Which of the following statements is true of hematopoiesis?
A) The process occurs in the spleen
B) It is the formation of plasma
C) It is the formation of blood cells
D) Breakdown of blood cells
It is the formation of blood cells

Which of the following is the correct sequence of blood flow through the kidneys on its route to the glomeruli of the nephrons?
A) renal artery → segmental artery → interlobular (cortical radiate) artery → arcuate artery, interlobar artery → afferent arteriole
B) renal artery → segmental artery → interlobar artery → arcuate artery → interlobular (cortical radiate) artery → afferent arteriole
C) renal artery → segmental artery →interlobar artery → interlobular (cortical radiate) artery → arcuate artery →afferent arteriole
D) renal artery → segmental artery → interlobular (cortical radiate) artery → interlobar artery arcuate artery →afferent arteriole
B) renal artery → segmental artery → interlobar artery → arcuate artery → interlobular (cortical radiate) artery → afferent arteriole
A 29 year old woman is referred to a diabetic clinic for poor diabetes management. She was diagnosed with type 1 diabetes at the age of 12 and prescribed actrapid insulin injections. Recently, the patient has been suffering fluctuations in her plasma glucose levels and her previously well-controlled glycated haemoglobin has risen to 8.1%. The patients admits she has recently been avoiding using her injections. On examination, the patient has a raised, smooth lump that is firm on palpation at the lower abdomen. The most likely diagnosis is:
A) Worsening of diabetes
B) Lipohypertrophy
C) Injection scarring
D) Lipoma
E) Injection abscess
Lipohypertrophy

A 45-year-old female complains of pain and swelling in both wrists and knees for three months. There is increased stiffness in the hands early in the morning, which lasts close to 40 minutes. On examination, the metacarpophalangeal joints and wrists are warm and tender. There are no other joint abnormalities. There is no alopecia, photosensitivity, kidney disease, or rash. What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
A) Rheumatoid arthritis
B) Polymyalgia rheumatica
C) Gouty arthritis
D) Osteoarthritis
Rheumatoid Arthritis
A 16-year-old boy is brought to the physician because of a 2-day history of a sore throat and fever that peaks in the late afternoon. He also has a 1-week history of progressive fatigue. He recently began having unprotected sexual intercourse with one partner. He appears ill. His temperature is 39°C (102.2°F). Physical examination shows cervical lymphadenopathy and pharyngeal erythema with a creamy exudate. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A) Candidiasis
B) Herpangina
C) Infectious mononucleosis
D) Mumps
E) Syphilis
Infectious mononucleosis

A 57-year-old woman with non-small cell lung cancer comes to the physician 4 weeks after her tumor was resected. She takes no medications. The physician starts her on a treatment regimen that includes vinblastine. This treatment puts the patient at highest risk for which of the following?
A) Pyruvate kinase
B) Glutathione receptor
C) Lactic acid dehydrogenase
D) Carbonic anhydrase
E) Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
Alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase
A 23-year-old man with a history of type 1 diabetes mellitus is brought to the emergency department due to confusion and weakness. His symptoms began 2 days ago after he started having mild diarrhea. He has missed several doses of insulin because his appetite has been poor. On examination, his breath has a fruity odor. This patient is most likely to demonstrate which of the following urine pH and urine HCO3- changes respectively?
A) Increased, decreased
B) Increased, increased
C) Decreased, decreased
E) Decreased, Decreased
Decreased, Decreased
An investigator studying hormone synthesis and transport uses immunocytochemical techniques to localize a carrier protein in the central nervous system of an experimental animal. The investigator finds that this protein is synthesized together with a specific hormone from a composite precursor. The protein is involved in the transport of the hormone from the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei to its destination. The hormone transported by these carrier proteins is most likely responsible for which of the following functions?
A) Increased insulin-like growth factor 1 production
B) Stimulation of thyroglobulin cleavage
C) Upregulation of renal aquaporin-2 channels
D) Maturation of primordial germ cells
E) Suppression of uterine contractions
Upregulation of renal aquaporin-2 channels

