tell a cocaine, LSD, or MDMA overdose from an opioid overdose is through what physical exam finding.
Bonus (300): What is the medication that is the exception to this rule?
What is Pupil size? (mydriasis in cocaine, LSD, MDMA overdose; miosis in an opioid overdose).
Meperidine
You are a neonatology fellow checking in on your patients in the nursery. You notice a neonate with a particular pink marking on one side of their face and decide to check their eyes. Fundoscopy shows papilledema. The condition this baby has has what type of gene mutation and inheritance pattern?
What is GNAQ (mutation) and somatic mutation resulting in mosaicism?
What is the parasympathetic innervation to the parotid gland?
What is the Glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)?
What is the most common congenital infection known to cause cataracts?
What is Rubella?
According to Jean Piaget’s theory of cognitive development, at what stage do children achieve object permanence?
What is the Sensorimotor stage (which lasts from birth - 2 years old)?
Some sources indicate that object permanence is achieved between 4 and 7 months, while other sources suggest a range of 6 to 12 months. According to First Aid (2023 edition), object permanence typically occurs by 9 months.
“Mad as a hatter, blind as a bat, red as a beet, hot as a hare, dry as a bone” describes this toxidrome, which involves antihistamines, TCAs, or atropine.
What is the Anticholinergic Toxidrome?
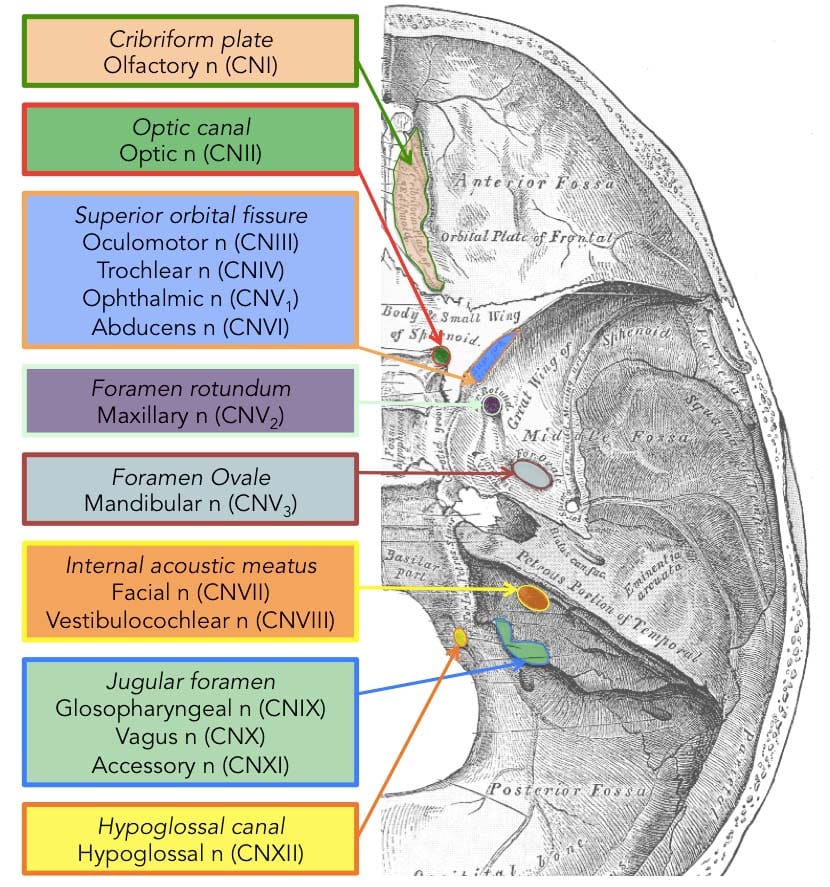
Please name the structures that exit the Jugular Foramen.
What are CN IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), XI (accessory), and the Jugular Vein?
As seen in this demyelinating disease characterized by sudden onset, post-infectious/innocuous white matter degeneration often seen in children, multiple sclerosis also involves white matter degeneration CAUSED BY cells from this germ cell layer.
