What type of organism is single-celled, prokaryotic, and can be helpful, harmless, or harmful?
Bacteria
In your own words, define what an infection is and explain how it begins inside the body.
An infection happens when microorganisms invade the body and begin multiplying. Once established, these microbes disrupt normal body functions.
Your little brother comes home with a runny nose and fever. What's one simple thing you can do to reduce your chances of getting sick too?
Wash your hands often
Avoid close contact
Disinfect any contaminated surfaces
What were some of the early symptoms that Zach's illness was more than just normal aches or a common cold?
Persistent pain and rising fever that worsened instead of improving with rest and OTC medicine.
This graph shows bacteria in a lab doubling quickly over time. Why can't this kind of rapid growth continue forever in the real world?
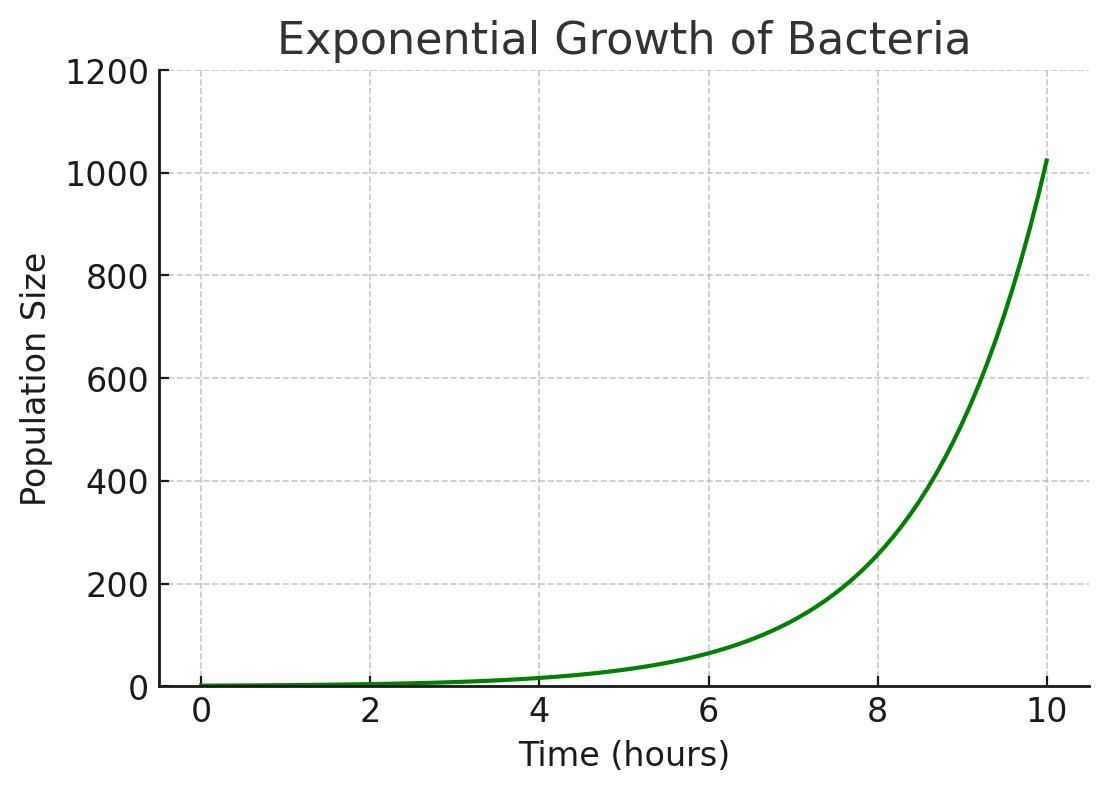
Because in nature, bacteria eventually run out of resources like food, space, or moisture, so their growth slows down instead of going on forever.
Viruses are considered nonliving particles. What key feature of their life cycle makes scientists classy them in this way?
They require a host cell to reproduce and cannot survive on their own.
What do we call an illness that is caused by pathogens and can spread from person to person? Give one example.
