Star nursery
What is a nebula
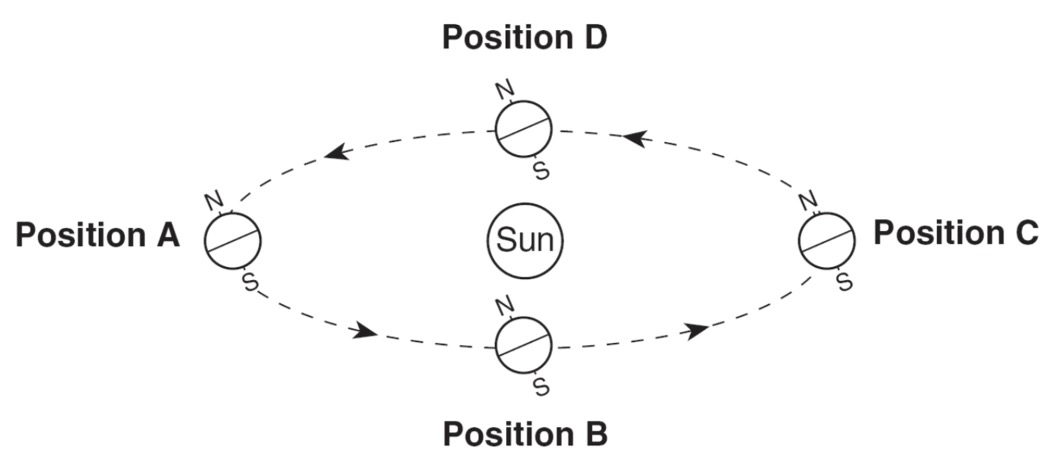
This causes day and night on Earth
What is rotation
Three phases that all stars go through
What are nebula, protostar, and main sequence
Distance between crests of two adjacent waves
What is wavelength
Tides with the greatest tidal variation
What are spring tides
Name of our home galaxy
What is Milky Way
These TWO things cause seasons
What is tilt on the axis and revolution or orbit around the Sun
Star with a temperature of 2,600K and luminosity of 10,000 suns
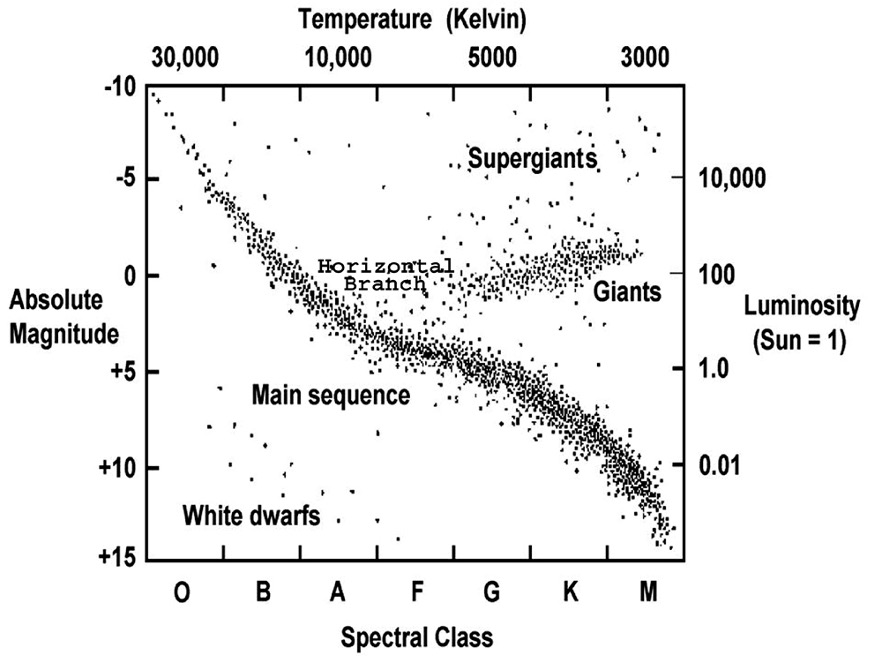
What is a supergiant
The kind of wave seen at a frequency of 3.9 x 1023 Hz.