A 33-year-old woman presents with a malar rash that is exacerbated by sun exposure. She has experienced episodes of myalgia, pleural effusion, pericarditis, and arthralgia without joint deformity over the course of several years. She has a history of hematuria and no history of drug intake prior to the onset of these symptoms. The best screening test for her disease would be:
A) Antinuclear antibody
B) Anti-ds-DNA antibody
C) Anti-RNP antibody
D) Anti-histone antibody
Antinuclear antibody
A 25-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of a 6-day history of fever, severe muscle pain, and diffuse, painful swelling of his neck, underarms, and groin area. The symptoms began after returning from a camping trip in New Mexico. He appears ill and lethargic and can barely answer questions. His temperature is 39.2°C (102.5°F), pulse is 120/min, respirations are 22/min, and blood pressure is 110/70 mm Hg. Physical examination shows generalized scattered black maculae. Examination of the right upper extremity shows an erythematous, solid, tender mass on the underside of the upper extremity just above the elbow; the mass is draining blood and necrotic material. The most effective antibiotic for this patient’s disorder will interfere with which of the following cellular processes or enzymes?
A) Cell wall synthesis
B) DNA helicase
C) Glucuronosyltransferase
D) Proteasomal degradation
E) Ribosomal assembly
F) Tetrahydrofolate reductase
Ribosomal assembly

In which of the following diseases is a massive splenomegaly not a characteristic feature?
A) Infectious Mononucleosis
B) Thalassemia
C)Chronic myeloid leukaemia
D) Kala-azar
E) Polycythaemia rubra vera
Infectious Mononucleosis
A 44-year-old man is brought to the hospital after being found unresponsive. Temperature is 35.6 C (96.1 F), blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg, and pulse is 110/min. He is responsive only to pain and has dry mucous membranes. The patient's condition is initially treated with intravenous fluids, and his mental status slowly improves, but urine output decreases and flank pain develops. A renal biopsy reveals marked ballooning and vacuolar degeneration of proximal renal tubules; multiple oxalate crystals are observed in the tubular lumen. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's acute kidney injury?
A) Direct tubular injury due to exogenous toxin ingestion
B) Direct tubular injury from filtered monoclonal light chains
C) Increased endogenous parathyroid hormone production
D) Microthrombosis of the glomerular capillaries
E) Prerenal azotemia due to splanchnic vasodilation
Direct tubular injury due to exogenous toxin ingestion
A 37 year old man presents with symptoms of an acute headache, vomiting, malaise and visual disturbance. A neurological examination reveals a bitemporal superior quadrantanopia. A CT scan shows a hyperdense area within the pituitary gland. The most likely diagnosis is:
A) Kallman syndrome
B) Septo-optic dysplasia
C) Sheehan’s syndrome
D) Empty sella syndrome
E) Pituitary apoplexy
Pituitary apoplexy

A 40-year-old female, with a known case of asthma for the last four years, presented with a two-month history of numbness in the right upper and both lower limbs. Examination revealed asymmetric neuropathy and palpable purpura over the lower limbs. Investigations revealed eosinophilia. What is the likely diagnosis?
A) Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)
B) Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)
C) Giant cell arteritis (GCA)
D) Churg-Strauss syndrome
Churg-Strauss syndrome

