This is an example of a ______ bone.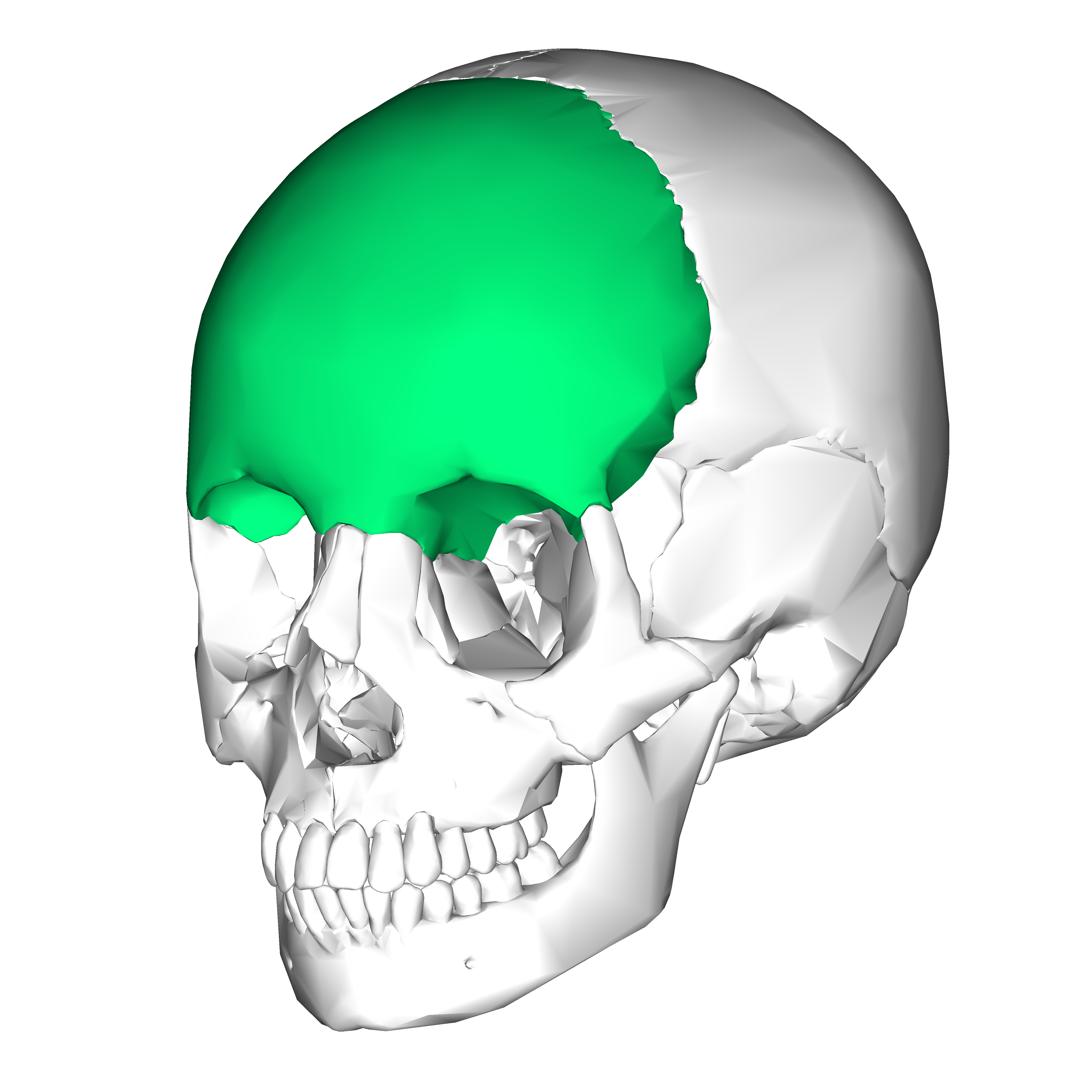
What is a flat bone?
This term refers to the process of bone tissue formation.
What is ossification or osteogenesis?
This type of fracture occurs when the bone ends are out of normal alignment.
What is a displaced fracture?
This structure is found within the diaphysis of long bones. It contains yellow bone marrow in adults and is the primary storage for fat.
This tubular shaft forms the long axis of a bone and is filled with yellow bone marrow.
What is the diaphysis?
These bone-building cells secrete a matrix of collagen and ground substance called an osteoid.
What are osteoblasts?
This type of growth is responsible for the lengthening of long bones at the epiphyseal growth plate.
What is interstitial growth?
This disease occurs when osteoclast activity exceeds osteoblast activity, leading to fragile bones.
What is osteoporosis?
This law states that bones grow or remodel in response to the stress placed on them.
What is Wolf's law?
This dense outer layer of bone appears smooth and solid.
What is compact bone?
These giant, multinucleate cells are responsible for the break down and resorption of bone.
What are osteoclasts?
This type of growth where bones increase in width/thickness can happen throughout life in response to stress or weight gain.
What is appositional growth?
This condition often caused by vitamin D deficiency results in poorly mineralized bones, leading to soft, weak bones.
What is osteomalacia?
This layer of bone covers external surfaces except for the joints and consists of an outer fibrous layer and an inner osteogenic layer.
What is the periosteum?
An example of this type of bone is the patella.
What is a sesamoid bone?
These mature bone cells sit in their lacunae and are responsible for maintaining their matrix, and therefore bone.
What are osteocytes?
Most bones except for the clavicles and skull bones are formed through this process during fetal development using a hyaline cartilage model.
What is endochondral ossification?
This type of fracture occurs when the skin is penetrated by the bone.
What is an open fracture?
This hormone, secreted by bones, helps regulate insulin secretion, glucose levels, and metabolism.
What is osteocalcin?
These are the concentric rings on bone matrix found within an osteon.
What are lamellae?
What are osteoprogenitor cells?
This bone forming process begins within fibrous connective tissue to form bones like the frontal and parietal bones and the clavicles.
What is intramembranous ossification?
This type of fracture occurs when the bone is not broken all the way through.
What is an incomplete fracture?
What is the proliferation (growth) zone?