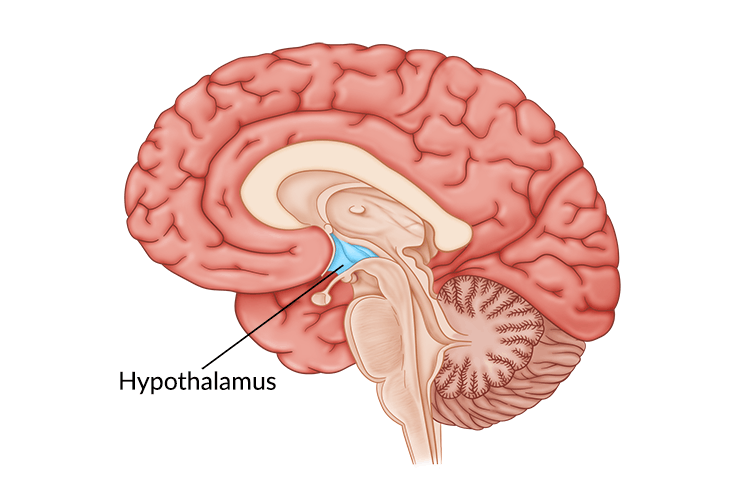
What is the hypothalamus?
Hearing and memory
What are the main functions of the Temporal lobe?

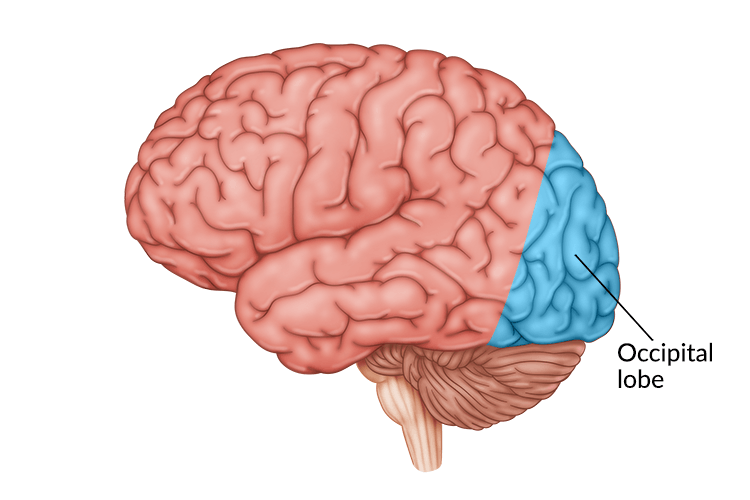
Function of the occipital lobe
What is vision?
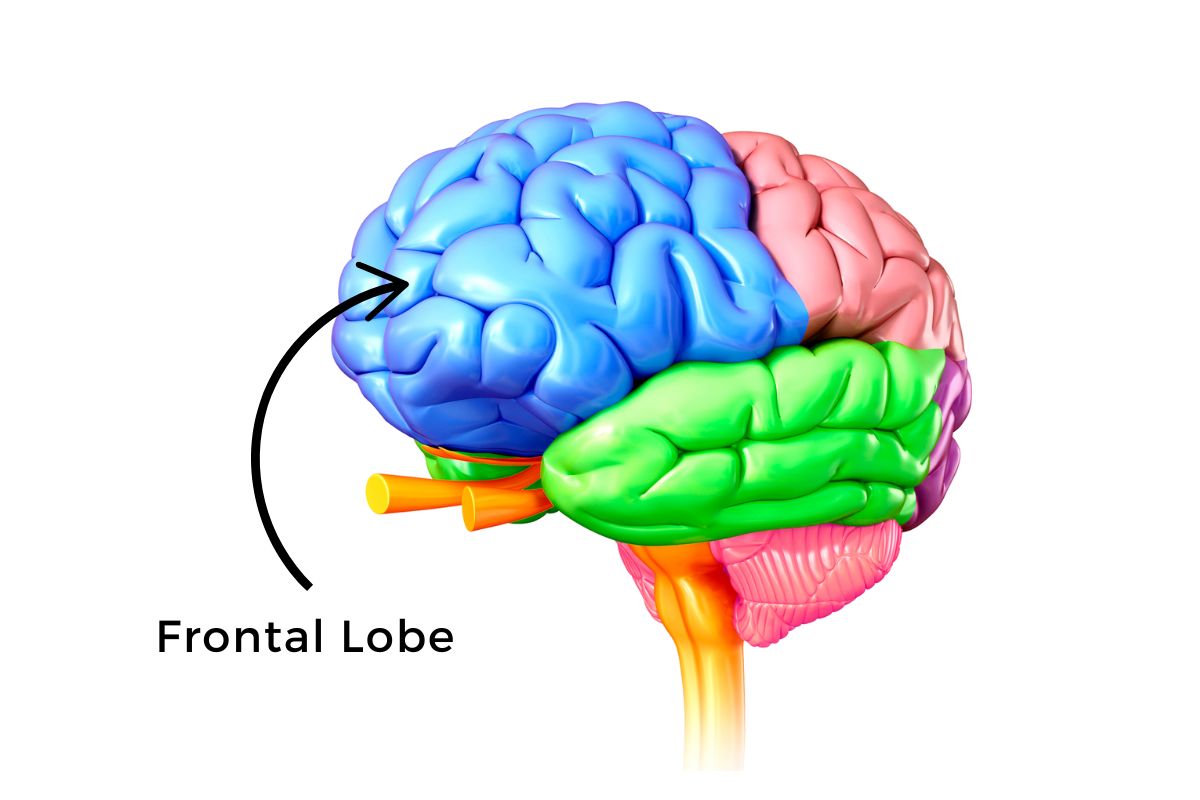
