Application of pulling force to restore or maintain alignment for fracture healing.
What is traction?
Blood clot along the intimal lining of large vein. Best treatment is prevention. Also, anticoagulants like lovenox or heparin
What is a DVT?
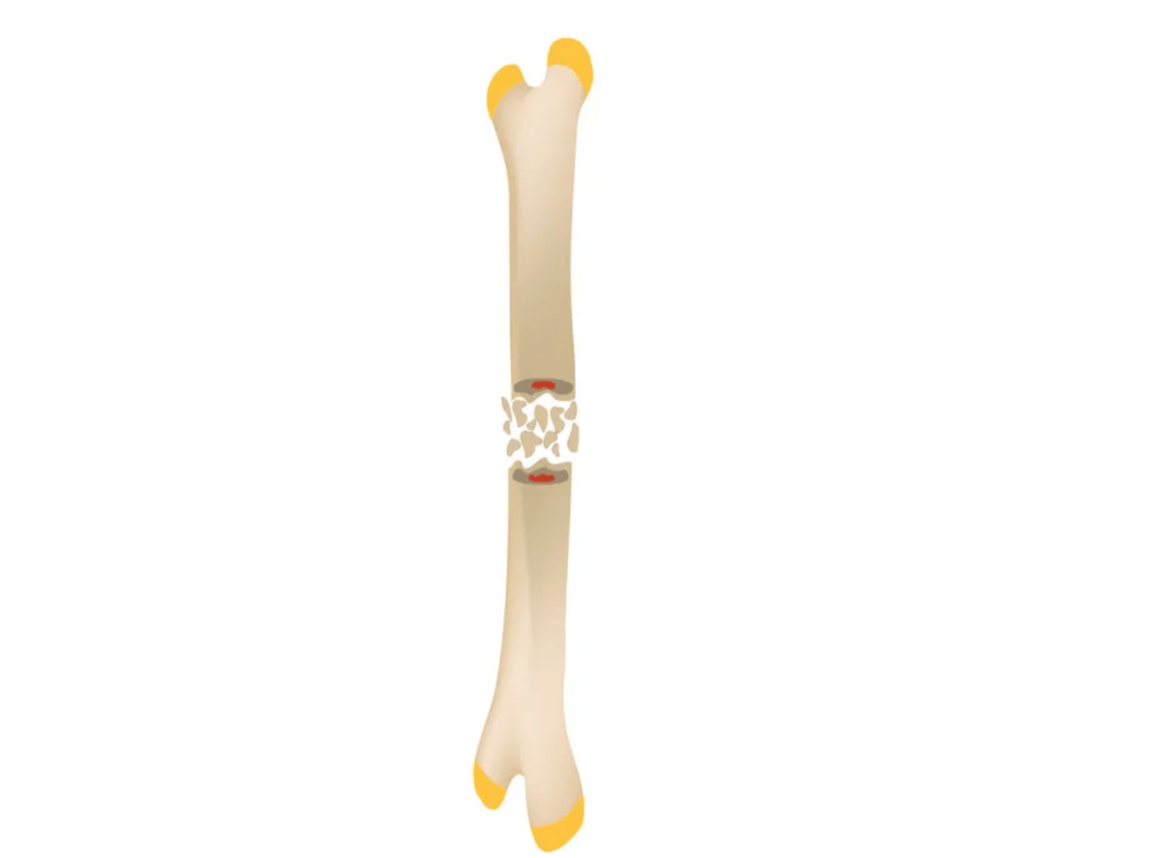
What is comminuted fracture?
Anterior trunk skin appears red, blistered, and blanch able after exposure to a thermal burn. What is the total body surface area?
18%
This type of fracture puts patients at greatest risk for infection
What is open fracture?
This condition is most likely to occur with open fracture. Requires long term abx therapy and sometimes surgical debridement in OR.
What is osteomyelitis?
This is the reasons patients initially receive splints before casts.
What is allowing for swelling to prevent compartment syndrome?
These are signs of inhalation injury
What is singled nasal hair, sooty sputum, burned eyebrow, ect.
Figure 8 wrap, ROM to keep preserved joint flexible, prone position several times a day, position in dependent position.
What is care for patient s/p below knee amputation?
This pain occurs after amputation on side of affected extremity. Higher risk if patient previously experienced pain in limb prior to amputation.
What Is phantom limb pain?
This is indicated after severe burn causing ridged crust around compartment with decreased blood flow
What is escahrotomy
Tachypnea, SOB, tachycardia and chest pain, ALOC may all be manifestations of this long bone fracture complication.
What is fat embolism syndrome?
The patient should do this if they recover a limb or appendage after a traumatic amputation.
What is place in bag,wrap in towel, place bag on ice.
These are the antibiotics that may be used for treatment with open fracture.
What is anecf, gentamicin, and flagyl?
These are priorities in emergent phase
Airway, calculate TBSA, fluid resuscitation, and pain control
Early signs are paresthesia pallor and pain. Pulselessness is late sign. Treatment is fasciotomy.
What is compartment syndrome?
What are pulses, motor, sensation?
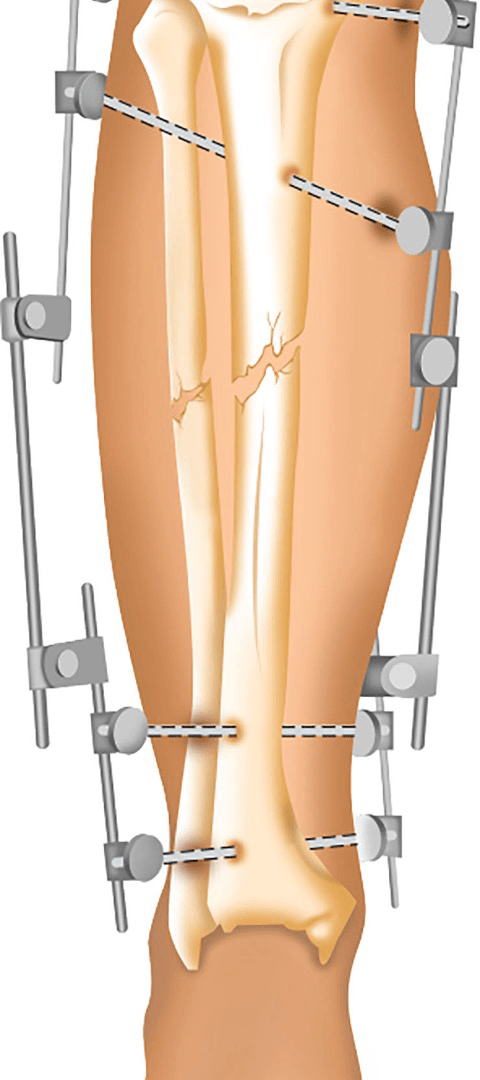
What is external fixation?
These are priorities in the acute phase
Prevent infection, nutrition, early ROM, pain control