The head is __cephalic__ to the neck.
What is superior?
Name the body region: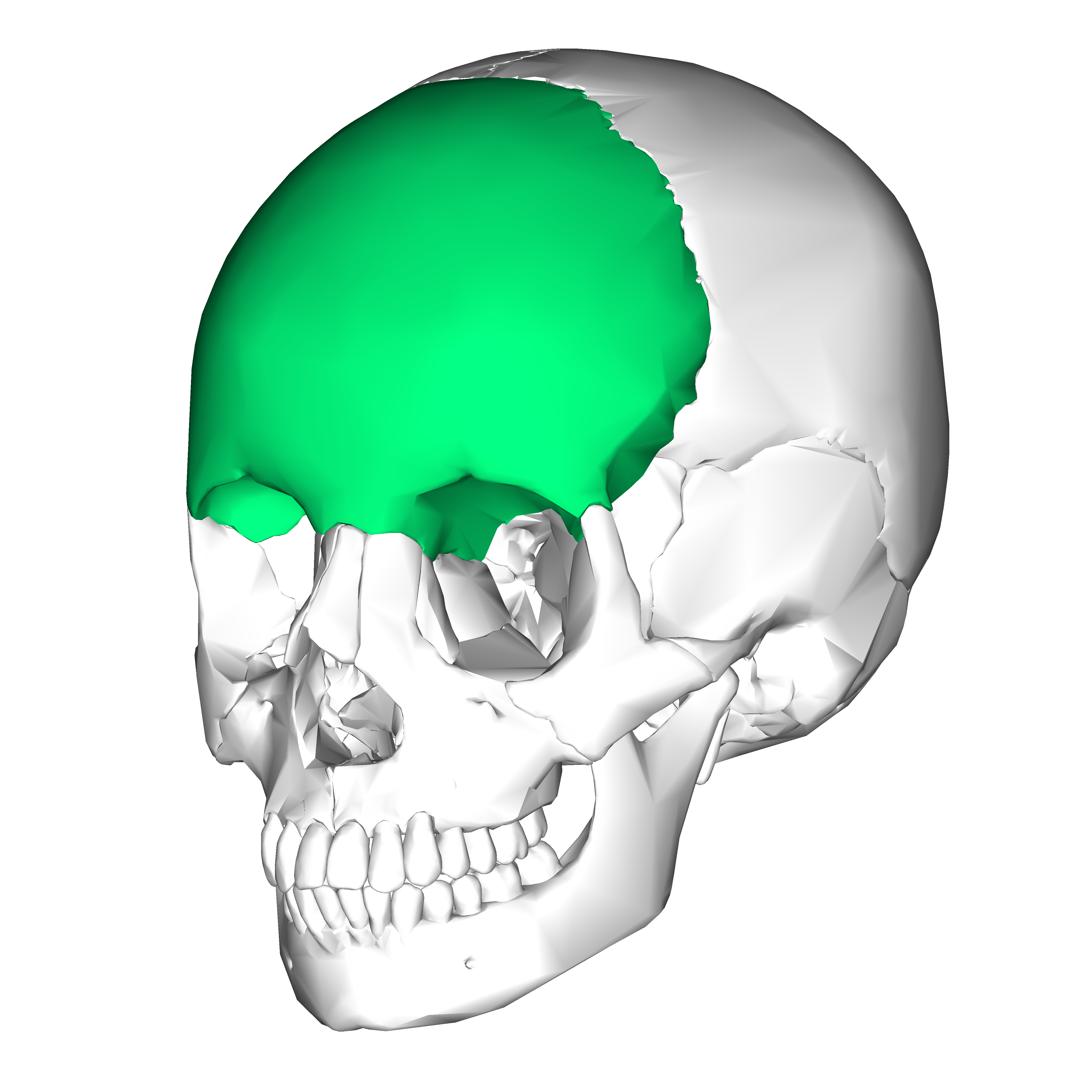
What is frontal region?
The monomers of proteins. glucose
What are amino acids?
amino acids are carbohydrates
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus.
What is the atomic number?
A molecule that regulates pH to help maintain homeostasis.
What is a buffer?
The arm is __Brachial__ to the sternum.
What is lateral?
Name this body cavity:

What is the thoracic cavity?
Thoracic cavity, also known as the chest cavity, is a hollow a space in the chest that contains organs, blood vessels, nerves and other important body structures
The building of larger more complex molecules using atoms or smaller molecules.
What is a synthesis reaction (or anabolic process)?
A variation of an element that has the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons.
What is an isotope?
The molecule required by our cells to perform work.
What is adenosine triphosphate (ATP)?
The ___midsagittal___ splits the body into anterior and posterior.
What is the coronal plane?
frontal interior to posterior
Name the outer layer of the serous cavity surrounding the heart.
What is the parietal pericardium?
Functions: structure, catalyze reactions, muscle contraction, protection, membrane transport
What are proteins?
True or false: enzymes speed up chemical reactions and are absorbed in the process.
What is false (enzymes remain unchanged after a reaction)?
A bond formed by the unequal sharing of electrons between 2 atoms.
What is a polar covalent bond?
The wrist is ____ to the elbow.
What is distal?
Name this body region: sural
What is the sural region?
sural region is a sensory nerve in the lower limb that provides sensation to the back of the lower leg,
Fat with one or more carbons linked via double bonds.
called monounsaturated fatty acids
What is an unsaturated fat?
unsaturated fat has one double bond
What does a pH of 11 suggest about the concentration of H+ ions in a solution?
What is a low H+ concentration/a high OH- concentration?
In RNA, adenine (A) pairs with ____.
What is uracil (U)?
The _____ splits the body into left and right halves.
What is the midsagittal plane?
Name the abdominopelvic region:
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/article/hypochondriac-region/8ROrFflBexwvxwnkGSzA_KL4uJOIWfbJW38zqAyTw_underwear-Hypochondriac-region.png)
What is hypochondriac region?
The build-up of a molecule via the removal of water.
What is dehydration synthesis?
A positively charged molecule.
cations
What is a cation?
cation is a positively-charged
Attractive force between an electronegative atom of one molecule and an electropositive H+ of another molecule. Common among H2O molecules. Weak.
What is a hydrogen bond?
