(30 seconds)
Increases across a period
Decreased down a column
State the preferred oxidation state of Ar.
(30 sec)
0 - Argon is a noble gas and does not like to bond or react.
Why do elements form bonds?
(30 sec)
To reduce their potential energy.
To achieve a lower energy state.
Which bond theory allows us to visualize orbital interaction in 3d space.
(30 sec)
Valence Bond Theory (VBT)
What is an alkyne?
(30 sec)
Any organic compound containing at least 1 carbon to carbon triple bond.
Majority of the observable trends on the periodic table are as a result one basic atomic property. What is this atomic property called?
(30 seconds)
Effective Nuclear Charge (Zeff)
Identify the oxidation states in the following compound: Na2SO4
(1 min)
Na = +1 (x2) = +2
S = +6
O = -2 (x4) = -8
What is the octet rule and how does it pertain to bonding?
(1 min)
All atoms want to have a full outer shell. (in most cases this means just a full s and p orbital which is 8 total electrons)
Atoms will bond in a manner that will ensure this occurs.
Are pi bonds cylindrically symmetric? Why or why not?
(1 min)
No, by VBT, if you rotate pi bonds 180 degrees on a horizontal axis, the phases of the overlap flip.
What would be the hybridization state of a carbon involved in a triple bond?
sp
Would it be easier to remove an electron from Sodium or Potassium? Which of these would handle being a cation the best.
(1 min)
Potassium has a lower Zeff than Sodium, resulting in a lower EN, EA, and IE. This means it is much easier to remove an electron from Potassium than Sodium.
Additionally, Potassium has a larger atomic radius, meaning electron density is already low so it will "notice the difference less than Sodium"
Make a proper chemical formula using the following elements and state oxidation states.
(1 min)
Ca2Ge
Ca = +2 (x2) = +4
Ge = -4
Rank the following compounds from least ionic to most ionic:
MgS, N2O, HF, RbI
(1 min 30 sec)
N2O < MgS < RbI < HF
A student makes an MO diagram for two different atoms. He finds that there are 12 bonding electrons and 8 antibonding electrons. What type of bond will the two atoms form?
(1 min)
Double bond.
Identify at least two functional groups in the following molecule:
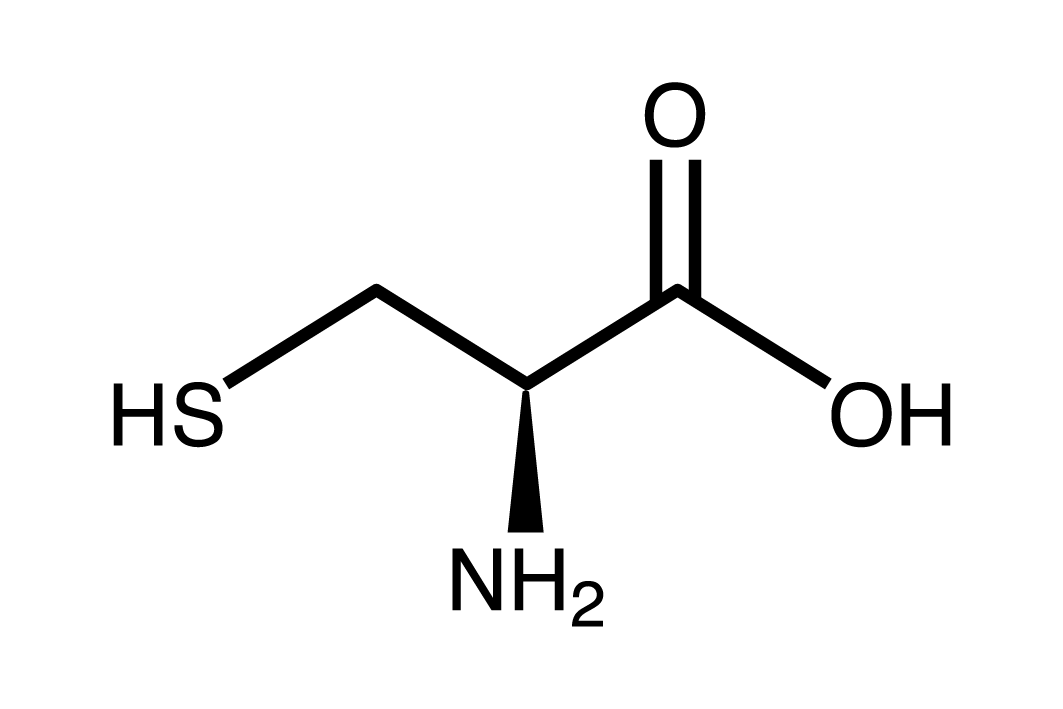
Sulfhydryl, amine, carboxylic
Please explain why, when offered excess electrons, Flourine would be a much better electron acceptor than Chlorine. Explain using at least 3 periodic trends.
(1 min 30 seconds)
Flourine has a higher EN and EA than chlorine, meaning it wants electrons more than chlorine does.
Flourine has a higher Zeff so it has greater ability to attract outer electrons.
Flourine has a smaller atomic radius which means its electron cloud is smaller, resulting in higher probability electron density.
Draw the Lewis Structure for the polyatomic ion chromate. State formal charge and net formal charge.
(1 min.)
(draw on whiteboard)
Rank the following from lowest bond length (BL) to highest bond length and from lowest bond dissociation energy (BDE) to highest bond dissociation energy (BDE): triple bond, double bond, single bond
(1 min)
single bond < double bond < triple bond
BL and BDE
Please explain using MO Diagrams and Bond order why it is not possible to form a multiple bond greater than a triple bond.
(3 min)
You would have to fill higher energy bonding orbitals and skip lower energy antibonding orbitals which violates Aufbau principle.
Please write the molecular formula for the following compound.

C14H10O3
Explain the phenomenon of Lanthanide Contraction using periodic trends.
(2 min)
Draw the most stable Lewis structure for the compound [SGeN]-. Explain why this structure is the most stable.
(2 min)
S = G = N
N should have negative formal charge because it is most EN.(1 min 30 sec)
Resonance means that there are delocalized electrons in pi bonds. These electrons can move around the structure, forming pi bonds wherever possible. All of these resonance structures contribute to a resonance hybrid which is a true representation of the molecule. Since each resonance capable bond is not always a single bond but not always a multiple bond, it displays hybrid bond character of a bond in between a single bond and a multiple bond.
Please explain what type of bond is formed in an O22- molecule using an MO Diagram and Bond Order.
(3 min)
single bond
Please state how many atoms are in an sp2 hybridization state in the structure below:

13
6 carbons from each benzyl ring, 1 oxygen =
6 + 6 + 1 = 13