What is an example of an insulator?
Glass, wood, cloth, foam, etc
What are two different kinds of magnets that we see?
Horseshoe Magnet
Bar Magnet
Which part of the electromagnetic spectrum can we can see?
Visible Light
What is an example of conductor?
Metal, salt water, etc.
Draw what happens to the a magnet that is exposed to iron fillings.

What is the loudness or softness of sound?
Sound Intensity
What is the difference between a conductor and an insulator?
A conductor allows electrons to jump from atom to atom. An insulator does not allow electrons to jump from atom to atom because they do not have space.
What happens when to the poles of a magnet when the magnet is broken in half?
Each piece of the magnet will have a north and south pole.
Which electromagnetic waves have the shortest wavelength and highest energy?
Gamma Rays

C. Rubber is a good insulator and copper is a good conductor.
How can you increase the strength of an electromagnet?
More coils and more power
Increase the size of the battery
What is the difference between light and sound?
Light is an electromagnetic wave.
Sound is a wave of moving air particles.
Helen puts four different spoons in a bowl of hot water. Each spoon is made of the following materials:
Plastic
Rubber
Silver
Wood
Which spoon will be the warmest after two minutes?
a) Plastic, because it is a poor conductor
b) rubber, because it a is a good conductor
c) silver, because it is a good conductor
d) wood, because it is a good conductor
C) Silver because it is a good conductor
How are magnets and electromagnets the same? How are the different?
Electromagnets are made of many parts and magnets are not. An electromagnet can be turned off and on and a permanent magnet is always on.
Label the wave!
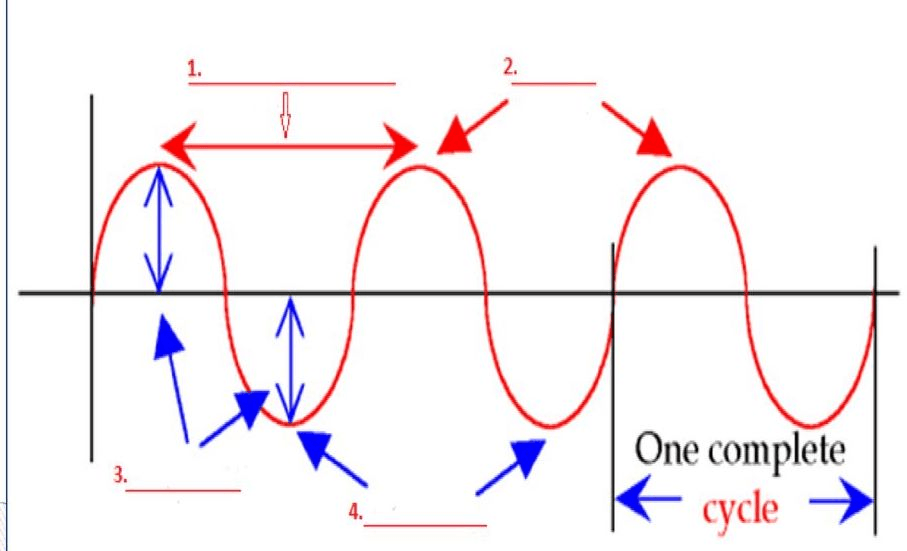
1.) Wavelength
2.) Peaks
3.) Amplitude
4.) Troughs, Valleys