
What is the rhythm above?
A. Normal sinus rhythm
B. Atrial flutter
C. Ventricular tachycardia
D. Atrial fibrillation
D. Atrial fibrillation
A patient with an occluded coronary artery is admitted and has an emergency percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty (PTCA). The patient is admitted to the cardiac critical care unit after the PTCA. For what complication should the nurse most closely monitor the patient?
A) Arrhythmias
B) Bleeding at insertion site
C) Left ventricular hypertrophy
D) Congestive heart failure
B. Bleeding at insertion site
Bonus: if a patient begins to bleed from a site what do you do?
The nurse is caring for a patient who is in status epilepticus. What medication does the nurse know may be given to halt the seizure immediately?
A) Intravenous phenobarbital (Luminal)
B) Intravenous diazepam (Valium)
C) Oral lorazepam (Ativan)
D) Oral phenytoin (Dilantin)
B. IV Valium
A nurse in the ICU receives report from the nurse in the ED about a new patient being admitted with a neck injury he received while diving into a lake. The ED nurse reports that his blood pressure is 85/54, heart rate is 53 beats per minute, and his skin is warm and dry. What does the ICU nurse recognize that the patient is probably experiencing?
A) Anaphylactic shock
B) Neurogenic shock
C) Septic shock
D) Hypovolemic shock
B. Neurogenic shock
The nurse is caring for a patient with a diagnosis of Addisons disease. What sign or symptom is most closely associated with this health problem?
A) Truncal obesity
B) Hypertension
C) Muscle weakness
D) Moon face
C. muscle weakness
When a patient has long-term atrial fibrillation, the nurse would expect to include which drug in the plan of care to minimize the greatest risk that is commonly associated with atrial fibrillation?
A. Beta blockers
B. Digitalis
C. Anticoagulants
D. Antiarrhythmics
C. Ineffective cardiopulmonary tissue perfusion related to coronary artery disease
A patient with increased ICP has a ventriculostomy for monitoring ICP. The nurses most recent assessment reveals that the patient is now exhibiting nuchal rigidity and photophobia. The nurse would be correct in suspecting the presence of what complication?
A) Encephalitis
B) CSF leak
C) Meningitis
D) Catheter occlusion
C. Meningitis
The nurse is transferring a patient who is in the progressive stage of shock into ICU from the medical unit. The medical nurse is aware that shock affects many organ systems and that nursing management of the patient will focus on what intervention?
A) Reviewing the cause of shock and prioritizing the patients psychosocial needs
B) Assessing and understanding shock and the significant changes in assessment data to guide the plan of care
C) Giving the prescribed treatment, but shifting focus to providing family time as the patient is unlikely to survive
D) Promoting the patients coping skills in an effort to better deal with the physiologic changes accompanying shock
B. Assessing and understanding shock and the significant changes in assessment data to guide the plan of care
You are developing a care plan for a patient with Cushing syndrome. What nursing diagnosis would have the highest priority in this care plan?
A) Risk for injury related to weakness
B) Ineffective breathing pattern related to muscle weakness
C) Risk for loneliness related to disturbed body image
D) Autonomic dysreflexia related to neurologic changes
A. Risk for injury related to weakness
Prior to discharge from the Emergency Department, the nurse prints a rhythm strip on a patient and notices that the P wave cannot be detected and the QRS complex is 0.24 seconds. This is a change in the patient's condition. What is the best action for the nurse to take?
a. Measure the PR interval.
b. Prepare the patient for discharge.
c. Notify the physician of this abnormal strip.
d. Continue to monitor for abnormalities.
C. Notify the provider of this abnormal strip
B. Mitral stenosis
C. Participate in interventions to increase cerebral perfusion pressure
C. The release of catecholamines that creates an increase in metabolic rate and caloric requirements
The nurse is planning the care of a patient with hyperthyroidism. What should the nurse specify in the patients meal plan?
A) A clear liquid diet, high in nutrients
B) Small, frequent meals, high in protein and calories
C) Three large, bland meals a day
D) A diet high in fiber and plant-sourced fat
B. small, frequent meals, high in protein and calories
A 38-year-old female is brought to the Emergency Department with complaints of her "heart beating out of her chest". She is diaphoretic, tachypneic and her BP is 70/40. The cardiac monitor shows supraventricular tachycardia. Valsalva maneuvers and three doses of Adenosine have not been successful. The nurse should immediately:
A. prepare the patient for synchronized cardioversion.
B. give Epinephrine 1 mg IV and repeat in 3 minutes.
C. give Adenosine 6 mg IV per protocol.
D. perform unilateral carotid massage.
A. prepare the patient for synchronized cardioversion
The staff educator is presenting a workshop on valvular disorders. When discussing the pathophysiology of aortic regurgitation the educator points out the need to emphasize that aortic regurgitation causes what?
A) Cardiac tamponade
B) Left ventricular hypertrophy
C) Right-sided heart failure
D) Ventricular insufficiency
B. Left ventricular hypertrophy
What should the nurse suspect when hourly assessment of urine output on a patient postcraniotomy
exhibits a urine output from a catheter of 1,500 mL for two consecutive hours?
A) Cushing syndrome
B) Syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone (SIADH)
C) Adrenal crisis
D) Diabetes insipidus
D. Diabetes insipidus
The nurse in the ICU is admitting a 57-year-old man with a diagnosis of possible septic shock. The
nurses assessment reveals that the patient has a normal blood pressure, increased heart rate, decreased
bowel sounds, and cold, clammy skin. The nurses analysis of these data should lead to what preliminary
conclusion?
A) The patient is in the compensatory stage of shock.
B) The patient is in the progressive stage of shock.
C) The patient will stabilize and be released by tomorrow.
D) The patient is in the irreversible stage of shock.
A. the client is in the compensatory stage of shock
A. A 75-year-old female patient with osteoporosis
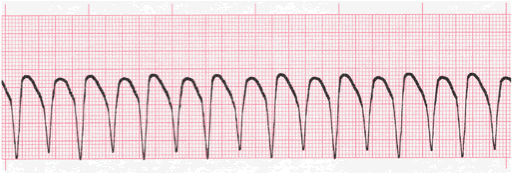
As the nurse, you see the following on the monitor of your patient. Which of the following will you do first? Select all that apply
A. RUN
B. assess your patient
C. cardioversion
D. give an anti-arrhythmic
E. if pulseless, initiate CPR
A, B, E
The nurse is assessing a patient with acute coronary syndrome (ACS). The nurse includes a careful history in the assessment, especially with regard to signs and symptoms. What signs and symptoms are suggestive of ACS? Select all that apply
A) Dyspnea
B) Unusual fatigue
C) Hypotension
D) Syncope
E) Peripheral cyanosis
A, B, D
The nurse caring for a patient in a persistent vegetative state is regularly assessing for potential complications. Complications of neurologic dysfunction for which the nurse should assess include which of the following? Select all that apply
A) Contractures
B) Hemorrhage
C) Pressure ulcers
D) Venous thromboembolism
E) Pneumonia
A, C, D, E
B, C, D
B, D