A 68-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a 1-day history of fever and pain and swelling of her left leg. She has a history of chronic lower extremity edema. Physical examination shows dry, scaly skin over the lower extremities, and a swollen, erythematous, hot, and tender left calf. One day later, blood cultures grow gram-positive, catalase-negative cocci that exhibit clear zones of hemolysis on blood agar plates. There is no growth when bacitracin is added to the plate. Which of the following species of Streptococcus is the most likely causal organism?
A) S. agalactiae (group B)
B) S. mitis
C) S. pneumoniae
D) S. pyogenes (group A)
E) Viridans streptococcus
S. pyogenes (group A)
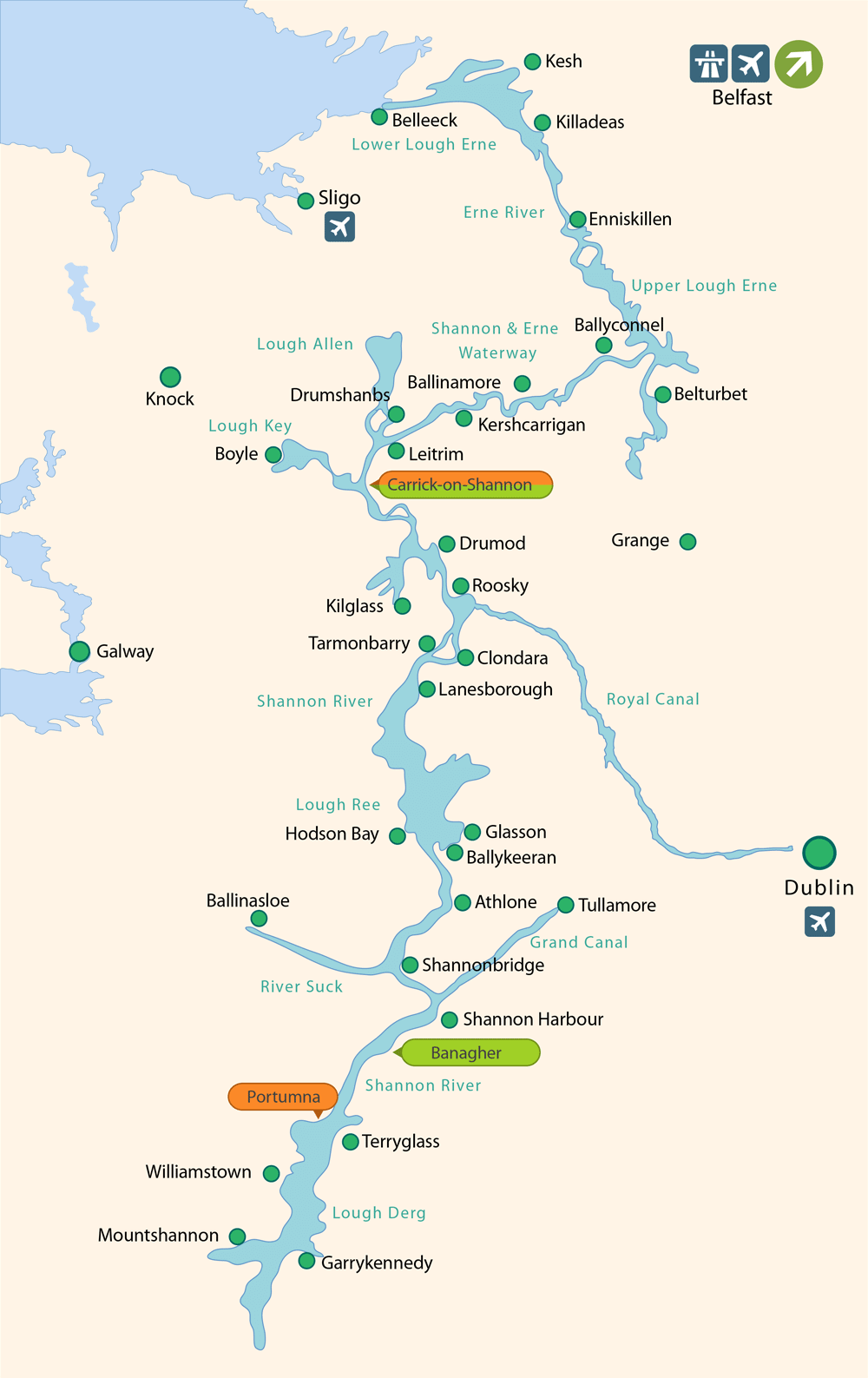
A 68-year-old man undergoes successful mechanical prosthetic aortic valve replacement for severe aortic valve stenosis. After the procedure, he is started on an oral medication and instructed that he should take it for the rest of his life and avoid consuming large amounts of dark-green, leafy vegetables. Which of the following laboratory parameters should be regularly monitored to guide dosing of this drug?
A) D-dimer
B) Thrombin time
C) Activated partial thromboplastin time
D) Prothrombin time
E) Anti-factor Xa activity
Prothrombin time
A 26-year-old male has developed renal failure from chronic glomerulonephritis and is undergoing dialysis therapy. His mother has the same blood group as her son and she wants to donate one of her kidneys to him. The patient has no chronic medical conditions and takes no medications. Vital signs are within normal limits, and physical examination shows no abnormalities. The patient understands that she may not be a compatible donor based on human leukocyte antigen (HLA) testing. In addition, which of the following age-related renal changes should be taken into consideration when assessing donor suitability?
A) Decreased number of functional glomeruli
B) Decreased solute excreting ability
C) Increase creatinine clearance
D) Increased renal blood flow
E) Increased sensitivity for renin release
Decreased number of functional glomeruli
A 50 year old Asian man is referred to the diabetes clinic after presenting with polyuria and polydipsia. He has a BMI of 30, a blood pressure measurement of 137/88 and a fasting plasma glucose of 7.7 mmol/L. The most appropriate first-line treatment is:
A) Dietary advice & exercise
B) Sulphonylurea
C) Exenatide
D) Thiazolidinediones
E) Metformin
Dietary advice & exercise
Which of the below medications are not considered TNF inhibitor?
A) Adalimumab
B)Certolizumab
C) Infliximab
D) Hydroxychloroquine
Hydroxychloroquine
A 26-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of abdominal pain, dizziness, shortness of breath, and swelling and pruritus of the lips, tongue, and throat for 1 hour. The symptoms began minutes after he started eating a lobster dinner. It is determined that his symptoms are due to surface crosslinking of IgE. This immunologic event most likely caused the release of which of the following?
A) Tryptase
B) Cathepsin
C) Serotonin
D) Bradykinin
E) Interferon gamma
Tryptase
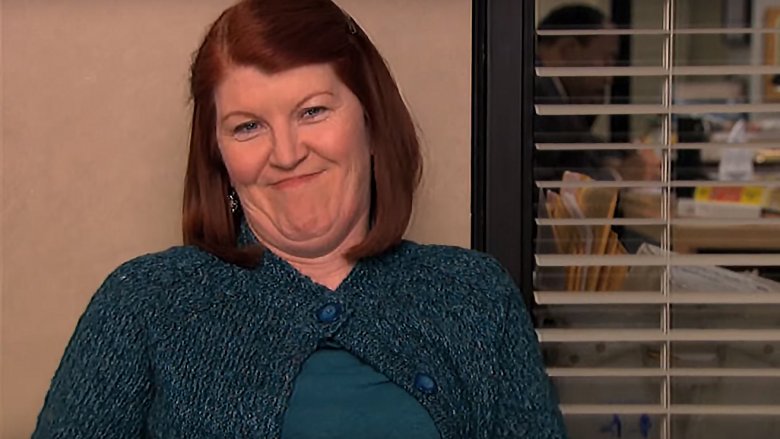
Who does Michael Scott hit with company property on company property in The Office?
Meredith Palmer

