Name the five types of bones.
Flat, irregular, short, long, and sesamoid.
What is the name of the highlighted bone?
Define endochondral and intramembranous ossification.
Endochondral: Hyaline cartilage serves as the template for bone formation.
Intramembranous: Compact and spongy bones are formed from mesenchymal tissue.
:watermark(/images/watermark_only.png,0,0,0):watermark(/images/logo_url.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/anatomy_term/flexion-of-knee/ldiYtHYtg1S9JtrHjGbC6g_Flexion_of_knee.png)
What type of movement is demonstrated in the image?
Flexion
What is the most important phrase in anatomy?
Structure determines function!
This category of bones is distinguished by their smooth surfaces that allow for muscle attachment.
Flat Bones
What is the function of short bones? (Structure determines function.)
Short bones provide flexibility, stability, and aid in movement.

What is the name of the structures represented by letter B?
Epiphysis
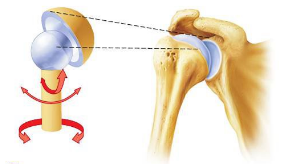
What type of synovial joint is demonstrated in the image?
Ball and socket

What structures are highlighted in the image?
Metatarsals

What is the name of this bone? What type of bone is it?
Femur - long

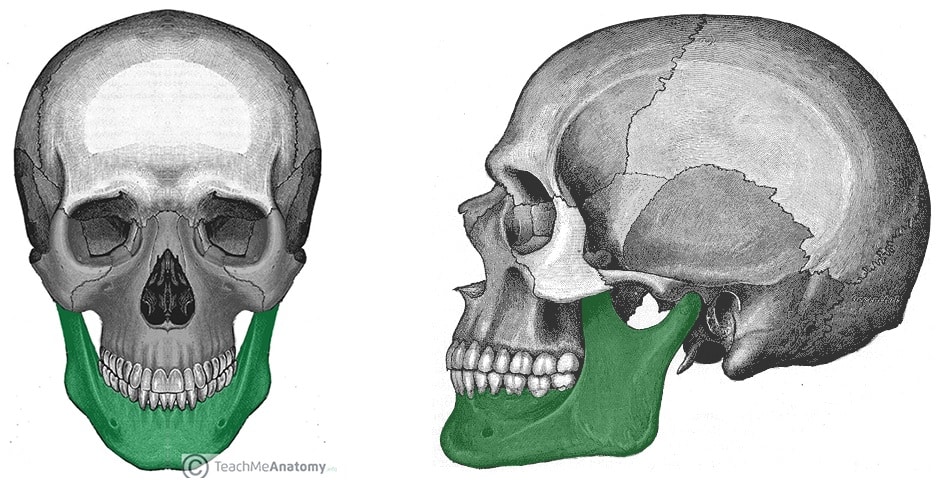
Name the bone highlighted in green.
Fibula
(Bonus 100: How would you describe the location of the green bone in regards to the blue bone using anatomically language?)
Define appositional versus interstitial growth. Where does each type of growth primarily occur?
Appositional: Bone growth in diameter. Most commonly seen in the diaphysis.
Interstitial: Bone growth in length . Most commonly seen in the epiphysis.
How many names does each type of joint have? What are the categories of each name? What does each name tell us?
2
One is the anatomical name and one is the physiological name.
The anatomical name tells us the joint make up, and the physiological movement tells us how well the joint moves.
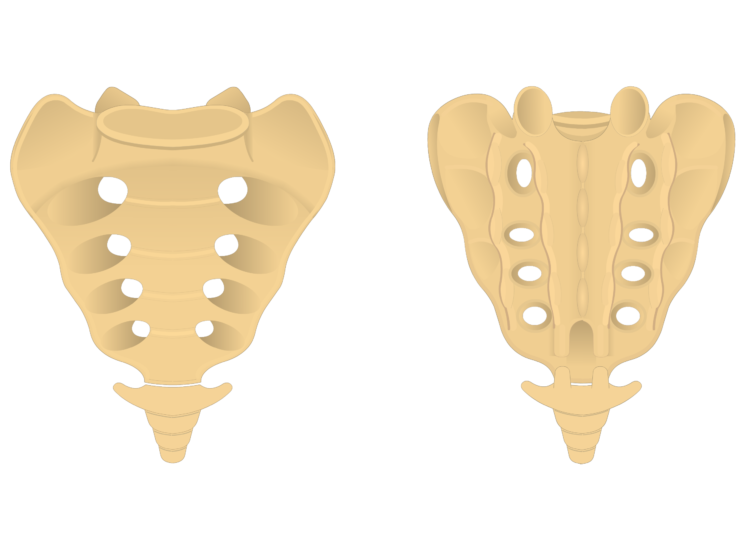
What bones are highlighted in the image? What type of bone are they?
Pelvis - flat
What is the name of this bone? What type of bone is it?
Irregular - sacrum
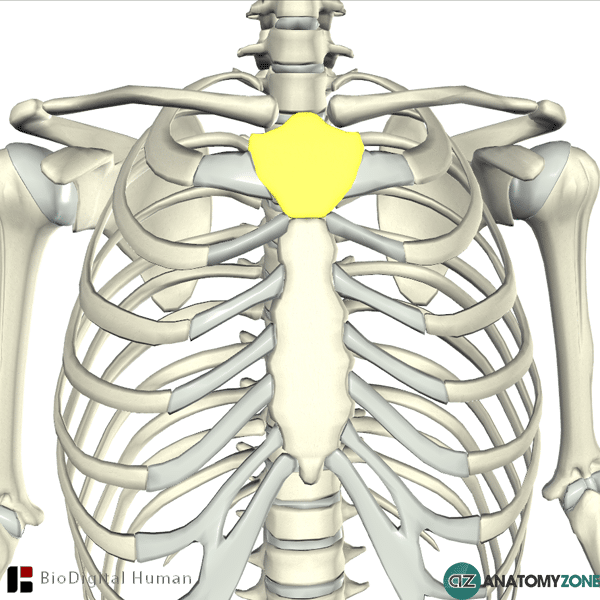
What is the name of this bone? What type of bone is it?
Manubrium - flat

What structure is demonstrated by letter C? What type of growth occurs here?
Epiphyseal plate - interstitial growth
What are the 2 names for each of the 3 joint types?
Fibrous - Synarthrosis
Cartilaginous - Amphiarthrosis
Synovial - Diarthrosis

Identify the bone in the image. What type of bone is it? What is its common name?
Patella - sesamoid - knee cap

What is the name of this bone? What type of bone is it?
Radius - long

Name the three different vertebral sections we discussed in class.
100 Bonus Points: Name the green and red sections.
Orange: Cervical
Pink: Thoracic
Blue: Lumbar
(Green: Sacral - Red: Coccyx)
Define osteoblast, osteoclast, and osteocytes.
Osteoclasts: Bone cells that are responsible for degrading old bone.
Osteoblasts: Bone cells that produce osteoid (new bone).
Osteocyte: Bone cells that maintain bone tissue and support the matrix.
Give an example of each type of joint.
Diarthrosis: Knee and shoulder
Synarthrosis: Cranial sutures and teeth sockets
Amphiarthrosis: Pubic symphysis and vertebrae
What is the function of each type of bone?
Short - flexibility/ wide range of movement
Long - support and aids in mechanical movement
Irregular - protects nerves
Flat - Protect tissue
Sesamoid - reduces friction