The branch of statistics that is used to summarize the main features of a collection of data is
Descriptive Statistics
is the intersection of the inequalities in the system.
feasible solution region
lines that intersect at only one point
intersecting lines
is when there are more payments than receipts.
deficit
This type of costs increase with the number of items produced
Variable cost
is found by dividing the sum of all the values by the number of values.
Mean
a company cannot sell or produce a negative number of items.
Non-negativity
what is the coordinate for point B
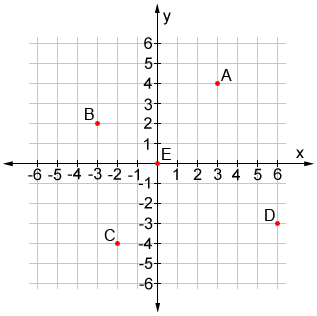
(-3,2)
The keeping of money records
Accountings
The point at which you stop losing money
Break even point
is the entire group of interest
population
a problem that uses a system of inequalities to maximize or minimize a function.
Linear Programming
what is the coordinate for point D

(6,-3)
is when there are more receipts than payments.
excess
Costs that remain the same no matter how many items are produced
Fixed costs
sample group with two modes is said to be
bimodal
a function that must be maximized to solve the problem.
Objective Function
lines that are equidistant apart at all points and do not intersect.
Parallel lines
Money or property that has any worth to your business.
assets
The break even point cannot must be a whole number because
it is a number of products
variable shows information that cannot be described by using numbers.
qualitative
the limiting factor
constraint
The coordinates receive this name because the order is important.
ordered pair
The amount you owe the department store.
liability
Which are the two ways to find the Break-even point
by graphing or by using the formula