Bonus (200): What disease is hinted at in the first portion of the question?
What is mesoderm?
Bonus: Acute Demyelinating Encephalomyelitis (ADEM)
Apologies for the confusing question, there's a lot of leaps you have to jump to get to the answer.
#1 Both diseases, MS and ADEM, are CNS neuroinflammatory (pretty much autoimmune-ish) diseases (meaning WBCs are going awry in the CNS brain and/or spinal cord).
#2 In both diseases, oligodendrocytes are destroyed by microglia (which are the monocytes/macrophages of the brain), causing their respective pathologies.
#3** Microglia (just like macrophages and other WBCs) come from mesodermal origin which is why the answer is mesoderm.
Oligodendrocytes do indeed come from neuroectoderm (aka neuroepithelial cells according to First Aid).
What are the three most common bacteria responsible for otitis media?
Bonus (100): What is the most common bacterium responsible for otitis externa?
What are Strep pneumonia, Haemophilus influenza, and Moraxella catarrhalis?
Bonus: Pseudomonas Aeroginosa
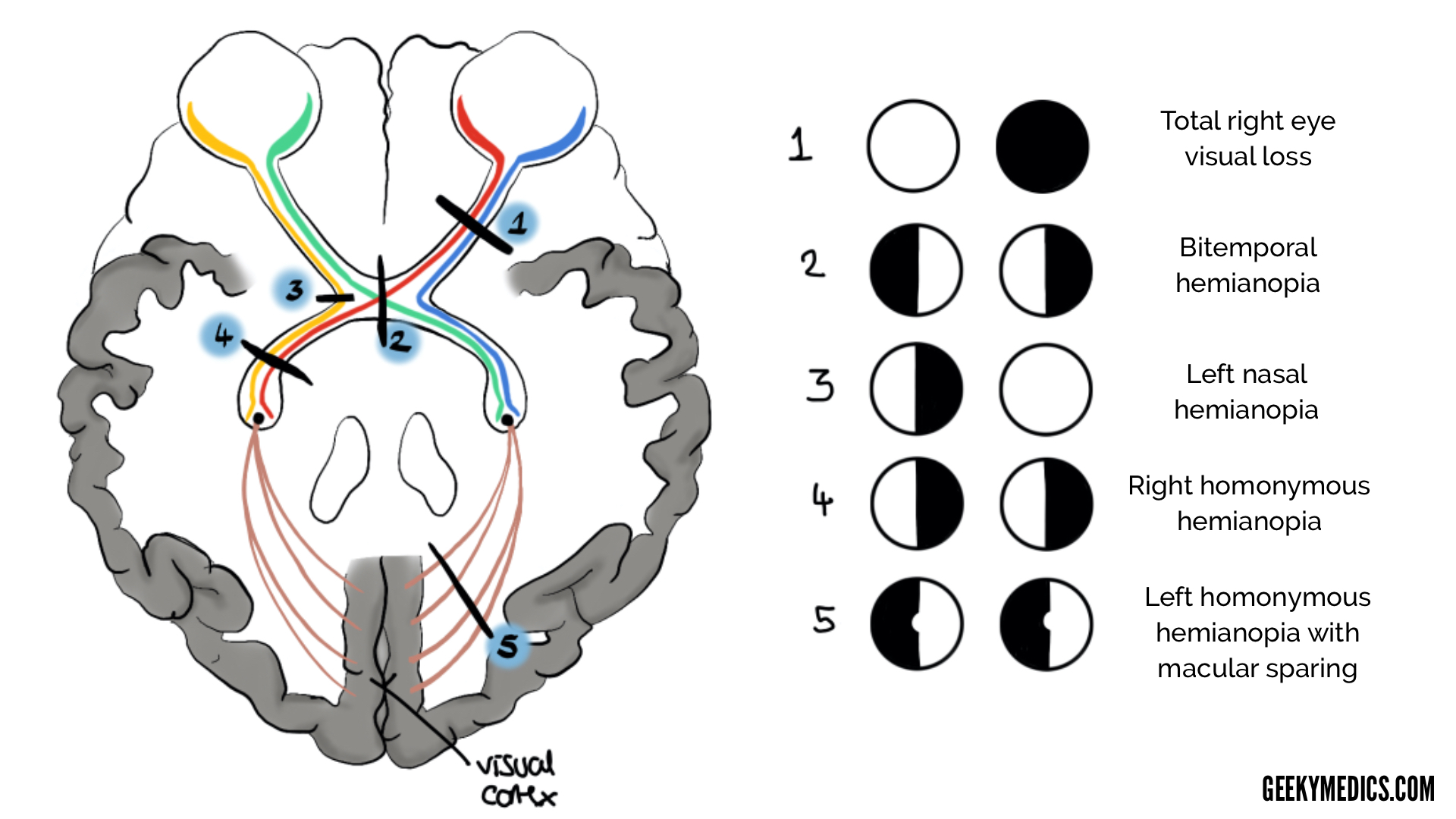
You have a patient who expresses that they have lost half of their vision on their left side (left visual field). A lesion to this location would result in this visual deficit.