This lobe helps you plan, organize, understanding and producing speech
What is the Frontal Lobe?
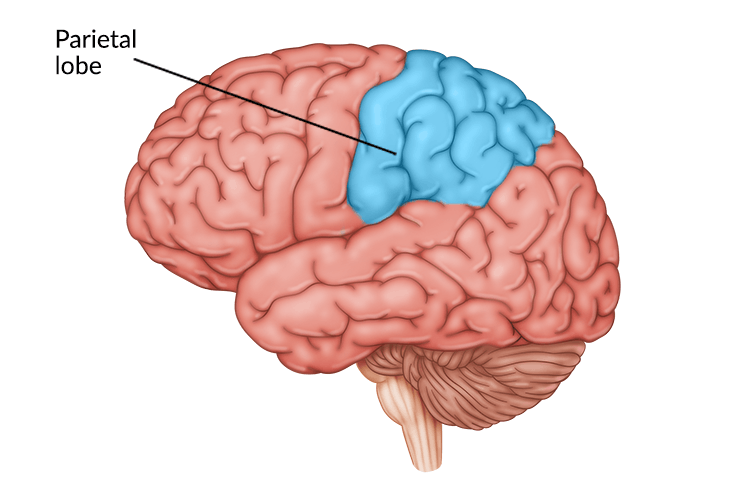
Between occipital lobe and central sulcus
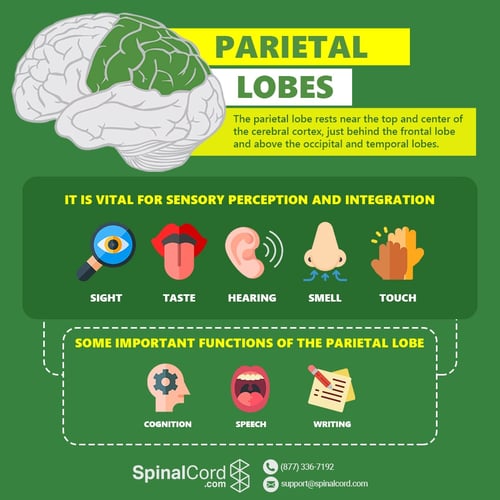
What is the location of the parietal lobe?
What is the location of the hypothalamus?