Infectious disease
Examples: Covid, Flu, Strep Throat, Tuberculosis, Scarlet Fever, Bubonic Plague, etc.
A customer at a restaurant orders a rare hamburger. Why could eating undercooked ground beef be dangerous?
Undercooked beef can still contain harmful bacteria like E. coli. Because the meat isn't heated enough to kill the bacteria, eating it can cause serious illness.
Zach later experienced confusion and hallucinations. What do these symptoms tell us about how an infection can affect the whole body, not just one area?
They show that infections can spread and disrupt major body systems, including the brain, when fevers and toxins overwhelm normal function.
This graph shows flu cases rising quickly from November to January and dropping by March. What does this pattern tell you about how the flu spreads during the year?
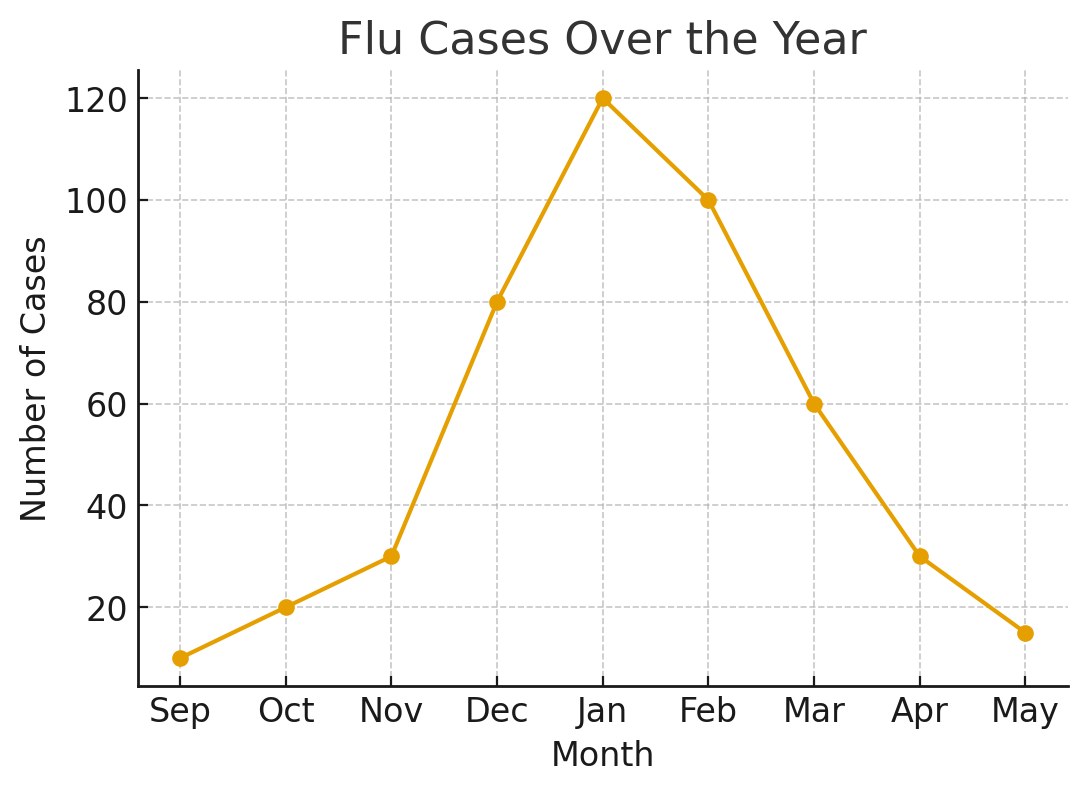
Flu cases peak in the winter and decline as the season changes.
If a type of bacteria is labeled "pathogenic," what does that mean for human health? Give one example.
Pathogenic bacteria can cause disease.
Examples: MRSA, E. coli, Salmonella, etc.
Which body system protects against invading microorganisms, and how does it respond when bacteria enter through a cut?
The immune system.
It responds by sending out white blood cells in an attempt to destroy the invading bacteria.