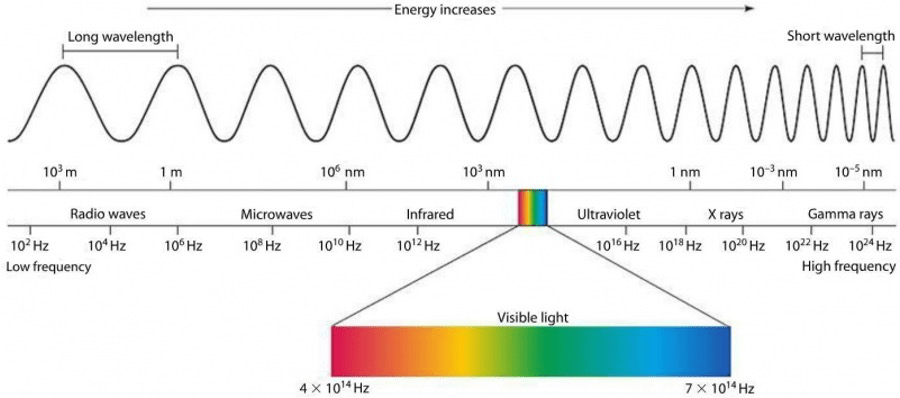
What is gamma ray
During these moon phases, we see little change or variation between high and low tides.
What is first quarter and third quarter moons
Three types of galaxies
Winter has shorter days. However, in Barrow, Alaska the sun will not rise for 67 days on average during the winter time for this reason.
What is the tilt of the earth.
During winter months doesn’t allow for daylight to reach the higher latitudes in the northern hemisphere.
Phase of life that stars spend 90% of their life; can range from hot and bright to dim and cool
What is main sequence
This increases with frequency
What is energy
This difference in the x-axis of an HR Diagram causes many students to make mistakes
A large, spherical celestial body consisting of a mass of gas that is hot enough to sustain nuclear fusion and thus produce radiant energy
What is a star
Location of summer in the Southern Hemisphere
What is A
Final stage of life for an average mass star
What is white dwarf
Increases in frequency and amplitude cause an increase in this
What is energy
This drives convection on Earth
What is the Sun
Our location in the our galaxy
On the Orion arm
Seasons at points A-D
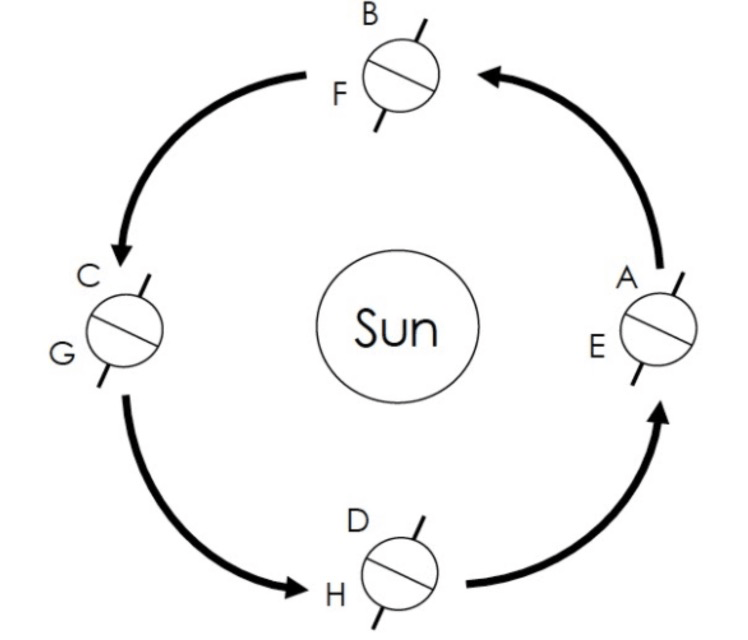
What is
A - Winter
B - Spring
C- Summer
D- Fall
Life cycle of a high mass star following Main Sequence
What is Red Supergiant—>Supernova—> Neutron star
The kind of relationship frequency and wavelength have
What is an inverse or indirect relationship
What is counterclockwise
On a HR Diagram, the x-axis measures temperature in Kelvin. This odd measurement is what luminosity is measured in on the y-axis
What is “Suns” or the brightness of our Sun.