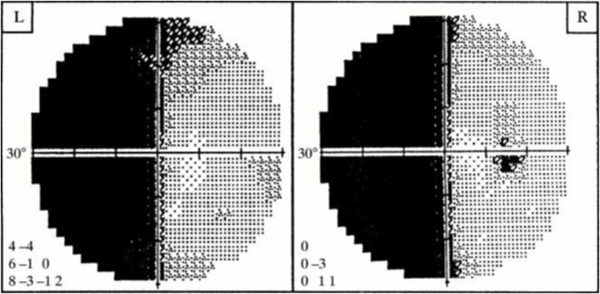
What is the Right optic tract?
Which hormone can dampen the amygdala/cingulate circuit and increase trust and social comfort?
What is Oxytocin?
Marked by instability in relationships, self-image, and affect, this disorder often involves impulsivity, chronic feelings of emptiness, and frantic efforts to avoid abandonment.
What is Borderline Personality Disorder?
(Other info: Splitting is an ego defense common in this condition)
What is the triad for Wernicke encephalopathy?
What is confusion, ophthalmoplegia/nystagmus, ataxia (CONA)?
You're on your emergency medicine rotation, and you get a call from EMS about a patient who was having the worst headache of their life and then suddenly lost consciousness. The patient is en route, and the attending tells you that this condition typically involves these vessels and is often associated with this genetic disorder.
What are
ACOM - ACA junction?
ADPKD or Ehler-Danlos Syndrome?

What is the Triad of Meniere's Disease, and how do you treat it?
What are Vertigo, tinnitus, and hearing loss?
Low-salt diet? (Acetazolamide/HCTZ therapy) is also acceptable.
What two systemic diseases are associated with lens dislocations?
Bonus (200): Where does the lens dislocate in both conditions?
What are
Marfan Syndrome and Homocystinuria?
Marfan - Up & Out
Homocystinuria - Down & In
Where is the master clock in the human body?
Suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus?
Not sure if they covered this, but here's a list of nuclei in the hypothalamus and what they're responsible for (i.e., hunger, thirst, circadian rhythm, etc.)
People with this disorder show detachment and a restricted range of emotional expression, often choosing solitary activities and appearing indifferent to praise or criticism.
What is Schizoid Personality Disorder?
What are the 3 major symptoms associated with the condition characterized by the MRI below?
 Hint: Elderly patients usually
Hint: Elderly patients usually
What are Wet, Wobbly, and Wacky?
Associated w/ Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus.
Of the CNS-related movement disorders characterized as trinucleotide repeats, the two main disorders we've discussed have resultant atrophy in the following regions.
Identify both the disease & regions.
What are the
1) Caudate nucleus degeneration in Huntington's Disease (also frontal, temporal atrophy)
2) Spinal & cerebellar degeneration in Friedreich's Ataxia (DCML, CST, and spinocerebellar tracts)?