We use the acronym FAT TOM to explain the conditions that allow bacteria to grow. What does each letter stand for?
Food Time
Acidity Oxygen
Temperature Moisture
Why did doctors eventually need to use life-support measures like a ventilator to keep Zach alive?
The infection had spread so severely that he was unable to get enough oxygen by breathing on his own. Medical machines were needed to keep him stable.
The population in this graph grows rapidly at first, but then levels off around year 6. What real world factors could explain why growth slowed?
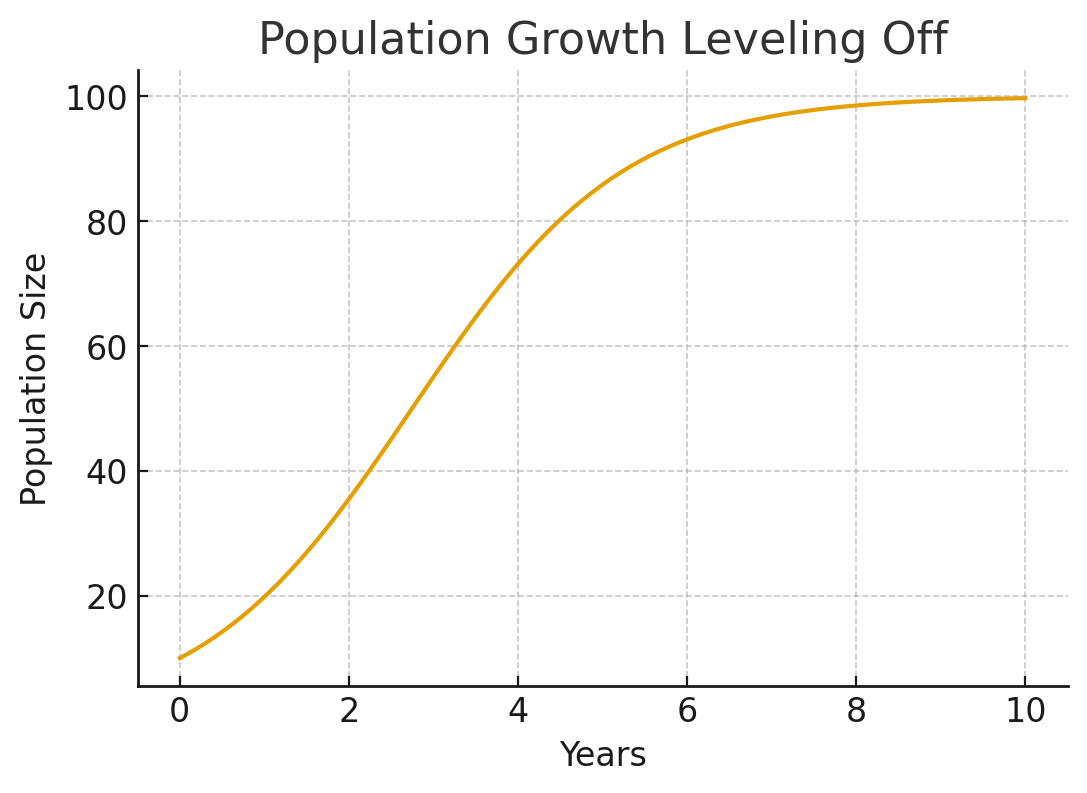
Resources like food, space, or other environmental conditions became limited, so the population couldn't keep growing.
Bacteria sometimes form sticky communities that cling to surfaces, like plaque on your teeth. What do we call this type of structure, and why does it make bacteria harder to remove or kill?
Biofilm
The bacteria are protected by a sticky protein-sugar matrix that shields them from antibiotics and the body's immune defenses.
Why is it important for doctors to correctly identify a MRSA infection? What could happen if it's mistaken for a regular staph infection?
Correct identification is critical because MRSA is resistant to many antibiotics.
If misidentified, doctors may use ineffective treatments, allowing the infection to worsen and potentially become life-threatening.
