This popular brand of insoles is named after a Chicago Medical School alumnus.
Dr. Scholl’s
These two clinical tests can be used to identify meningitis.
Kernig sign and Brudzinski sign

What medication should you start in patient with intermittent claudication who has been on a statin, antiplatelet monotherapy with continued symptoms?
Double points for mechanism of action ;)
Cilostazol
(a phosphodiesterase inhibitor with antiplatelet and vasodilator activity)
This rare disorder of metabolism can present with neurological changes, psychiatric changes, and elevated ALT/AST.
Wilson's disease
This autoimmune condition is characterized by hyperthyroidism, exophthalmos, and pretibial myxedema.

Graves Disease
This soft drink was created in the nineteenth century by pharmacist Charles Alderton.
Dr Pepper
This test is positive when a patient standing with their eyes open starts to sway upon closing their eyes.
Romberg test
Name the following rhythm and the most common underlying condition it’s associated with.
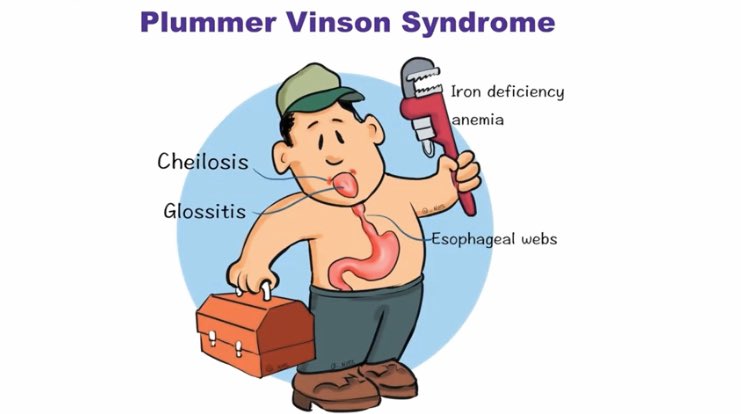
This disease is described by a classic triad of dysphagia, iron-deficiency anemia, and esophageal webs
Plummer Vinson Syndrome
These antihyperglycemics have the most proven cardiovascular benefit in patients with known ASCVD risks.
GLP-1 agonists and SGLT2 inhibitors
This brand of footwear is often associated with punk subculture.
Doc Martens
To perform this test, the physician scrapes the lateral aspect of the sole from heel to toe, then observes how the toes respond.
Babinski sign
Correctly name 4 of the 5 different types of NSTEMI and how they’re defined.
Type 1: a primary CAD event (plaque rupture or erosion -> thrombus)
Type 2: caused by imbalanced oxygen supply and demand
Type 3: sudden cardiac death w/ presumed new EKG changes or v-fib; no biomarkers obtained before death
Type 4: procedure-associated MI (</=48 hours after PCU, stent thrombosis)
Type 5: procedure-associated MI during or </=48 hours after a CABG
This type of tumor can lead to diarrhea, episodic flushing, wheezing, and right-sided valvular heart disease if the hormone/molecule secreted by the tumor reaches systemic circulation via liver metastasis.
Carcinoid tumor
Name at least 2 first-line tests that must be abnormal to confirm the diagnois of Cushing syndrome
Overnight low-dose dexamethasone suppression test
24 hour urine free cortisol measurement
Late-night salivary cortisol measurement
This brand of headphones boasts many celebrity endorsements.
Beats by Dr. Dre
Which nerve is being assessed?
Patient is asked to shrug as the physician applies inferior resistance.
CN XI, Accessory Nerve
What are the aortic valvular area sizes that categorize mild, moderate, and severe aortic stenosis?
Mild: >1.5 cm2
Moderate: 1.0-1.5 cm2
Severe: <1.0 cm2
This test will help to determine the cause of recurrent ulcers in the duodenum and jejunum, abdominal pain, and diarrhea.
Secretin stimulation test
Secretin stimulation test is used for evaluation of gastrinoma. Increased gastrin levels after administration of secretin is indicative of a gastrinoma. Secretin normally inhibits gastrin release. May be associated with MEN1.
Name all of the hormones secreted by the anterior pituitary gland.
FSH, LH, ACTH, TSH, Prolactin, GH
This soda brand is often found at Jewish delicatessens and Passover seders.
Dr. Brown’s
Name the disorder:
When the patient looks left, both eyes gaze left.
When the patient looks right, the left eye cannot adduct past midline.
Intranuclear Ophthalmoplegia
Name the device and its specific function.
Watchman Device
Filter implant inserted into the left atrial appendage for patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
It prevents the formation of LAA clots, preventing the risk of thromboembolism, and is an alternative to blood thinners
There are 3 drug classes that must be avoided in “Acute severe” presentation of this condition. Symptoms include bloody diarrhea, tenesmus, and abdominal pain. Inflammation is limited to the mucosa and submucosa. (bonus points if you can name associated complications with each drug class)
NSAIDs, Opioids, Anticholinergics
NSAIDs can inhibit prostaglandin synthesis and worsen mucosal inflammation. This will increase the risk of relapse, bleeding, and ulcer formation
Opioids will slow down GI motility by increasing smooth muscle tone. This can increase risk of toxic megacolon and perforation
Anticholinergics inhibit ACh-mediated parasympathetic activity, leading to reduced bowel motility. The risk of toxic megacolon and perforation
List the 4 symptoms associated with primary hyperparathryoidism.
Renal stones (Stones)
Polyuria (Thrones)
Bone pain (Groans)
Neuropsychiatric disturbance/Altered mental status (Psychiatric overtones)
"Stones, thrones, groans, and psychiatric overtones"