This structure will induce formation of the neural plate and underlie the neural tube
What is the notochord?
the telencephalon turns into these adult brain structures
What is the cerebrum?
neural crest cells migrate away from the neural tube to form these structures (be very general)
What are ganglia and other special tissues?
neuroblasts form the mantle layer around the neuroepithelial cells that will ultimately become this structure
What is gray matter?
spinal nerves are formed by these structures
What are processes from dorsal and ventral nerve roots?
closure of the anterior and caudal neuropore is highly dependent on availability of this substance
What is folic acid?
the mesencephalon turns into these adult brain structures
What is the midbrain of the brainstem?
this is the origin of neural crest cells
What are the neural folds?
gliablasts will ultimately become these cells
What are astrocytes and oligodendrocytes?
the pituitary gland is derived from these two structures
What is Rathke's pouch and the infundibulum?
TGF-B is an important signaling molecule in this type of differentiation
What is longitudinal differentiation?
*BONUS: What is longitudinal differentiation?
the metencephalon turns into these adult brain structures
What is the pons of the brainstem and the cerebellum?
name three cells that are derived from neural crest cells
microglial cells come from this cell lineage
What is the mesenchymal cell lineage?
The alar plate and basal plate of the myelencephalon (medulla) ultimately have two different functions. These are those functions.
alar plate => sensory (dorsal and lateral)
Basal plate => motor (ventral and medial)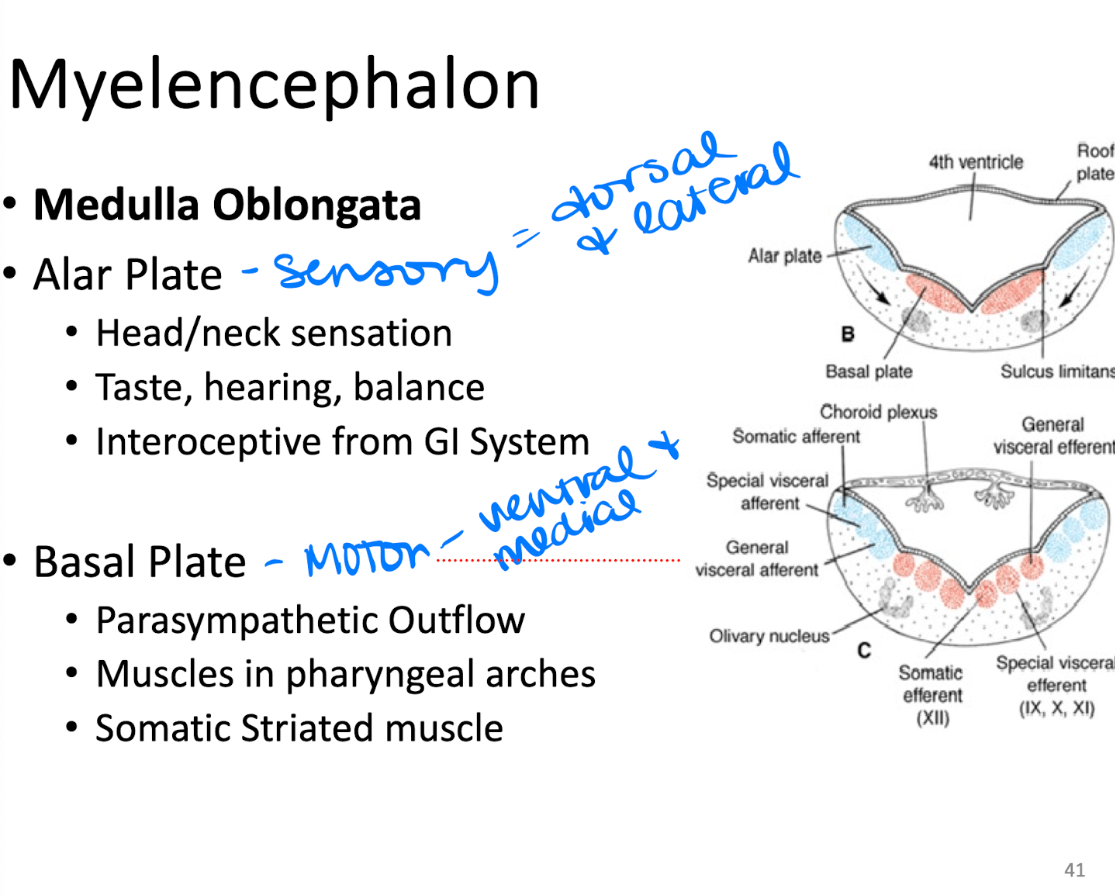
Around day 28, the neural tube is divided into three parts, the prosencephalon, mesencephalon, and rhombencephalon, which are known as the primary ventricles. The primary ventricles further differentiate into secondary ventricles known as....
prosencephalon => telencepalon & diencephalon
mesencephalon => mesencephalon
rhombencephalon => metencephalon & myelecephalon
the myelencephalon turns into these adult brain structures
What is the medulla of the brainstem?
It is important to differentiate between derivatives from the neural tube vs the neural crest. These are the three main structures that are derived from the neural tube.
What are
1. CNS neurons and supporting cells
2. motor neurons of PNS
3. presynaptic autonomic neurons
The marginal layer will contain nerve fibers emerging from neuroblasts that will become this structure
What is white matter?
What are Purkinji cells?
transverse differentiation is also dependent on signaling systems, these are the signaling pathways important for dorsal vs ventral pattterning
Wnt, BMP for dorsal patterning
Shh for ventral patterning
The secondary brain vesicles turn into which adult neural canal regions?
telencephalon = lateral ventricles
diencephalon = third ventricle
mesencephalon = cerebral aquaduct
metencephalon & myelencephalon = fourth ventricle
neural crest cells that do not migrate and stay near the neural crest become this structure
What is the DRG?
this is the initial shape of neuroblasts
What is round and apolar?
the roof plate of the diencephalon gives rise to this structure where as the base give rise to this structure.
roof = choroid plexus
base = hypothalamus