Imagine you're helping at a sandwich shop. Why is using the same knife for raw chicken and ready-to-eat vegetables dangerous? What type of illness could this mistake cause in customers?
It allows cross-contamination. Bacteria such as Salmonella could spread to ready-to-eat food, leading to food-borne illness.
What big lesson does Zach's story teach us about the dangers of antibiotic-resistant infections and the importance of early medical treatment?
Resistant infections can get out of control quickly and become life-threatening. Early detection and specialized treatment gives doctors the best change to save lives.
This graph shows antibiotic use increasing while bacterial resistance also increases. What conclusion can you draw about the relationship between the two?
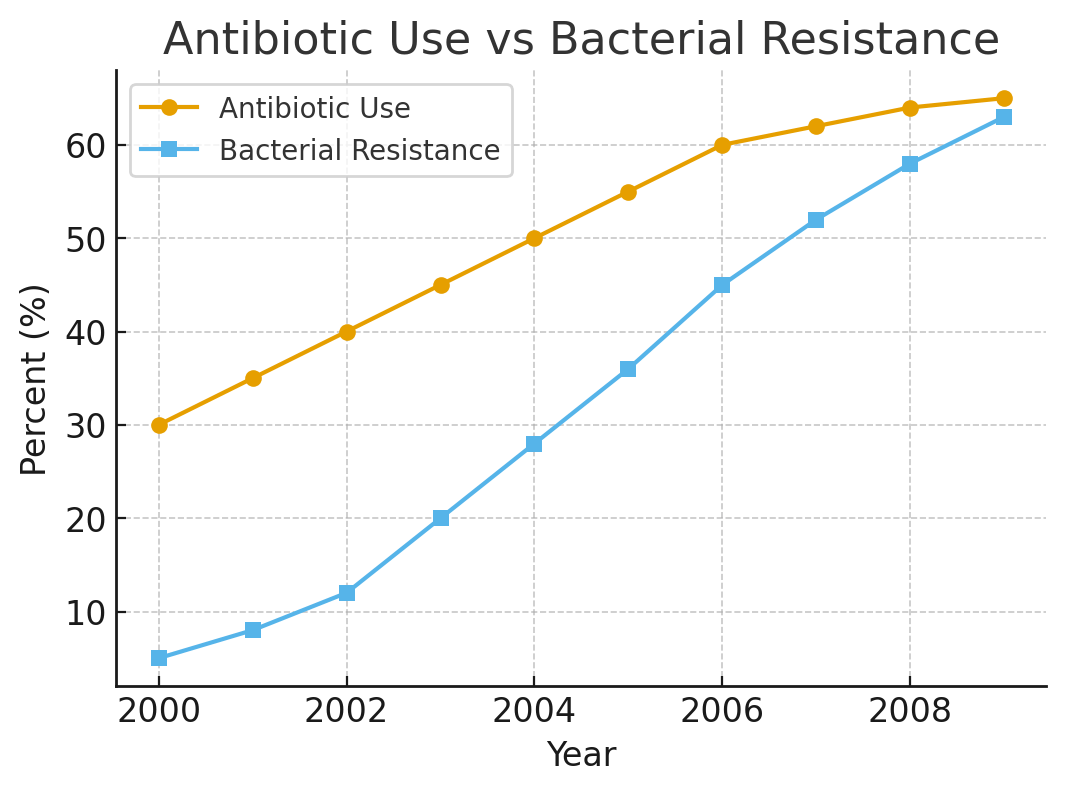
As antibiotics are used more, resistant bacteria also became more common. This shows a direct connection between human behavior and bacterial adaptation.
Doctors sometimes test for strains of bacteria. Why is identifying the strain important when treating a patient?
Different strains may respond to treatment differently. Some strains are resistant; others are harmless.
Explain how frequent or unnecessary antibiotic use can increase antibiotic-resistance infections over time.
Give one way people can help to slow this problem.
When antibiotics are used too often, most bacteria are killed, but some may have mutations or adaptations that allow them to survive. These resistant bacteria keep growing and spreading, making future infections harder to treat.