The amygdala, hippocampus, and the fusiform gyrus
What are the key structures of the temporal lobe?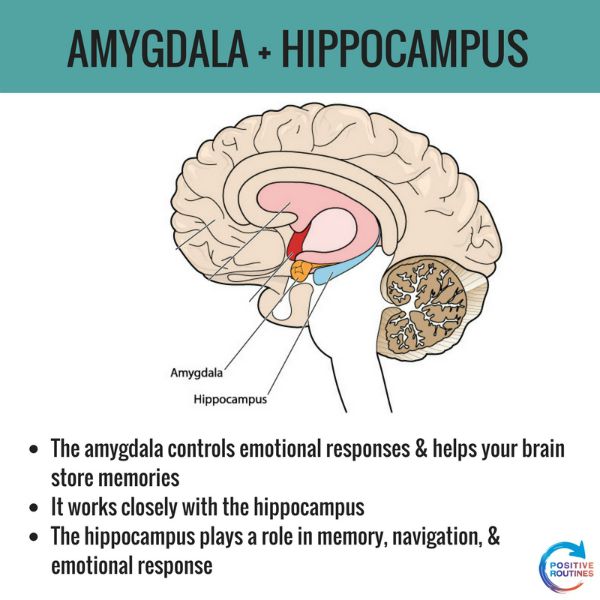
The occipital lobe is located where in the brain?
What is, Posterior?
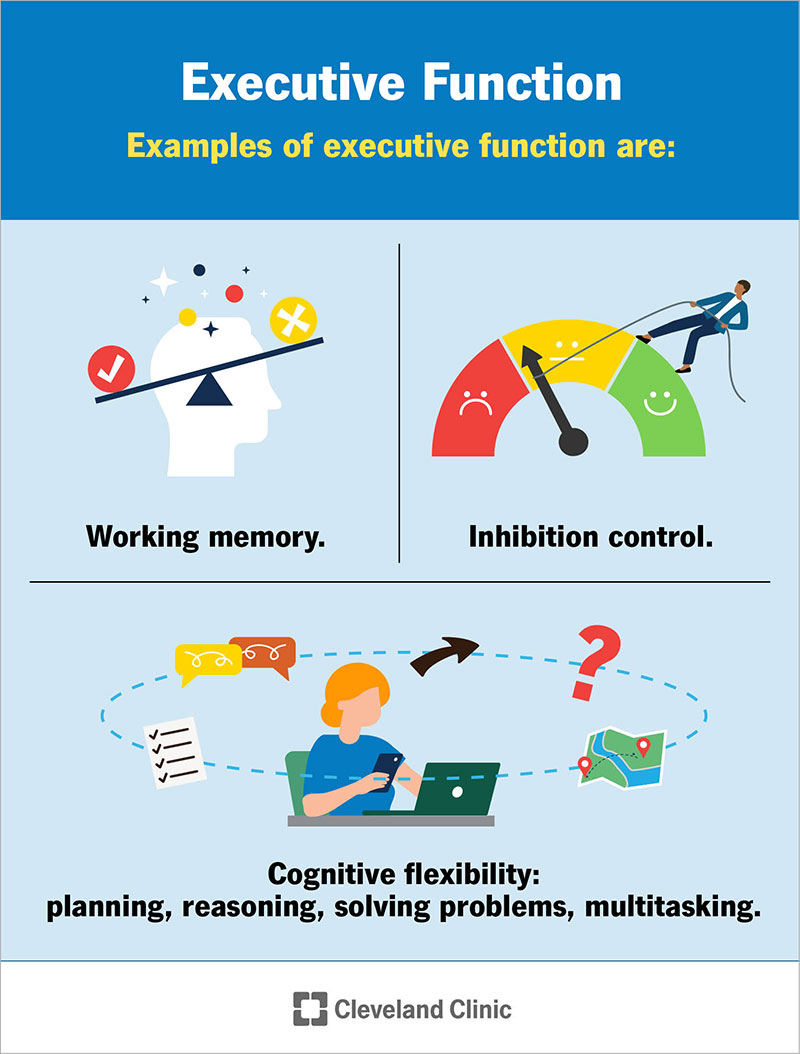
Lots of complex functions that include making decisions and working memory
What is the prefrontal cortex?
Receives sensation from touch receptors, muscle-stretch receptors, and joint receptors
What is the postcentral gyrus?
