Name the muscle most prominent in a patient that clenches and grinds.
What is masseter?
temporalis and pterygoid muscles are muscles of mastication.
Zygomaticus and buccinators are muscles of facial expression.
Buccinator assists in mastication.
Name the widest and strongest root of the mandibular first molar.
What is mesial?
This condition is associated with Candida albicans.
Linea alba Retro cuspid papillae
Leukoedema
Median rhomboid glossitis
What is median rhomboid glossitis?

Of the following list which is typically an acute metabolic complication of uncontrolled diabetes mellitus.
Atherosclerosis Retinal damage
Ketoacidosis End-stage kidney failure
What is ketoacidosis?
All the other choices are long-term
Name the oral conditions that are contagious.
Chronic perio Herpetic gingivostomatitis
Acute pericoronitis
necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis
What is herpetic gingivostomatitis?
Name the structures that separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
What is the palatine bone?
Name the nerve that generates sensation to the anterior 2/3rds of the tongue.
What is lingual?
V3 a branch of the trigeminal
TASTE is facial nerve VII
Motor innervation of the tongue hypoglossal XII
Amalgam tattoo is known as
melanoma
nevus
focal argyrosis
multiple myeloma
What is focal argyosis--a condition exposed to chemical compound. Element of silver-silver dust

A white lesion that cannot be rubbed off and cannot be diagnosed on the basis of clinical characteristics is termed:
Leukoplakia squamous cell carcinoma
dentinogenesis imperfecta erythroplakia
What is Leukoplakia?
Chronic irritation. Could be the beginning of cancer. Seen in smokers
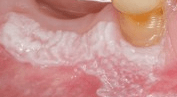
The types of periodontal surgery that increase the predictability of growth of new tissue of the periodontal apparatus is called
Pocket reduction or elimination
Treatment of osseous defects Access to root surface
Guided tissue regeneration
What is guided tissue regeneration?
This technique uses barrier membrane that excludes epithelial cells between the perio flap and bone only cells from the PDL space and the bone are allowed to repopulate the site of lost tissue.
Name the following that are divisions of central nerve V.
Occipital, Maxillary, Mandibular
Maxillary, Mandibular, Lingual
Opthalmic, Maxillary, Mandibular
What is Ophthalmic, Maxillary, Mandibular?
They are V1, V2, V3 are divisions of Trigeminal or cranial nerve V
Name the artery that provides blood supply to the mandible.
What is maxillary artery?
 Gray-white opalescent film on buccal mucosa seen in 85% of black adults.
Gray-white opalescent film on buccal mucosa seen in 85% of black adults.
What is leukoedema?
Epulis fissuratum is caused by
Denture suction chamber
allergic reaction
denture cleaner ill-fitting denture
What is an ill-fitting denture?
Epulis-means growth--tumor like enlargement on gingiva or alveolar mucosa
benign hyperplasia of fibrous connective tissue
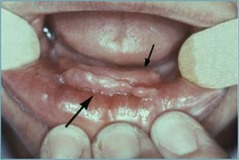
Name the principal fiber bundles in the connective tissue that run from the cementum to the alveolar crest and protect the PDL are the __________group
dentoperiosteal transeptal fiber
circular fiber alveologingival
What is dentoperiosteal?
Name the branch that is NOT a part of the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve.
Deep Temporal Lingual
Superior alveolar Inferior alveolar
Masseteric
What is superior alveolar?
It is part of the maxillary branch V2
all others listed are mandibular division V3
These arteries carry deoxygenated blood.
Super thyroid Pulmonary
Facial Lingual
Maxillary
What is pulmonary?
Name the area where you would find a ranula.
Where is the floor of the mouth?
ranula a fluid filled cyst that forms in the mouth under the tongue. It is filled with saliva that has leaked out of a damaged sublingual salivary gland.
Mucocele is an enlargement or protrusion of the mucous membrane of the lachrymal passages
The type of immunity received after the full series of immunizations against hepatitis B is called
Acquired/artificial immunity
acquired/artificial passive immunity
natural active immunity natural passive immunity
What is acquired/artificial active immunity
The histopathological phase that occurs within 4 to 7 days after biofilm accumulation is called
What is early?
Initial is 2-4 days
early 4-7 days
established after 14 days
advanced after inflammation invades supporting periodontal tissues
Name the exocrine gland.
Parathyroid
Thymus Pituitary
Thyroid Parotid
What is parotid?
If they have a duct they are exocrine glands
Buccinator Orbicularis Oris
Risorius Depressor Anguli Oris
Mentalis
What is mentalis?
Radiographic features, including cotton-wool radiopacities and hypercementosis, are especially helpful in the diagnosis of
Dentnogenesis imperfecta anemia
Paget disease Diabetes
What is Paget disease?
A rare bone disorder
commonly have fractures
weaker bones
Erythema multiforme and Stevens-Johnson syndrome are both primarily considered as:
Autoimmune disorders
Immunologic responses to various triggers
Allergic reaction to foods
What is immunologic responses to various triggers?
Treponema pallidum
Actinomyces viscosus Streptoccous sanguis
Porphyromonas gingivalis
What is porphyromonas gingivalis?
tissue-invading, collagen-and-bone destroying anaerobic bacteria another is
Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans