vasodilation and vasoconstriction in the arterioles due to a reflexic response to cellular need in the body such as an abnormal PH, increased CO2, decreased O2, increased temperature.
What is Autoregulation?
The outer connective tissue layer of arteries and veins that contains elastic and collagen fibers.
What is Tunica Adventitia
refers to the proportion of the cells in blood and indicates viscosity of the blood. Elevated levels could indicate dehydration or decreased levels could indicate excess blood loss.
What is Hematocrit?
clear yellowish fluid and solutes remaining after the cells have been removed.
What is Plasma?
the various blood cells develop from a single stem cell during this process.
What is Hemopoesis or Hematopoesis?
a hormone originating from the kidney that stimulates erythrocyte production in the red bone marrow in response to tissue hypoxia.
What is Erythropoietin?
consists of the globin portion, which is 2 pairs of amino acid chains, and four heme groups, each containing a ferrous iron atom to which oxygen molecules can attach.
What is Hemoglobin?
a poisoning that is recognized by a bright cherry-red color in the face and lips. The responsible ion displaces oxygen from hemoglobin by binding tightly to iron causing a fatal hypoxia.
What is Carbon Monoxide Poisoning ?
The most common leukocyte. They are first responders to any tissue damage and commence phagocytosis. An immature one of these is called a band and lab reports can reflect a "left shift" when there is an increased number of these immature cells in response to a bacterial infection.
What are Neutrophils?
also called platelets, they are an essential part of the blood-clotting process, or hemostasis.
What are Thrombocytes?
This is required for the synthesis of most clotting factors. specifically it is required by the liver for synthesis of prothrombin. It is also the known antidote for excess warfarin, an oral anticoagulant.
What is Vitamin K?
this type of reaction results in agglutination and hemolysis of RBC's. s/s of this reaction include, fever, headache, back and chest and abdominal pain, flushed face, hypotension and tachycardia.
What is a Transfusion Reaction or antigen-antibody reaction?
This serum level indicates bone marrow function.
What is Reticulocyte count?
Due to the absence of A & B antigens this blood type is considered the universal donor
What is O blood type?
This anemia is is due to a specific insufficiency that impedes the synthesis of hemoglobin. Causes could include dietary insufficiencies, chronic blood loss (**bleeding ulcer, hemorrhoids, cancer, excessive menstrual blood flow), impaired duodenal absorption, or severe liver disease.
What is Iron Deficiency Anemia?
This anemia is known to to exhibit large immature RBC's and can directly cause demyelination of the peripheral nerves and eventually the spinal cord.
What is Pernicious Anemia or Vitamin B-12 deficiency?
**************DAILY DOUBLE****************
#1-This anemia results from impairment or failure of the bone marrow leading to loss of stem cells and decreased number of erythrocytes, leukocytes and platelets in the blood.
#2-This is the medical term for decreased number for erythrocytes, Leukocytes and platelets.
What is Aplastic anemia?
What is Pancytopenia?
This anemia results in major problems with obstruction of small blood vessels by the elongated and rigid RBC's resulting in thrombus formation and repeated infarctions or areas of tissue necrosis.
What is Sickle Cell Anemia?
This blood clotting disorder exhibits the following s/s: prolonged and severe hemorrhage from minor tissue trauma, hematomas due to persistent oozing of blood with minor injuries, spontaneous hemarthrosis, hematuria.
What is Hemophilia A?
This process causes multiple thromboses and infarction, but also consumes the available clotting factors and platelets and stimulates the fibrinolytic process.
What is Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation?
this disease is characterized by a high portion of very immature, nonfunctional cells in the bone marrow and peripheral circulation; the onset is usually abrupt, with marked signs and complications.
What is Acute leukemia?
This disease is characterized by higher proportion of mature cells with a chronic onset and mild signs and is typically diagnosed in adulthood.
What is Chronic Leukemias?
The aorta on the top of this image reveals signs of what condition?
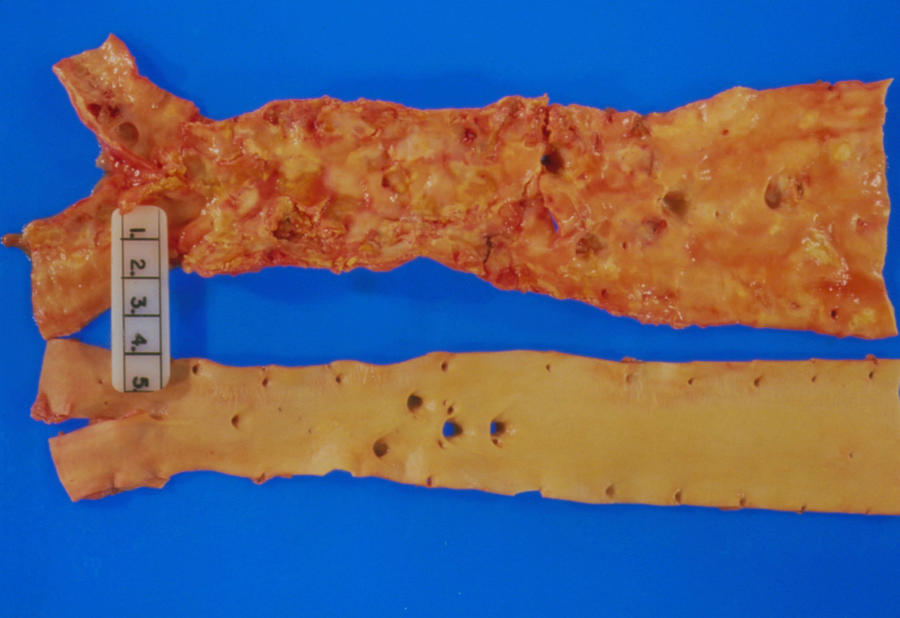
What is Atherosclerosis?
this lipo-protein transports cholesterol from the liver to the cell and has a high lipid content, because of this it is a major contributor to atheroma formation.
What is LDL or Low-Density Lipoprotein?
this thrombus forms spontaneously in a vein and is less firmly attached putting the patient at a higher risk of pulmonary embolus.
What is Phlebothrombosis?