One way to help is to only use antibiotics when they are really needed and to finish the full prescription.
In 1999, the Mexia Supermarket in Fort Worth, Texas went bankrupt and the owner abandoned the store without properly disposing of the food. During the following three months, the unrefrigerated meat and other foods began to rot and created a biohazard.
What does this incident teach us about the dangers of neglecting proper food storage and management?
When food is abandoned or improperly stored, it can quickly turn into a public health hazard. Decay and contamination create conditions for dangerous pathogens to grow, putting the whole community at risk.
Zach survived his MRSA infection, but faced lasting complications. Why is it important to consider the long term effects of serious infections, not just whether someone recovers at the hospital?
Because infections like MRSA can cause permanent damage (e.g. nerve damage, muscle weakness, differences in leg length).
Recovery doesn't always mean a full return to health, and long term effects can change someone's daily life.
This graph shows measles cases dropping sharply after 1963. What major public health event explains this change? Why was it so effective?
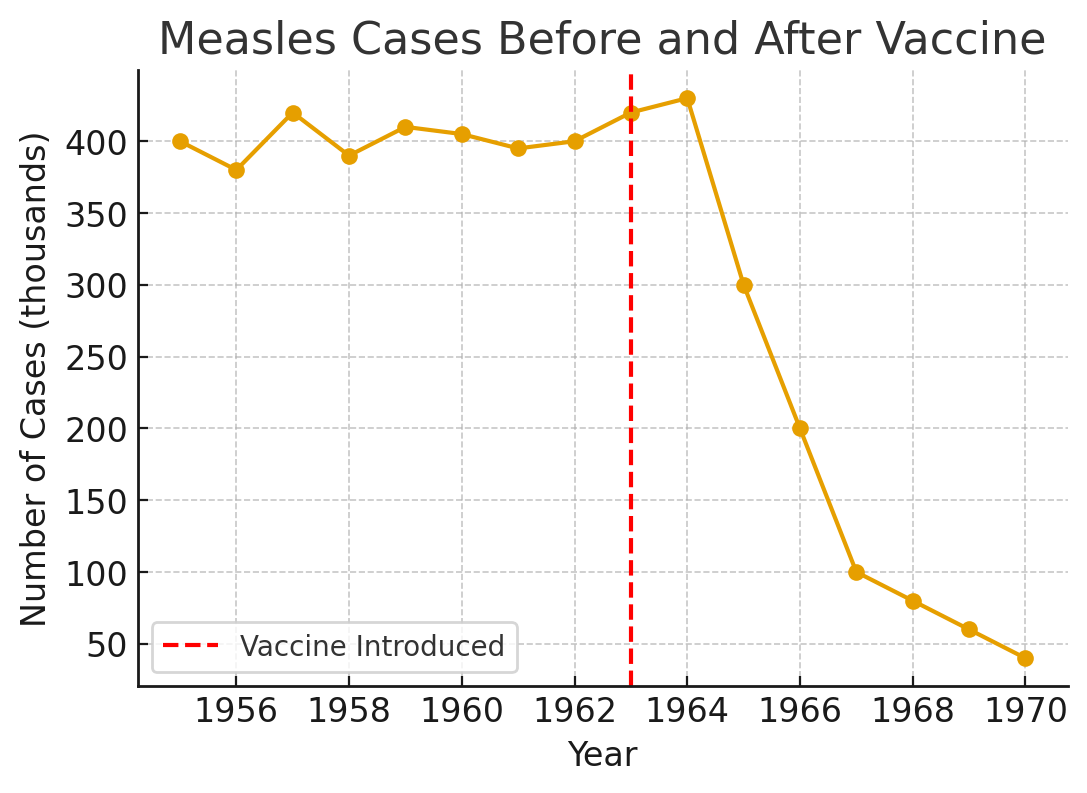
The introduction of the measles vaccine.
Once people were vaccinated, far fewer got sick, so the disease spread much less in the community.