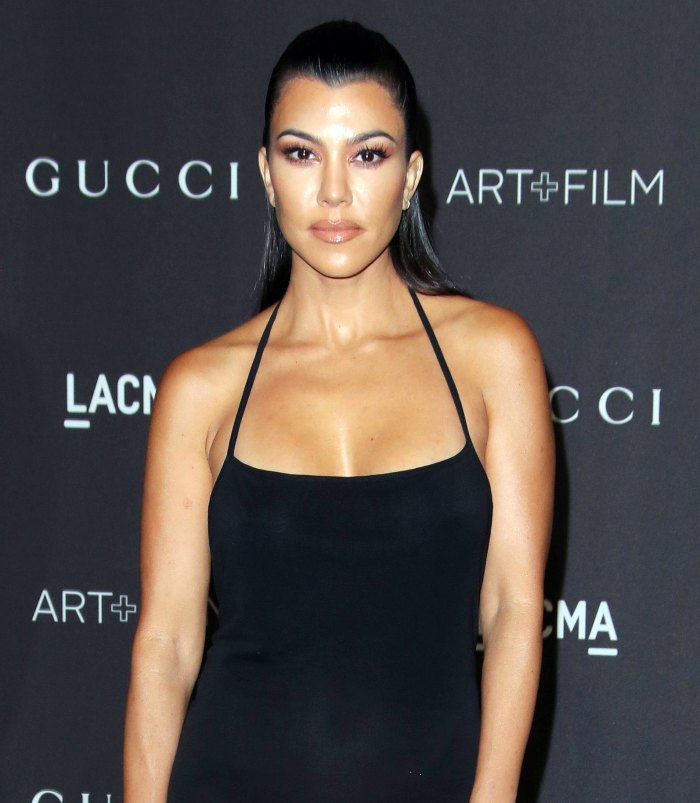
Who is the oldest Kardashian sister?
Kourney

