What are the three main types of blood vessels?
1. capillaries
2. Veins
3. Arteries
Perfusion of a capillary bed is completed to what type of transport?
Bulk flow
What are the three branches of the Aorta?
1. Ascending Aorta
2. Aortic arch
3. Descending Aorta
The posterior part of the circle receives blood from the ______ artery.
Vertebral artery
Edema
T/F: The hepatic vein and the hepatic portal system are the same.
False
The left gonad vein drains into the left ___ vein.
renal
T/F: Capillaries are capable of dilation and constriction
False.
They are not capable as they contain no muscle layer
Fill in the blanks: Hydrostatic pressure is ____ on the inside of the capillary. This is what drives fluids __ of the capillaries.
1. Higher
2. Out
The right common carotid supplys blood to what side of the head?
right
Fill in the blank" The anterior part of the circle receives blood from ___ ___ artery
internal carotid artery
What artery enters through the magnum foramen and supplies oxygen to the brain?
1. Femoral vein
2. External Iliac vein
The right gonadal vein drains in the ____ __ ___
Inferior vena cava (IVC)
T/F: Tunica Media (smooth muscle) is always thicker in arteries than veins?
True.
This is because of the high vs. low pressure system
Fill in the blanks: Hydrostatic's opposing force is called ___ ____
Osmotic pressure
What is the name of the receptors that detect BP in the Aorta?
Baroreceptors
What is letter m?
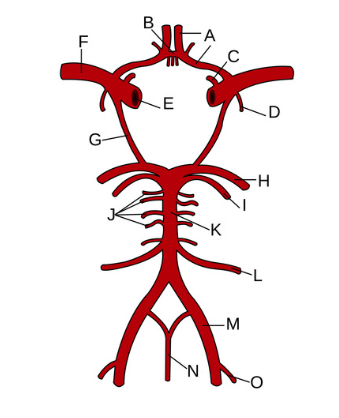
vertebral arteries
Which of the following is NOT a type of capillary?
Fenestrated
Sinusoidal
Continuous
Distributing
Distributing
Name this deep vein:
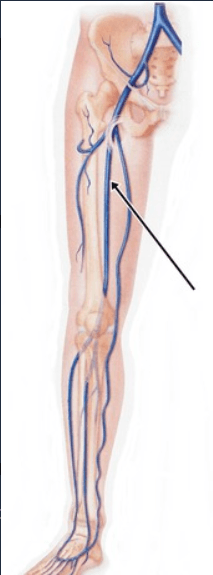
Femoral Vein
What is the equation for mean arterial pressure?
MAP = DP + 1/3 (PP)
List the three layers of blood vessels from superficial to deep
1. Tunica externa
2. Tunica Media
3. Tunica intima
Arterial or Venous?
arterial
T/F: The descending aorta is posterior to the heart.
True
What is letter F?
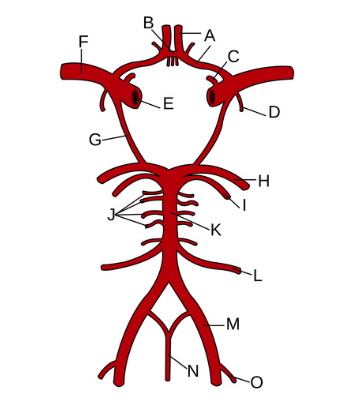
Internal carotid artery
If you have a blood pressure of 120/80 mmHg, what is your diastolic pressure?
(include unit)
80 mm Hg
What artery feeds into the right intestines?
Super mesenteric artery
List three things that can affect peripheral resistance
1. Blood viscosity
2. Vessel length
3. vessel radius
Superficial to deep
1. Tunica externa - epithlium
2. Tunica Media - Muscle
3. Tunica intima - connective tissue
What happens with leftover fluid that was not reabsorbed after the bulk flow process?
it is picked up by the lympahtic system and returned to circulation
The Descending aorta is divided into two parts.
Part 1: What are their names?
Part 2: What is the landmark in the body that divides them.
Part 1:
1. Thoracic aorta
2. Abdominal aorta
Part 2:
Diaphragm
What is letter K?

Basilar artery
If you have a blood pressure of 110/80 mmHg, what is your pulse pressure?
(include unit)
30 mm HG
The cephalic trunk lies in the upper portion of the abdominal aorta. It is divided into three branches. What are the names of the three branches?
1. Splenic artery
2. L. gastric artery
3. common hepatic artery
What is the MAP of a patient whos blood pressure is
120/80 mm Hg
93.3 mmHg