What was left of H.M.'s memory after his surgery?
Left with amnesia that only provided him with memories of past and facts about his family and self, but was left unable to form NEW memories
What type of memory is in use when you run back to your locker to retrieve you phone and jot down a phone number you friend just gave you?
working memory
What is synaptic plasticity?
The ability for the synapses to remodel themselves
Fusiform face area (FFA)
Which layer during development signals for secretion of the sonic hedgehog signaling molecule?
mesoderm
no
What type of memory would one of being with you family on a summer vacation in 2018 be?
Episodic memories
Integrates emotion into memories, especially episodic memories
If a patient came in, presenting with the ability to understand words, but the inability to produce coherent words, what might they have?
Broca's aphasia (nonfluent)
What is the purpose of a growth cone?
located at the tip of the axon explores the enviornment and seeks out destination during growth of axon
What operation did H.M. undergo that left him unable to form new memories?
H.M. had his medial temporal lobes removed along with most of his hippocampus
Grid cells are involved in what type of emory and what are their function?
Grid cells are involved in spatial memory, and allow one to perceive exactly where they are in a place.
the lateral habenula
Damage to the left temporal lobe might result in what?
Wernicke's aphasia (fluent)
During synapse formation, what is the purpose of the astrocytes?
they contact neurons and provide support and scaffolding to neurons.
why was H.M.'s non-declaritive memory still intact?
His PFC, cerebellum, basal ganglia were all intact, which are all involved in this type of memory
What part of the brain is involved in working memory?
The PFC (prefrontal cortex) is most active during this type of memory
Which part of the PFC allows for one to have self regulation and dicipline in decision making?
The lateral PFC
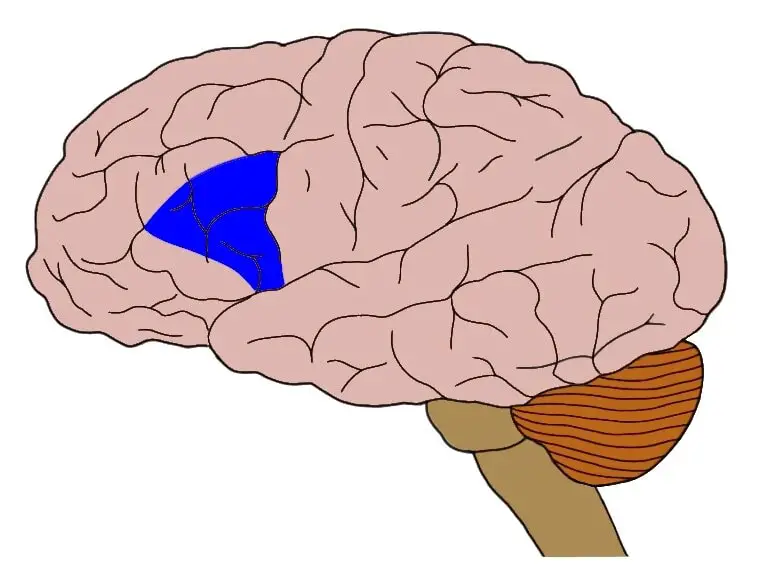 what area of the brain is this?
what area of the brain is this?
brocas area
why do alcohol, cocaine, and other unsafe suba=stances affect the neurological state of the baby?
they disrupt migration, leading to disability or epilepsy
If H.M. had instead had parts of his PFC Removed, what types of memory might have been affected?
Working, nondeclaritive, semantic
What part of the brain aids the hippocampus in determining the "what" of episodic memories?
The parahippocampal region
It is involved in pain perception and stress response and contains receptors such as those for morphine and oxycodone for reducing pain
Damage to FOXP2 gene results in what?
difficulty moving jaw and mouth
90% of migration is controlled by what?
the radial glia