:watermark(/images/watermark_only_413.png,0,0,0):watermark(/logos/logo_url_sm.png,-10,-10,0):format(jpeg)/images/learnable/postcentral-gyrus/UWnG1CKZRoRDtJOTUsfVg_Gyrus_postcentralis_02.png)
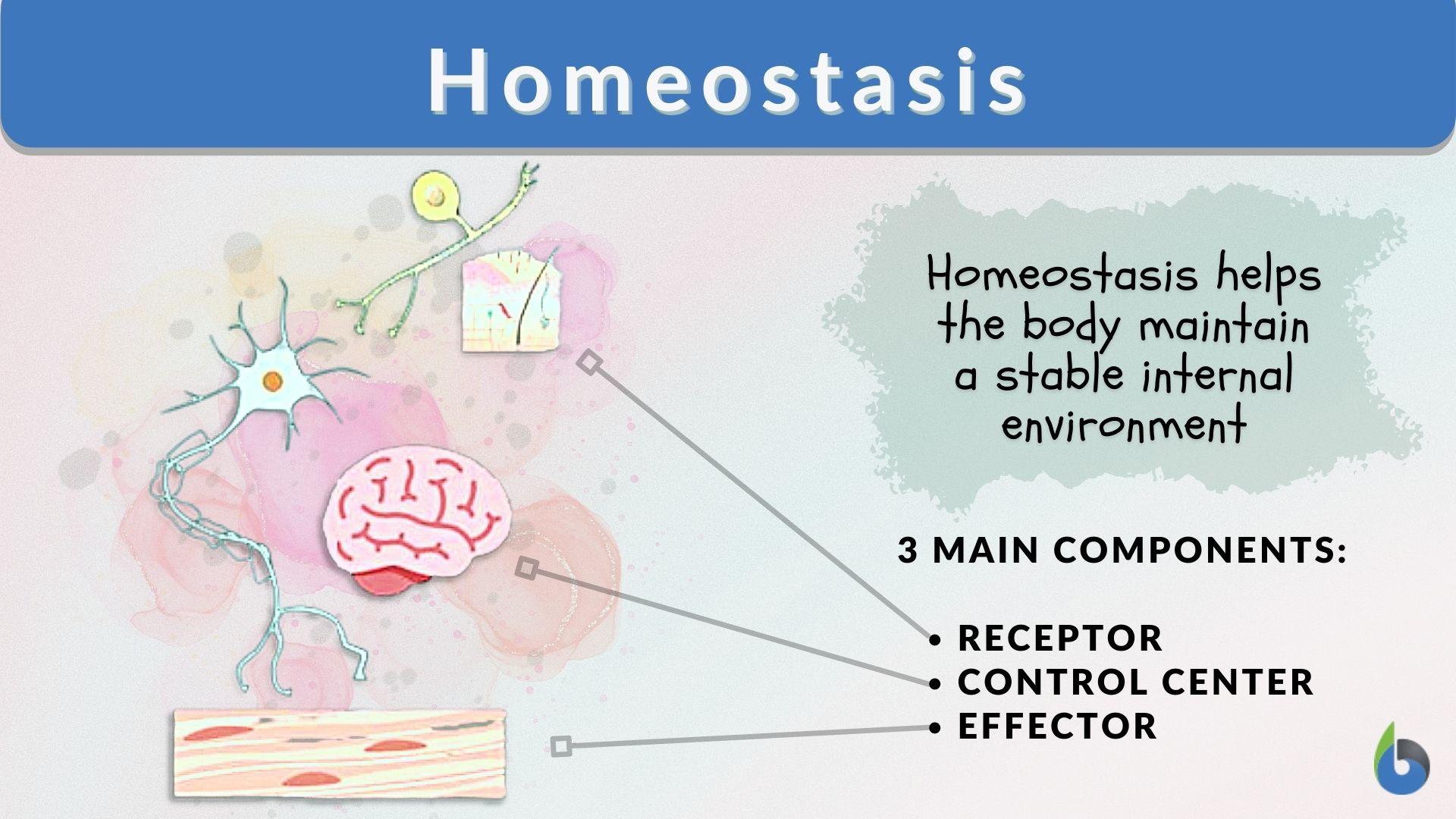
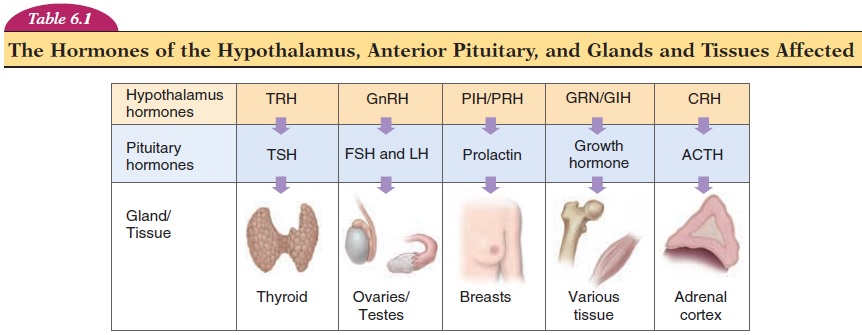
Maintain homeostasis by linking the endocrine system and nervous system
What is the main function of the hypothalamus?