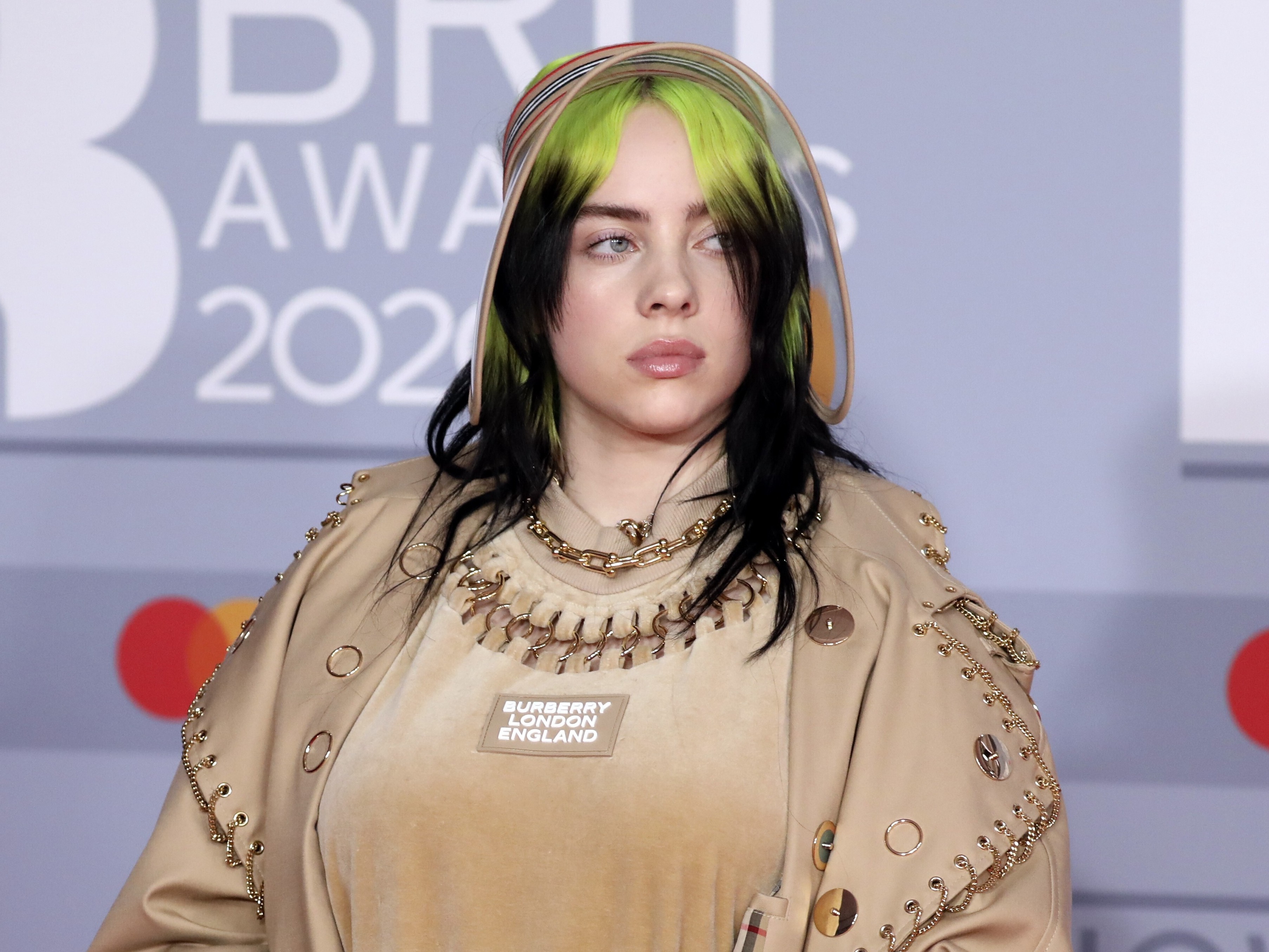
Which artist made history in 2020 as the youngest winner of the Grammys‘ four main categories?
Billie Eilish