What did monkeys fail to display after temporal lobe damage?
Damage to this lobe leads to what?
What is no vision in dreams, no visual imagery, and no conscious visual perception?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/what-are-the-symptoms-of-an-occipital-stroke-3146433-FINAL-814dee4ff85a44e08251a4bcee9536ff.png)
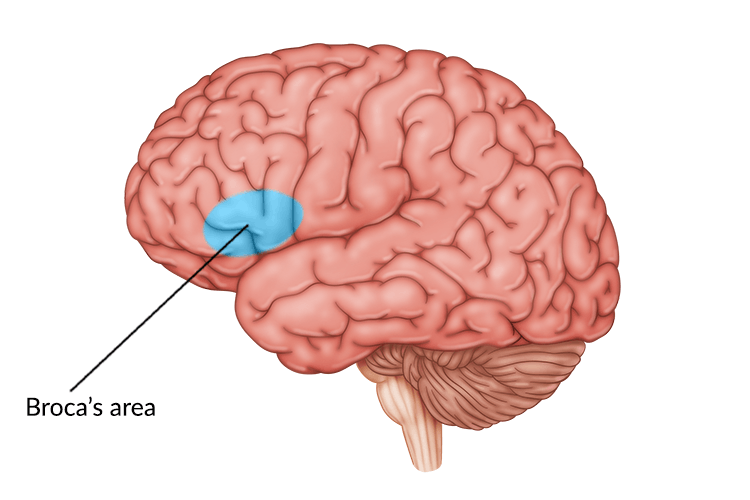
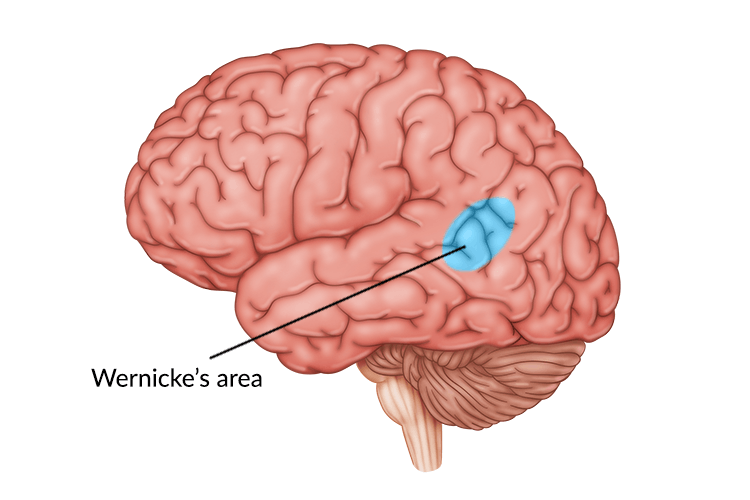
Critical for language production
What is Broca’s Area?
The area responsible for motor-planning/control
What is the somatosensory area of the parietal lobe?
Feeding, fight or flight, sexual behavior, temperature regulation, and drinking
What are the motivated behaviors?
What is a clinical presentation of damage to the temporal lobe?
This part of the occipital lobe interprets basic visual info, like orientation and size.
What is the Primary Visual Cortex?
Causes personality shifts and changes in executive function abilities
What is the damage to the frontal lobe?
Spatial disorientation, hemispatial neglect, motor coordination problems, sensory deficits
What happens when the parietal lobe is damaged?
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH), gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GRH), growth hormone-releasing hormone (GHRH), corticotropin-releasing hormone (CRH), somatostatin, and dopamine.
What are the hormones produced by the hypothalamus?
selective transcortical amygdalohippocampectomy (removal of the temporal lobe)
What eliminates or significantly terminates seizures in >80% of patients with temporal lobe seizures?
This disorder caused by occipital damage, results in the inability to recognize faces
What is prosopagnosia?

Damage to frontal lobe can lead to trouble switching between different concepts
What is cognitive flexibility?
Loss of skilled movement
What is apraxia?