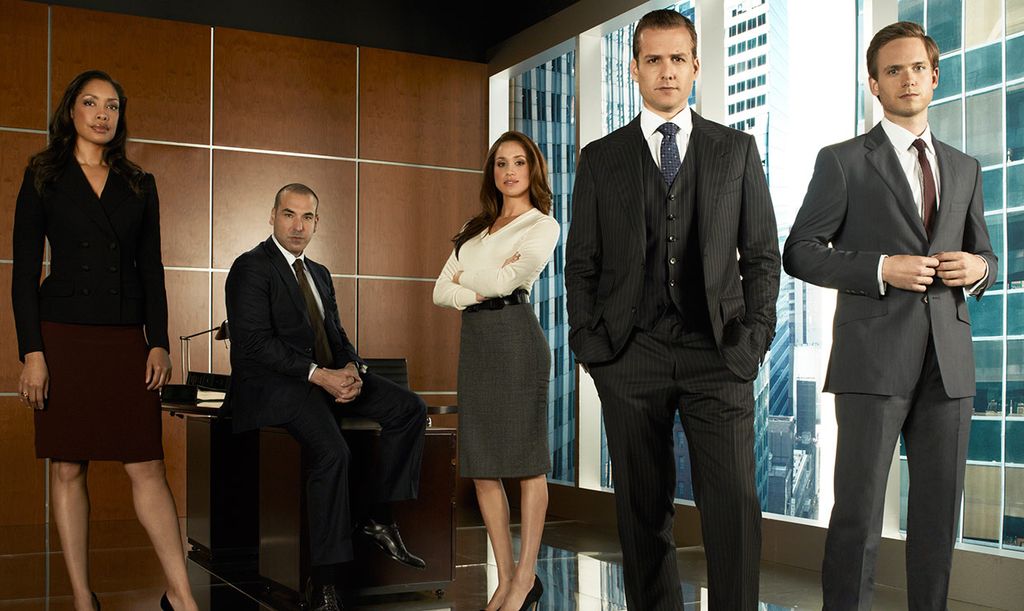
Before she married Prince Harry, Meghan Markle was on a TV show that ran from 2011 to 2019. What’s the name of that TV show?
Suits

What is the longest River in Ireland?
The River Shannon